Abstract
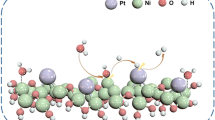
Development of transition metal phosphides with tunable morphology and chemical composition is a potential way to construct electrocatalysts with superior hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) activity in a wide range of pH values. In this work, vertical nanorods are constructed from nickel and iron phosphide grown on a carbon cloth (Ni2P-Fe2P/CC) via a hydrothermal treatment followed by low-temperature phosphorization method to achieve an effective catalyst for sufficient HER activity and strong stability. The Ni2P-Fe2P/CC exhibits remarkable overpotentials of 78, 80, and 87 mV to achieve a current density of 10 mAcm−2 in acidic, alkaline, and neutral electrolytes, respectively. Furthermore, it shows strong stability without significant performance change for 20 h, 30 h, and 30 h under 100 mAcm−2 in acidic, alkaline, and neutral electrolytes, respectively. This outstanding catalytic performance for HER in a wide pH range can be accredited to the synergistic effect induced by the coexistence of Ni and Fe atoms. Additionally, the integration of nanorods on the nanosheet also initiates fast transfer of hydrogen bubbles within the electrolyte, thereby enhancing its HER activity. The results present an opportunity to construct a low-cost, effective transition metal phosphide with unique architecture and strong durability for efficient HER activity in a wide range of pH values.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and the supplementary information files.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Shi YM, Zhang B (2016) Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Soc Rev 45:1529–1541
Tang C, Cheng NY, Pu ZH, Xing W, Sun XP (2015) NiSe nanowire film supported on nickel foam: An efficient and stable 3D bifunctional electrode for full water splitting. Angew Chem Int Ed 127:9483–9487
Koper MTM, Bouwman E (2010) Electrochemcial hydrogen production: Bridging homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:3723–3725
Walter MG, Warren EL, McKone JR, Boettcher SW, Mi QX, Santori EA, Lewis NS (2010) Solar water splitting cell. Chem Rev 110:6446–6473
Liu T, Ma X, Liu D, Hao S, Du G, Ma Y, Asiri AM, Sun X, Chen L (2017) Mn doping of CoP nanosheets array: An efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction with enhanced activity at all pH values. ACS Catal 7:98–102
Tang C, Gan L, Zhang R, Lu W, Jiang X, Asir AM, Sun X, Wang J, Chen L (2016) Ternary FexCo1-xP nanowire array as a robust hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst with Pt-like activity: Experimental and theoretical insight. Nano Lett 16:6617–6621
Read CG, Callejas JF, Holder CF, Schaak RE (2016) General strategy for the synthesis of transition metal phosphide films for electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution. ACS Appl Mater Interf 8:12798–12803
Harman WH, Peters JC (2012) Reversible H2 addition across a nickel-borane unit as a promising strategy for catalysis. J Am Chem Soc 134:5080–5082
Liu T, Liu D, Qu F, Wang D, Zhang L, Ge R, Hao S, Ma Y, Du G, Asiri AM, Chen L, Sun X (2017) Enhanced Electrocatalysis for Energy-Efficient Hydrogen Production over CoP Catalyst with Nonelectroactive Zn as a Promoter Adv. Energy Mater 7:1700020
Yu SH, Chen W, Wang H, Pan H, Chua DHC (2019) Highly stable tungsten disulfide supported on a self-standing nickel phosphide foam as a hybrid electrocatalyst for efficient electrolytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 55:193–202
Xu YF, Gao MR, Zheng YR, Jiang J, Yu SH (2013) Nickel/nickel (II) oxide nanoparticles anchored onto cobalt (IV) diselenide nanobelts for the electrochemical production of hydrogen. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:8546–8550
Pu ZH, Amiinu IS, Wang M, Yang YS, Mu SC (2016) Semimetallic MoP2: An active and stable hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst over the whole pH range. Nanoscale 8:8500–8504
Li X, Zhao H, Liang J, Luo Y, Chen G, Shi X, Lu S, Gao S, Hu J, Liu Q, Sun X (2021) A-site perovskite oxides: An emerging functional material for electrocatalysis and photocatalysis. J Mater Chem A 9:6650–6670
Hossain MD, Liu Z, Zhuang M, Yan X, Xu G, Gadre CA, Tyagi A, Abidi IH, Sun C, Wong H, Guda A, Hao Y, Pan X, Amine K, Luo Z (2019) Rational design of graphene-supported single atom catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Energy Mater 9:1803689
