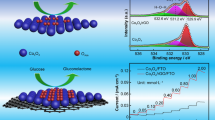
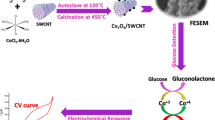
Abstract
The detection of glucose plays an important role in monitoring and controlling diabetes as well as its complications caused by high blood glucose levels. There have been a lot of research on glucose sensors and integrated flexible sensing platforms; however, the detection in oxygen-restrictive environments is few reported. Herein, we described the use of a novel system made up of TiO2 and ceria-cerium phosphate (CeO2-CePO4) composite nanostructures synthesized by a simple procedure to address the oxygen dependence problem confronted in the first-generation amperometric glucose biosensors. The enzymatic activity of sensors was tested in both oxygen-rich and restrictive environments. Our results showed that the resulting composites present good electro-catalytic activity towards glucose oxidation. The electrodes decorated by TiO2/CeO2-CePO4 showed a wide linear range from 0.1 to 1.7 mM with a low detection limit of 17.1 μM while the CeO2-CePO4 showed the linear range of 0.1–2.5 mM with limit of detection of 58.0 μM in oxygen-rich environment. Two types of decorated electrodes both responded to glucose well under the oxygen-restrictive environment but former showed better response performance. The as-fabricated electrodes also owned the good anti-interference, stability, and reproducibility. This strategy promises for increasing the sensitivity of glucose biosensors and provides more opportunities for operation in oxygen-restrictive conditions.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkkan A, Seçkin Aİ, Pekmez K, Tamer U (2010) Amperometric enzyme electrode for glucose determination based on poly(pyrrole-2-aminobenzoic acid). J Solid State Electrochem 14(6):975–980
Yan X, Yang J, Ma L, Tong X, Wang Y, Jin G, Guo X-Y (2015) Size-controlled synthesis of Cu2O nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide sheets and their application as non-enzymatic glucose sensor materials. J Solid State Electrochem 19(10):3195–3199
Wu Q, Wang L, Yu H, Wang J, Chen Z (2011) Organization of glucose-responsive systems and their properties. Chem Rev 111(12):7855–7875
Wang J (2008) Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem Rev 108(2):814–825
Cass AEG, Davis G, Francis GD, Hill HAO, Aston WJ, Higgins IJ, Plotkin EV, Scott LDL, Turner APF (1984) Ferrocene-mediated enzyme electrode for amperometric determination of glucose. Anal Chem 56(4):667–671
He H, Xu X, Wu H, Jin Y (2012) Enzymatic plasmonic engineering of Ag/Au bimetallic nanoshells and their use for sensitive optical glucose sensing. Adv Mater 24(13):1736–1740
Ronkainen NJ, Halsall HB, Heineman WR (2010) Electrochemical biosensors. Chem Soc Rev 39(5):1747–1763
Shan C, Yang H, Song J, Han D, Ivaska A, Niu L (2009) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on graphene. Anal Chem 81(6):2378–2382
Xu C, Song Z, Xiang Q, Jin J, Feng X (2016) A high performance three-phase enzyme electrode based on superhydrophobic mesoporous silicon nanowire arrays for glucose detection. Nanoscale 8(14):7391–7395
Han X, Zhu Y, Yang X, Zhang J, Li C (2011) Dendrimer-encapsulated Pt nanoparticles on mesoporous silica for glucose detection. J Solid State Electrochem 15(3):511–517
Medeiros NG, Ribas VC, Lavayen V, Da Silva JA (2016) Synthesis of flower-like cuo hierarchical nanostructures as an electrochemical platform for glucose sensing. J Solid State Electrochem 20(9):2419–2426
Martín M, O’Neill RD, González-Mora JL, Salazar P (2014) The use of fluorocarbons to mitigate the oxygen dependence of glucose microbiosensors for neuroscience applications. J Electrochem Soc 161(10):H689–H695
Chen D-J, Lu Y-H, Wang A-J, Feng J-J, Huo T-T, Dong W-J (2012) Facile synthesis of ultra-long Cu microdendrites for the electrochemical detection of glucose. J Solid State Electrochem 16(4):1313–1321
