Abstract
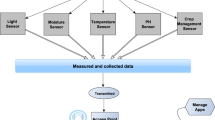
Wireless sensor networks have a wide range of applications, such as natural environmental monitoring, object tracking, and environmental control in residential spaces or plants. In wireless sensor networks, many sensor nodes with limited resources are placed in an observation area and used to gather information about environments. Therefore, a data gathering scheme (or a routing algorithm) for saving and balancing the energy consumption of each sensor node is needed to prolong the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. This article proposes a new bio-inspired data transmission scheme for the long-term operation of wireless sensor networks. By using the proposed scheme, autonomous load-balancing data transmission to multiple sinks can be actualized. We evaluate the proposed scheme using computer simulations to verify its effectiveness, and also discuss its development potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz I, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, et al (2002) Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Networks J 38(4):393–422
Rajagopalan R, Varshney PK (2006) Data aggregation techniques in sensor networks: a survey. IEEE Commun Surveys Tutorials 8:48–63
Dasgupta K, Kalpakis K, Namjoshi P (2003) An efficient clustering-based heuristic for data gathering and aggregation in sensor networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communication and Network Conference (WCNC), p 16–20
Wakamiya N, Murata M (2005) Synchronization-based data gathering scheme for sensor networks. IEICE Trans Commun E88-B(3):873–881
Nakano H, Utani A, Miyauchi A, et al (2009) Data gathering scheme using chaotic pulse-coupled neural networks for wireless sensor networks. IEICE Trans Funds E92-A(2):459–466
Ohtaki Y, Wakamiya N, Murata M, et al (2006) Scalable and efficient ant-based routing algorithm for ad-hoc networks. IEICE Trans Commun E89-B(4):1231–1238
Utani A, Orito E, Kumamoto A, et al (2008) An advanced antbased routing algorithm for large-scale mobile ad-hoc sensor networks. Trans SICE 44(4):351–360
Oyman EI, Ersoy C (2004) Multiple sink network design problem in large-scale wireless sensor networks. Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications (ICC)
Ferriere HD, Estrin D, Stathopoulos T (2004) Efficient and practical query scoping in sensor networks. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Sensor Systems, pp 564–566
Orito E, Utani A, Yamamoto H (2009) Load-balanced and reduced data transmission scheme for wireless sensor networks with multiple sinks. IEICE Tech Rep 108(447):13–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 15th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, February 4–6, 2010
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, K., Utani, A. & Yamamoto, H. Bio-inspired data transmission scheme to multiple sinks for the long-term operation of wireless sensor networks. Artif Life Robotics 15, 189–194 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-010-0792-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-010-0792-9