Pi M, Wu T, Zhang D, Chen S, Wang S (2016) Self-supported three-dimensional mesoporous semimetallic WP2 nanowire arrays on carbon cloth as a flexible cathode for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 8:19779–19786
Meng T, Qin J, Xu D, Cao M (2019) Atomic hetero interface induced local charge distribution and enhanced water adsorption behavior in a cobalt phosphide electrocatalyst for self-powered highly efficient overall water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interf 11:9023–9032
Son CY, Kwak IH, Lim YR, Park J (2016) FeP and FeP2 nanowires for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Commun 52:2819–2822
Tian J, Liu Q, Cheng N, Asiri AM, Sun X (2014) Self-supported Cu3P nanowire arrays as an integrated high-performance three-dimensional cathode for generating hydrogen from water. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:9577–9581
Zhang L, Li S, Tan H, Khan SU, Ma Y, Zang H, Wang Y, Li Y (2017) MoP/Mo2C@C: A new combination of electrocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution over the entire pH range. ACS Appl Mater Interf 9:16270–16279
Xu Y, Wu R, Zhang JF, Shi YM, Zhang B (2013) Anion exchange synthesis of nanoporous FeP nanosheets as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Commun 49:6656–6658
Liu RW, Gu S, Du HF, Li CM (2014) Controlled synthesis of FeP nanorod arrays as highly efficient hydrogen evolution cathode. J Mater Chem A 2:17263–17267
Wang M, Zhao RZ, Li XY, Zhao XS, Jiang LH (2019) Three-dimensional assembly of iron phosphide nanosheets: Synthesis and enhanced catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reaction. ChemNanoMat 5:593–598
Yan Q, Chen X, Wei T, Wang G, Zhu M, Zhuo Y, Cheng K, Ye K, Zhu K, Yan J, Cao D, Li Y (2019) Hierarchical edge rich nickel phosphide nanosheet arrays as efficient electrocatalysts toward hydrogen evolution in both alkaline and acidic conditions. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:7804–7811
Popczun EJ, McKone JR, Read CG, Biacchi AJ, Wiltrout AM, Lewis NS, Schaak RE (2013) Nanostructured nickel phosphide as an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Am Chem Soc 135:9267–9270
Popczun EJ, Read CG, Roske CW, Lewis NS, Schaak RE (2014) Highly active electrocatalysis of the hydrogen evolution reaction by cobalt phosphide nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:5427–5430
McEnaney JM, Crompton JC, Callejas JF, Popczun EJ, Biacchi AJ, Lewis NS, Schaak RE (2014) Amorphous molybdenum phosphide nanoparticles for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem Mater 26:4826–4831
McEnaney JM, Crompton JC, Callejas JF, Popczun EJ, Read CG, Lewis NS, Schaak RE (2014) Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using amorphous tungsten phosphide nanoparticles. Chem Commun 50:11026–11028
Gong M, Zhou W, Tsai MC, Zhou JG, Guan MY, Lin MC, Zhang B, Hu YF, Wang DY, Yang J, Pennycook SJ, Hwang BJ, Dai HJ (2014) Nanoscale nickel oxide/nickel heterostructures for active hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Nat Commun 5:4695
Los P, Lasia A (1992) Electrocatalytic properties of amorphous nickel boride electrodes for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solution. J Electroanal Chem 333:115–125
Jiang P, Liu Q, Liang Y, Tian J, Asiri AM, Sun X (2014) A cost effective 3D hydrogen evolution cathode with high catalytic activity: FeP nanowire array as the active phase. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:12855–12859
Jiang P, Liu Q, Ge C, Cui W, Pu Z, Asiri AM, Sun X (2014) CoP nanostructures with different morphologies: Synthesis, characterization and a study of their electrocatalytic performance toward the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 2:14634–14640
Jiang P, Liu Q, Sun X (2014) Ni2P nanosheet arrays supported on carbon cloth: An efficient 3D hydrogen evolution cathode in both acidic and alkaline solutions. Nanoscale 6:13440–13445
Tian J, Liu Q, Asiri AM, Sun X (2014) Self-supported nanoporous cobalt Phosphide nanowire arrays: An efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0–14. J Am Chem Soc 136:7587–7590
Wang J, Yang W, Liu J (2016) CoP2 nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide sheets as a super-efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for full water splitting. J Mater Chem A 4:4686–4690
Pu Z, Liu Q, Tang C, Asiri AX, Sun X (2014) Ni2P nanoparticle films supported on a Ti plate as an efficient hydrogen evolution cathode. Nanoscale 6:11031–11034