Chen L, Xie H, Li J (2012) Electrochemical glucose biosensor based on silver nanoparticles/multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 16(10):3323–3329
Hovancová J, Šišoláková I, Oriňaková R, Oriňak A (2017) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for detection of glucose and insulin. J Solid State Electrochem 21(8):2147–2166
Clark LC Jr, Lyons C (1962) Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 102(1):29–45
Huang F, Wang F, Feng S, Li Y, Li S, Li Y (2013) Direct electrochemistry and electrochemical biosensing of glucose oxidase based on CdSe@CdS quantum dots and MWNT-modified electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 17(5):1295–1301
Li S-J, Chen T-W, Xia N, Hou Y-L, Du J-J, Liu L (2013) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on sulfonated graphene/gold nanoparticle hybrid and its application to glucose biosensing. J Solid State Electrochem 17(9):2487–2494
Liu L, Cheng Y, Sun F, Yang J, Wu Y (2012) Enhanced direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase based on a protic ionic liquid modified electrode and its biosensing application. J Solid State Electrochem 16(3):1003–1009
Lee H, Hong YJ, Baik S, Hyeon T, Kim DH (2018) Enzyme-based glucose sensor: from invasive to wearable device. Advanced healthcare materials 7(8):e1701150
Chen C, Xie Q, Yang D, Xiao H, Fu Y, Tan Y, Yao S (2013) Recent advances in electrochemical glucose biosensors: a review. RSC Adv 3(14):4473–4491
Harper A, Anderson MR (2010) Electrochemical glucose sensors—developments using electrostatic assembly and carbon nanotubes for biosensor construction. Sensors 10(9):8248–8274
Heller A, Feldman B (2008) Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem Rev 108(7):2482–2505
Chen D, Huang Y, Jiang H, Yasen W, Guo D, Su Y, Xue B, Jin X, Zhu X (2018) Fabrication of activity-reporting glucose oxidase nanocapsules with oxygen-independent fluorescence variation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(31):26005–26015
GS S, CV A, Mathew BB (2014) Biosensors: a modern day achievement. Journal of Instrumentation Technology 2(1):26–39
Narayanan JS, Anjalidevi C, Dharuman V (2013) Nonenzymatic glucose sensing at ruthenium dioxide–poly(vinyl chloride)–Nafion composite electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 17(4):937–947
Yu Z, Kong C, Lv J, Ma B, Zhang X, Yang Z (2020) Ultrathin CuxO nanoflakes anchored Cu2O nanoarray for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. J Solid State Electrochem 24(3):583–590
Gough DA, Lucisano JY, Tse PHS (1985) Two-dimensional enzyme electrode sensor for glucose. Anal Chem 57(12):2351–2357
Reach G, Wilson GS (1992) Can continuous glucose monitoring be used for the treatment of diabetes? Anal Chem 64(6):381A–386A
Cui Y, Barford JP, Renneberg R (2006) Development of an oxygen-rich biosensor using enzymatic reaction. Biotechnol Lett 28(22):1835–1840
Willner I, Katz E (2000) Integration of layered redox proteins and conductive supports for bioelectronic applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 39(7):1180–1218
Toghill K, Compton R (2010) Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: a perspective and an evaluation. Int J Electrochem Sci Int J 5:1246–1301
Wolfart F, Maciel A, Nagata N, Vidotti M (2013) Electrocatalytical properties presented by Cu/Ni alloy modified electrodes toward the oxidation of glucose. J Solid State Electrochem 17(5):1333–1338
Karimi A, Othman A, Andreescu S (2016) Portable enzyme-paper biosensors based on redox-active CeO2 nanoparticles. Methods Enzymol 571:177–195
Charbgoo F, Ramezani M, Darroudi M (2017) Bio-sensing applications of cerium oxide nanoparticles: advantages and disadvantages. Biosens Bioelectron 96:33–43
Vinothkumar G, Amalraj R, Babu KS (2017) Fuel-oxidizer ratio tuned luminescence properties of combustion synthesized Europium doped cerium oxide nanoparticles and its effect on antioxidant properties. Ceram Int 43(7):5457–5466
