Abstract
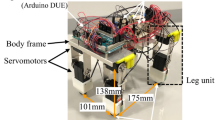
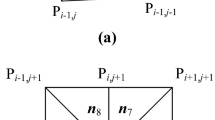
In obstacle avoidance by a legged mobile robot, it is not necessary to avoid all of the obstacles by turning only, because it can climb or stride over some of them, depending on the obstacle configuration and the state of the robot, unlike a wheel-type or a crawler-type robot. It is thought that mobility efficiency to a destination is improved by crawling over or striding over obstacles. Moreover, if robots have many legs, like 4-legged or 6-legged types, then the robot's movement range is affected by the order of the swing leg. In this article a neural network (NN) is used to determine the action of a quadruped robot in an obstacle-avoiding situation by using information about the destination, the obstacle configuration, and the robot's self-state. To acquire a free gait in static walking, the order of the swing leg is realized using an alternative NN whose inputs are the amount of movement and the robot's self-state. The design parameters of the former NN are adjusted by a genetic algorithm (GA) off-line.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KK Şafak GG Adams (2002) ArticleTitleDynamic modeling and hydrodynamic performance of biomimetic underwater robot locomotion Auton Robots 13 223–240
S Hirose K Yoneda (1993) ArticleTitleToward development of a practical quadruped walking vehicle J Robotics Mechatronics 5 498–504
H Kimura I Shimoyama H Miura (1990) ArticleTitleDynamics in the dynamic walk of a quadruped robot Adv Robotics 4 283–301
X Chen K Watanabe K Kiguchi et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAn ART-based fuzzy controller for the adaptive navigation of a human-coexistent quadruped robot. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatronics 7 318–328
X Chen K Watanabe K Kiguchi et al. (2002) ArticleTitlePath tracking based on closed-loop control for a quadruped robot in a cluttered environment ASME J Dyn Syst Measure Control 124 272–280
Nakamura T, Seki M, Mori Y, et al. (1999) Free gait planning using Monte Carlo method for locomotion on rugged terrain (in Japanese). 1999 JSME Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics, 1A1-42-061 (CD-ROM)
T Yamaguchi K Watanabe K Izumi et al. (2003) ArticleTitleAcquisition of an obstacle-avoiding path in quadruped robots J Adv Comput Intell 7 115–123
Yamaguchi T, Watanabe K, Izumi K, et al. (2003) Obstacle avoidance of quadruped robots with consideration to the order of swing leg. 2003 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, TP08-2 (CDROM)
J Furusho (1993) ArticleTitleResearch deployment of the walking robot (in Japanese) J Robotics Soc Jpn 11 306–313
VTS Elanayar YC Shin (1994) ArticleTitleRadial basis function neural network for approximation and estimation of nonlinear stochastic IEEE Trans Neural Networks 5 594–603
Z Michalewicz (1996) Genetic algorithms + data structure = evolution programs EditionNumber3rd revised and extended edition Springer Heidelberg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 9th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Oita, Japan, January 28–30, 2004
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, T., Watanabe, K. & Izumi, K. Neural network approach to acquiring free-gait motion of quadruped robots in obstacle avoidance. Artif Life Robotics 9, 188–193 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-005-0344-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-005-0344-x