Xu S, Zhao H, Li T, Liang J, Lu S, Cheng G, Gao S, Asiri AM, Wu Q, Sun X (2020) Iron-based phosphides as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction : recent advances and future prospects. J Mater Chem A 8:19729–19745
Feng Y, Yu XY, Paik U (2016) Nickel cobalt phosphides quasi hollow nanocubes as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution in alkaline solution. Chem Commun 52:1633–1636
Yu J, Li QQ, Li Y, Xu CY, Zhen L, Dravid VP, Wu JS (2016) Ternary metal phosphide with triple-layered structure as a low-cost and efficient electrocatalyst for bifunctional water splitting. Adv Funct Mater 26:7644–7651
Li Y, Zhang H, Jiang M, Kuang Y, Sun X, Duan X (2016) Ternary NiCoP nanosheet arrays: An excellent bifunctional catalyst for alkaline overall water splitting. Nano Res 9:2251–2259
Li Y, Liu J, Chen C, Zhang X, Chen J (2017) Preparation of NiCoP hollow quasi-polyhedra and their electrocatalytic properties for hydrogen evolution in alkaline solution. ACS Appl Mater Interf 9:5982–5991
Du HT, Xia L, Zhu SY, Qu F, Qu FL (2018) Al-Doped Ni2P nanosheet array: a superior and durable electrocatalyst for alkaline hydrogen evolution. Chem Commun 54:2894–2897
Dinh KN, Sun X, Dai Z, Zheng Y, Zheng P, Yang J, Xu J, Wang Z, Yan Q (2018) O2 plasma and cation tuned nickel phosphide nanosheets for highly efficient overall water splitting. Nano Energy 54:82–90
Sun Z, Zhu M, Lv X, Liu Y, Shi C, Dai Y, Wang A, Majima T (2019) Insight into iron group transition metal phosphides (Fe2P, Co2P, Ni2P) for improving photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Appl Catal B 246:330–336
Wang Y, Wu C, Wu Z, Cui G, Xie F, Guo X, Sun X (2018) FeP Nanorod arrays on carbon cloth: A high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Chem Commun 54:9341–9344
Yan Y, Xia BY, Ge X, Liu Z, Fisher A, Wang X (2015) A flexible electrode based on iron phosphide nanotubes for overall water splitting. Chem Eur J 21:18062–18067
Owusu KA, Qu L, Li J, Wang Z, Zhao K, Yang C, Hercule KM, Lin C, Shi C, Wei Q, Zhou L (2017) Low crystalline iron oxide hydroxide nanoparticle anode for high performance supercapacitors. Nat Commun 6:1–1
Xu J, Qi Y, Wang C, Wang L (2019) NH2-MIL-101(Fe)/Ni(OH)2-derived C, N-codoped Fe2P/Ni2P cocatalyst modified g-C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water splitting. Appl Catal B 241:178–186
Tang C, Pu ZH, Liu Q, Asiri AM, Sun XP, Luo YL, He YQ (2015) In situ growth of NiSe nanowire film on nickel foam as an electrode for high-performance supercapacitors. ChemElectroChem 2:1903–1907
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Ma M, Ren X, Liu Z, Du G, Asiri AM, Sun X (2017) A Mn-doped Ni2P nanosheet array: an efficient and durable hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in alkaline media. Chem Commun 53:11048–11051
Li X, Zhang R, Luo Y, Liu S, Chen G, Gao S, Chen S, Sun X (2020) Cobalt-phosphorous nanoparticles decorated N-doped carbon nanosheet array for efficient and durable hydrogen evolution at alkaline pH. Sustain Energy Fuels 4:3884–3887
Zhang Q, Yan D, Nie Z, Qiu X, Wang S, Yuan J, Su D, Wang G, Wu Z (2018) Iron-doped NiCoP porous nanosheet arrays as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1:571–579
Ji X, Liu B, Ren X, Shi X, Asiri AM, Sun X (2018) P-Doped Ag nanoparticles embedded in N-doped carbon nanoflake: An efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:4499–4503
Tang C, Xie L, Wang K, Du G, Asiri AM, Luo Y, Sun X (2016) A Ni2P nanosheet array integrated on 3D Ni foam: An efficient, robust and reusable monolithic catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane toward on-demand hydrogen generation. J Mater Chem A 4:12407–12410
Pan Y, Sun K, Lin Y, Cao X, Cheng Y, Liu Y, Liu Z, Liu S, Zeng L, Cheong W, Zhao D, Wu K, Wang D, Peng Q, Chen C, Li Y (2019) Electronic structure and D-band center control engineering over M-doped CoP (M = Ni, Mn, Fe) hollow polyhedron frames for boosting hydrogen production. Nano Energy 56:411–419
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (52006055), the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0702001), and Guangdong Key R&D Program (2020B0909040001 and 2019B090909003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boakye, F.O., Fan, M., Zhang, F. et al. Growth of branched heterostructure of nickel and iron phosphides on carbon cloth as electrode for hydrogen evolution reaction under wide pH ranges. J Solid State Electrochem 26, 875–885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05117-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05117-x