Abstract.
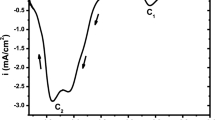
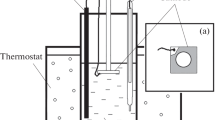
An investigation on electrochemical ZnSe thin film growth from acidic aqueous baths of Se(IV) and Zn(II) species is described. The range of co-deposition potentials is predicted on a thermodynamic basis according to a known electrochemical model. A study on the voltammetric behavior of Ti and Ni electrode substrates in the working solutions at various temperatures provides the main features of the applied electrochemical process. Cathodic electrodeposition at high temperatures (>65 °C) results in the formation of polycrystalline cubic, randomly oriented, ZnSe crystallites suffering, in general, from the presence of a crystalline Se phase in excess. Annealing of as-grown films adjusts the stoichiometry and leads to the production of semiconductive ZnSe with a band gap width of 2.7 eV.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouroushian, M., Kosanovic, T., Loizos, Z. et al. Electrochemical formation of zinc selenide from acidic aqueous solutions. J Solid State Electrochem 6, 272–278 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080100215
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080100215