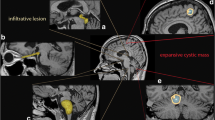
Abstract
Cytological differences between infiltrating lesions of the diffusely infiltrating astrocytoma (DIA) and reactive gliosis at its periphery have not yet been established. We compared histological specimens from cytological crush preparations of 200 brain tumors to characterize the cytology of the DIA and to discriminate it from reactive gliosis. First, the cytological findings of the backgland brain parenchyma were assessed. Second, we looked at the nuclear characteristics of the DIA, comparing them with those of other brain tumors. Third, the cytology of the infiltrating DIA was assessed together with brain parenchymal elements. Finally, we characterized discriminative points of the area of infiltration of the DIA versus those of the reactive gliosis. In addition, we assessed the relations between the cytological findings of the DIA and its MRI images. The cytological findings of this area are important because the surgeon may have to make a rapid diagnosis regarding the existence of the tumor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
InstitutionalAuthorNameThe Committee of Brain Tumor Registry of Japan, The Japanese Pathological Society (2002) General rules for clinical and pathological studies on brain tumors EditionNumber2nd edn. Kanehara-shyuppan Tokyo 102–107
R Kim W Michael S Stephen et al. (2004) Direct sampling of the central nervous system Modern cytopathology Churchill Livingstone New York 335–344
H Yamazaki H Yoko J Hirato et al. (2003) ArticleTitleImprint cytology of the astrocytic tumors (in Japanese) J Jpn Soc Clin Cytol 42 405–411
M Takahasi (2000) Central nervous system M Takahashi (Eds) Color atlas of cancer cytology EditionNumber3rd edn. Igku-Shoin Tokyo 425–448
R Walter (1995) Cerebrospinal fluid examination and direct brain preparations W Gray (Eds) Diagnostic cytopathology Churchill Livingstone Edinburgh 901–930
H Namiki M John Hardman et al. (1997) The central nervous system SG Silverberg (Eds) Surgical pathology and cytopathology EditionNumber3rd edn. Churchill Livingstone NewYork 2905–3036
S Kobayashi H Miki M Ohmori et al. (1989) ArticleTitleCytodiagnosis of brain tumors by squash method: comparative study of meningioma, neurilemmomas and astrocytomas J Jpn Soc Clin Cytol 28 378–383
T Inagaki K Ohtsu M Hara et al. (1996) ArticleTitleA proposed study of normal neurocytology of the central nervous system and comparison to the cytology of astrocytomas J Jpn Soc Clin Cytol 35 105–113
T Mizutani (2003) Regional neuropathology (in Japanese) Shinkouigasku-shyuppan Tokyo
M Kudo (2001) ArticleTitleIntraoperative diagnosis of central nervous system lesions Pathol Clin Med 19 IssueID1 21–26
H Okazaki O Imazu (1996) NoChapterTitle H Okazaki W Bernd Scheithauer (Eds) Atlas of neuropathology (in Japanese) Igaku-shoin Tokyo 57–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, H., Mori, O., Ohaki, Y. et al. Cytological interface of diffusely infiltrating astrocytoma and its marginal tissue. Brain Tumor Pathol 22, 59–74 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-005-0190-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-005-0190-5