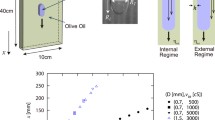
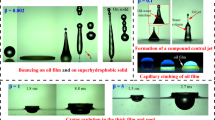
Abstract
Rise and fall velocities of oil drops in water and water drops in oil, respectively, are measured in a liquid column. The main perspective is on the similarity of the flows in these largely different cases. When the experimental data are plotted as the normalized rise velocity, which is the Reynolds number, versus the Archimedes number a common curve appears. This proves that similarity exists at least with respect to the velocity. Larger drops deviate considerably from the spherical shape. Nevertheless the data set can be represented by a formula derived from data on hard spheres. In particular the Stokes limit for Re→0 is nicely confirmed by measuring down to 10− 4.
Zusammenfassung
Untersucht wird das Aufsteigen von Öltropfen in Wasser und das Absinken von Wassertropfen in Öl. Das Hauptinteresse liegt auf der strömungsmechanischen Ähnlichkeit dieser beiden sehr verschiedenen Fälle. Die Messdaten werden in dimensionsloser Form als Reynolds-Zahl gegen die Archimedes-Zahl aufgetragen. Sowohl für das Aufsteigen als auch für das Absinken ergibt sich eine gemeinsame Kurve. Zumindest in Bezug auf die Tropfengeschwindigkeit kann daraus Ähnlichkeit gefolgert werden. Bei größeren Tropfen nimmt die Deformation stetig zu. Trotzdem kann für die genannte Kurve über den gesamten Messbereich eine Gleichung angegeben werden, die aus der Beschreibung von Kugelumströmungen bekannt ist. Insbesondere wird die Stokes’sche Lösungen für Re→0 sehr gut bestätigt bis zu Messwerten nahe 10− 4.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ar:
-
Archimedes number
- Eo:
-
Eötvös number
- Mo:
-
Morton number
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- cD :
-
Drag coefficient (−)
- de :
-
Equivalent diameter of the drop (m)
- di :
-
Inner diameter of capillary (m)
- do :
-
Outer diameter of capillary (m)
- g:
-
Gravitational acceleration (m/s2)
- T:
-
Temperature (°C)
- U:
-
Rise/fall speed of the drop (m/s)
- VC :
-
Manufacturer declaration of inner capillary volume (m3)
- Δx:
-
Travelling distance of the drop for velocity measurement (m)
- νex :
-
Kinematic viscosity of external fluid (m2/s)
- ρex :
-
Density of external fluid (kg/m3)
- ρin :
-
Density of drop fluid (kg/m3)
- σ:
-
Interfacial tension between external and internal drop fluid (N/m)
- W:
-
Water
- AK:
-
Silicon oil, e.g. AK10 → ν = 10.0 mm2/s at 25 °C
References
Chemie Ingenieur Technik (2013) Special issue: Campus Blasensäulen. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 85:965–1155
Peters F, Gaertner B (2011) Scaling parameters of bubbles and drops; interpretation and case study with air in silicon oil. Acta Mechanica 219:189–202
Peters F, Els C (2012) An experimental study on slow and fast bubbles in tap water. Chemical Engineering Science 82:194–199
Clift R, Grace JR, Weber ME (1978) Bubbles, drops and particles. Academic Press, New York
Wacker Chemie, München (2001) Manufacturer data sheet: Wacker Silikonöle AK. http://www.drawin.de/dasat/images/2/100212-siliconoleak.pdf. Accessed Feb 2014
Peters F, Arabali D (2013) Interfacial tension between oil and water measured with a modified contour method. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 426:1–5
Nüllig M, Peters F (2013) Diffusion of small gas bubbles into liquid studied by the rotary chamber technique. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 85:1074–1079
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, F., Nüllig, M. & Miletic, D. Rise of oil drops in water and fall of water drops in oil. Forsch Ingenieurwes 78, 87–91 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10010-014-0176-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10010-014-0176-8