Abstract
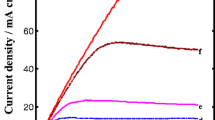
The repassivation kinetics of pure aluminium have been explored in aqueous alkaline solutions as functions of applied anodic potential and pH by using an abrading electrode technique and a rotating disc electrode. The repassivation rate of the abraded bare surface of pure aluminium increased with increasing applied anodic potential in aqueous alkaline solutions, while it decreased with increasing pH. These results revealed that the growth rate of the passivating oxide film is enhanced by an applied electric field, but it is lowered due to the chemical attack by hydroxyl ions. A potentiostatic anodic current decay transient obtained from the abraded electrode surface showed a constant repassivation rate in neutral and weakly alkaline solutions. In contrast, in concentrated alkaline solutions it was observed to consist of three stages: a high repassivation rate in the initial stage due to a high formation rate of the oxide film on the abraded bare surface; a zero value of the repassivation rate in the second stage due to the dissolution of the oxide film by the attack of OH−; a high repassivation rate in the third stage due to a lowered dissolution rate of the oxide film. The dissolution rate of the passivating oxide film was observed to depend on the removal rate of aluminate ions from the oxide/solution interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 April 1998 / Accepted: 3 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, SM., Pyun, SI. Effects of applied anodic potential and pH on the repassivation kinetics of pure aluminium in aqueous alkaline solution. J Solid State Electrochem 3, 104–110 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080050135
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080050135