Sardesai NP, Karimi A, Andreescu S (2014) Engineered Pt-doped nanoceria for oxidase-based bioelectrodes operating in oxygen-deficient environments. ChemElectroChem 1(12):2082–2088
Zhou Y, Uzun SD, Watkins NJ, Li S, Li W, Briseno AL, Carter KR, Watkins JJ (2019) Three-dimensional CeO2 woodpile nanostructures to enhance performance of enzymatic glucose biosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(2):1821–1828
Sung M-C, Lee G-H, Kim D-W (2019) CeO2/Co(OH)2 hybrid electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen and oxygen evolution reaction. J Alloys Compd 800:450–455
Uzunoglu A, Stanciu LA (2016) Novel CeO2-CuO-decorated enzymatic lactate biosensors operating in low oxygen environments. Anal Chim Acta 909:121–128
Uzunoglu A, Zhang H, Andreescu S, Stanciu LA (2015) CeO2–MOx(M: Zr, Ti, Cu) mixed metal oxides with enhanced oxygen storage capacity. J Mater Sci 50(10):3750–3762
Vinothkumar G, Lalitha AI, Suresh Babu K (2019) Cerium phosphate-cerium oxide heterogeneous composite nanozymes with enhanced peroxidase-like biomimetic activity for glucose and hydrogen peroxide sensing. Inorg Chem 58(1):349–358
Li G, Chao K, Peng H, Chen K, Zhang Z (2008) Facile synthesis of CePO4 nanowires attached to CeO2 octahedral micrometer crystals and their enhanced photoluminescence properties. J Phys Chem C 112(42):16452–16456
Al-Agel FA, Al-Arfaj E, Al-Ghamdi AA, Stein BD, Losovyj Y, Bronstein LM, Shokr FS, Mahmoud WE (2015) Structure and magnetic properties of diluted magnetic metal oxides based on Cu-doped CeO2 nanopowders. Ceramics International 41(1, Part B):1115–1119
Asuvathraman R, Gnanasekar KI, Clinsha PC, Ravindran TR, Govindan Kutty KV (2015) Investigations on the charge compensation on Ca and U substitution in CePO4 by using XPS, XRD and Raman spectroscopy. Ceramics International 41(3, Part A):3731–3739
Kitsuda M, Fujihara S (2011) Quantitative luminescence switching in CePO4:Tb by redox reactions. J Phys Chem C 115(17):8808–8815
Celebioglu A, Vempati S, Ozgit-Akgun C, Biyikli N, Uyar T (2014) Water-soluble non-polymeric electrospun cyclodextrin nanofiber template for the synthesis of metal oxide tubes by atomic layer deposition. RSC Adv 4(106):61698–61705
Balamurugan A, Chen S-M (2007) Silicomolybdate doped polypyrrole film modified glassy carbon electrode for electrocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). J Solid State Electrochem 11(12):1679–1687
Doménech A, García H, Marquet J, Bourdelande JL, Herance JR (2006) Modelling electrocatalysis of hydroquinone oxidation by nicotinamide adenine dinucleaotide coenzyme encapsulated within SBA-15 and MCM-41 mesoporous aluminosilicates. Electrochim Acta 51(23):4897–4908
Schröder U, Oldham KB, Myland JC, Mahon PJ, Scholz F (2000) Modelling of solid state voltammetry of immobilized microcrystals assuming an initiation of the electrochemical reaction at a three-phase junction. J Solid State Electrochem 4(6):314–324
Meng F, Miao H, Shi J, Hu Z, Li G, Ding Y (2017) The synthesis of carbon/cerium oxide composites clusters with the assistance of the glucaminium-based surfactant and their electrochemical performance in the glucose monitoring. J Alloys Compd 713:125–131
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant 2018YFC1901202), NSF of China (81771976), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the joint fund of Southeast University and Nanjing Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by JX and KY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JX and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 823 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Yang, K., Zhang, X. et al. TiO2/CeO2-CePO4-decorated enzymatic glucose biosensors operating in oxygen-restrictive environments. J Solid State Electrochem 25, 1937–1947 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-021-04956-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-021-04956-4