Abstract
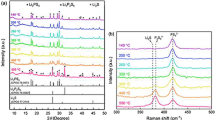
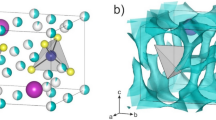
All-solid-state batteries are typically manufactured under high pressure to decrease the resistance of the solid interface. However, until now, there has been a lack of research concerning changes in the structure of solid electrolytes owing to pressurization. Our study addresses this gap by exploring the structural modifications of the sulfide solid electrolyte Li3PS4 under high-pressure conditions. We observed a tendency for PS4 molecules to converge upon each other in both β-Li3PS4 and g-Li3PS4 crystals when subjected to a pressure of 100 MPa. In g-Li3PS4, X-ray scattering and pair distribution function analyses following pressure application and subsequent return to ambient conditions remained consistent with pre-compression measurements. Conversely, in β-Li3PS4 crystals, post-pressure X-ray scattering differed from pre-compression measurements, suggesting pressure-induced atomic rearrangement within the crystal lattice. This underscores the importance of accounting for pressure-induced structural changes, especially in computational simulation studies where crystal structures are often assumed to remain static pre- and post-pressurization. Our findings demonstrate that under high pressure, the crystal structure of Li3PS4 slightly changes by approximately 1~2%, rendering it a viable candidate for utilization as a solid electrolyte in all-solid-state batteries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kato Y, Hori S, Saito T, Suzuki K, Hirayama M, Mitsui A, Yonemura M, Iba H, Kanno R (2016) Nat Energy 1:16030
Hayashi A, Sakuda A, Tatsumisago M (2016) Development of sulfide solid electrolytes and interface formation processes for bulk-type all-solid-state Li and Na batteries. Front Energy Res 4:25
Sakuda A, Hayashi A, Takigawa Y, Higashi K, Tatsumisago M (2013) J Ceram Soc Jpn 16:946–949
Doux J, Nguyen H, Tan DHS, Banerjee A, Wang X, Wu EA, Jo C, Yang H, Meng YS (2020) Adv Enegy Mater 10:1903253
Doux J, Yang Y, Tan DHS, Nguyen H, Wu EA, Wang X, Banerjee A, Meng YS (2020) J Mater Chem A 10:5049
Sakka Y, Yamashige H, Watanabe A, Takeuchi A, Uesugi M, Uesugi K, Orikasa Y (2022) J Mater Chem A 10:16602–16609
Kato A, Nose M, Yamamoto M, Sakuda A, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2018) J Ceram Soc Jpn 126:719–727
Kato A, Yamamoto M, Sakuda A, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2018) ACS Appl Energy Mater 1:1002–1007
Sakuda A, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2013) Sci Rep 3:2261
Kimura T, Inaoka T, Izawa R, Nakano T, Hotehama C, Sakuda A, Tatsumisago M, Hayashi A (2023) J Am Chem Soc 145:14466–14474
Ohara K, Mitsui A, Mori M, Onodera Y, Shiotani S, Koyama Y, Orikasa Y, Murakami M, Shimoda K, Mori K, Fukunaga T, Arai H, Uchimoto Y, Ogumi Z (2016) Sci Rep 6:21302. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21302
Homma K, Yonemura M, Kobayashi T, Nagao M, Hirayama M, Kanno R (2011) Solid State Ionics 182:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2010.10.001
Ohara K, Tominaka S, Yamada H, Takahashi M, Yamaguchi H, Utsuno F, Umeki T, Yao A, Nakada K, Takemoto M, Hiroi S, Tsuji N, Wakihara T (2018) J Synchrotron Radiat 25:1627–1633
Ohara K, Onodera Y, Murakami M, Kohara S (2021) J Phys Condens Matter 33:383001
Tominaka S, Yamada H, Hiroi S, Kawaguchi SI, Ohara K (2018) ACS Omega 3:8874–8881
Izumi F, Momma K (2007) Solid State Phenom 130:15–20
Sasaki A (2016) Development History of the PDXL Structure Analysis Package, Rigaku newsletters. https://www.rigaku.com/newsletters/mabu/april2017/app.note_xrd_01.pdf
Blöchl PE (1994) Phys Rev B 50:17953–17979
Kresse G, Hafner J (1993) Phys Rev B 47:558–561
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Phys Rev B 54:11169–11186
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Kudu OU, Famprikis T, Cretu S, Porcheron B, Salager E, Demortiere A, Courty M, Viallet Virginie, Mercier TL, Fleutot B, Braida MD, Masquelier C (2022) Structural details in Li3PS4: Variety in thiophosphate building blocks and correlation to ion transport. Energy Storage Mater 44:168–179
Funding
Synchrotron radiation experiments were performed with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (Proposal Nos. 2020A1702, 2020A1703, 2021A1267, 2021B1744, 2022A1238, and 2022B1224). This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number JP19H05814) and the Green Technologies of Excellence program (Grant Number JPMJGX23S5) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (GteX, JST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by A. Y., S. K., and F. U. Data collection was performed by A. Y., S. K., H. Y., J. T., F. U., and K. O. Data analysis were performed by all authors. The first draft of the manuscript was written by A. Y., S. K., S. H., F. U., and K. O. and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, A., Kadota, S., Hiroi, S. et al. In situ structural characterization of Li3PS4 solid electrolytes under high pressure. J Solid State Electrochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-024-05889-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-024-05889-4