Abstract.
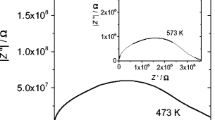
The conductivity, σ, of a samaria-doped ceria electrolyte is studied as a function of temperature and dopant concentration, x, which was from 5 to 30 mol%. It is shown that a maximum in σ versus x corresponds to a minimum in activation energy. It is found that the conductivity is completely due to oxygen vacancy conduction. The conductivity increases with increasing samaria doping and reaches a maximum for (CeO2)0.8(SmO1.5)0.2, which has a conductivity of 5.6×10–1 S/cm at 800 °C. A curvature at T=T c, the critical temperature, has been observed in the Arrhenius plot. This phenomenon may be explained by a model which proposed that, below T c, nucleation of mobile oxygen vacancies into ordered clusters occurs, and, above T c, all oxygen vacancies appear to be mobile without interaction with dopant cation. In addition, the composition dependences of both the critical temperature and the trapping energy are consistent with that of the activation energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, GB., Huang, TJ. & Chang, CL. Effect of temperature and dopant concentration on the conductivity of samaria-doped ceria electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 6, 225–230 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080100238
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080100238