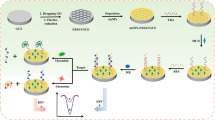
Abstract
We describe a label-free electrochemical aptasensor for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) assay based on bifunctional Fe3O4@Au nanocomposites. Due to the introduction of Au nanoparticles, the resulting bifunctional Fe3O4@Au nanocomposites can be easily modified with ATP-specific aptamer molecules through Au–S interaction to build the nanoprobe and used to immobilize on a glassy carbon electrode simply with the assistance of a magnet. Once exposed to the target ATP, the current signal obtained at nanoprobe-containing magnetic glassy carbon electrode decreases immediately. The decrease in sensor current is a result of the less methylene blue adsorbed on the aptamer caused by the fact that the ATP-specific aptamer prefers to bind with ATP rather than with methylene blue. The decrease in sensor current can be used for electrochemical determination of ATP, for example, to determine ATP in human serum samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wongkaew N, Simsek M, Griesche C, Baeumner AJ (2019) Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing electrochemical biosensors and lab-on-a-chip performances: recent progress, applications, and future perspective. Chem Rev 119(1):120–194
Freitas M, Couto MS, Barroso MF, Pereira C, de-los-Santos-Alvarez N, Miranda-Ordieres AJ, Lobo-Castanon MJ, Delerue-Matos C (2016) Highly monodisperse Fe3O4@Au superparamagnetic nanoparticles as reproducible platform for genosensing genetically modified organisms. ACS Sens 1(8):1044–1053
Amin MO, D’Cruz B, Madkour M, Al-Hetlani E (2019) Magnetic nanocomposite-based SELDI probe for extraction and detection of drugs, amino acids and fatty acids. Microchim Acta 186(8):503
Wu L, Mendoza-Garcia A, Li Q, Sun S (2016) Organic phase syntheses of magnetic nanoparticles and their applications. Chem Rev 116(18):10473–10512
Chowdhury AD, Agnihotri N, Doong R, De A (2017) Label-free and nondestructive separation technique for isolation of targeted DNA from DNA−protein mixture using magnetic Au−Fe3O4 nanoprobes. Anal Chem 89(22):12244–12251
Jamshaid T, Neto ETT, Eissa MM, Zine N, Kunita MH, El-Salhi AE, Elaissari A (2016) Magnetic particles: from preparation to lab-on-a-chip, biosensors, microsystems and microfluidics applications. Trends Anal Chem 79:344–362
Zhou H, Zou F, Koh K, Lee JJ (2014) Multifunctional magnetoplasmonic nanomaterials and their biomedical applications. Biomed Nanotechnol 10(10):2921–2949
Luo L, Li X, Crooks RM (2014) Low-voltage origami-paper-based electrophoretic device for rapid protein separation. Anal Chem 86(24):12390–12397
Miao P, Tang Y, Wang L (2017) DNA modified Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanoparticles as selective probes for simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(4):3940–3947
Zhu C, Zhu W, Xu L, Zhou X (2019) A label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on magnetic biocomposites with Pb2+-dependent DNAzyme for the detection of thrombin. Anal Chim Acta 1047:21–27
Wang H, Tang H, Yang C, Li Y (2019) Selective single molecule nanopore sensing of microRNA using PNA functionalized magnetic core–shell Fe3O4–Au nanoparticles. Anal Chem 91(12):7965–7970
Gu W, Deng X, Gu X, Jia X, Lou B, Zhang X, Li J, Wang E (2015) Stabilized, superparamagnetic functionalized graphene/Fe3O4@Au nanocomposites for a magnetically-controlled solid-state electrochemiluminescence biosensing application. Anal Chem 87(3):1876–1881
Schoukroun-Barnes LR, Macazo FC, Gutierrez B, Lottermoser J, Liu J, White RJ (2016) Reagentless, structure-switching, electrochemical aptamer-based sensors. Annu Rev Anal Chem 9(1):163–181
Cunningham JC, Brenes NJ, Crooks RM (2014) Paper electrochemical device for detection of DNA and thrombin by target-induced conformational switching. Anal Chem 86(12):6166–6170
Wang D, Xiao X, Xu S, Liu Y, Li Y (2018) Electrochemical aptamer-based nanosensor fabricated on single Au nanowire electrodes for adenosine triphosphate assay. Biosens Bioelectron 99:431–437
Kashefifi-Kheyrabadi L, Mehrgardi MA, Wiechec E, Turner APF, Tiwari A (2014) Ultrasensitive detection of human liver hepatocellular carcinoma cells using a label-free aptasensor. Anal Chem 86(10):4956–4960
Zhang YJ, Clausmeyer J, Babakinejad B, Cordoba AL, Ali T, Shevchuk A, Akahashi Y, Novak P, Edwards C, Lab M, Gopal S, Chiappini C, Anand U, Magnani L, Coombes RC, Gorelik J, Matsue T, Schuhmann W, Klenerman D, Sviderskaya EV, Korchev Y (2016) Spearhead nanometric field-effect transistor sensors for single-cell analysis. ACS Nano 10(3):3214–3221
Li X, Peng Y, Chai YQ, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2016) A target responsive aptamer machine for label-free and sensitive non-enzymatic recycling amplification detection of ATP. Chem Commun 52(18):3673–3676
Li MJ, Zheng YN, Liang WB, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2017) Using p-type PbS quantum dots to quench photocurrent of fullerene−Au NP@MoS2 composite structure for ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical detection of ATP. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(48):42111–42120
Ding XJ, Wang YH, Cheng W, Mo F, Sang Y, Xu LL, Ding SJ (2017) Aptamer based electrochemical adenosine triphosphate assay based on a target-induced dendritic DNA nanoassembly. Microchim Acta 184(2):431–438
Santos-Cancel M, Simpson LW, Leach JB, White RJ (2019) Real-time detection of adenosine triphosphate release from astrocytes in three-dimensional culture using an integrated electrochemical aptamer-based sensor. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(4):2070–2079
Li S, Zhao X, Yu X, Wan Y, Yin M, Zhang W, Cao B (2019) Fe3O4 nanozymes with aptamer-tuned catalysis for selective colorimetric analysis of ATP in blood. Anal Chem 91(22):14737–14742
Rohs R, Sklenar H, Lavery R, Roder B (2000) Methylene blue binding to DNA with alternating GC base sequence: a modeling study. J Am Chem Soc 122(12):2860–2866
Mezni A, Balti I, Mlayah A, Jouini N, Smiri LS (2013) Hybrid Au–Fe3O4 nanoparticles: plasmonic, surface enhanced Raman scattering, and phase transition properties. J Phys Chem C 117(31):16166–16174
Peng Y, Li D, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2018) A catalytic and dual recycling amplification ATP sensor based on target-driven allosteric structure switching of aptamer beacons. Biosens Bioelectron 105:1–5
Ma Y, Geng F, Wang Y, Xu M, Shao C, Qu P, Zhang Y, Ye B (2019) Novel strategy to improve the sensing performances of split ATP aptamer based fluorescent indicator displacement assay through enhanced molecular recognition. Biosens Bioelectron 134:36–41
Feng L, Sivanesan A, Lyu Z, Offenhäusser A, Mayer D (2015) Electrochemical current rectification–a novel signal amplification strategy for highly sensitive and selective aptamer-based biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 66:62–68
Lu L, Si JC, Gao ZF, Zhang Y, Lei JL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2015) Highly selective and sensitive electrochemical biosensor for ATP based on the dual strategy integrating the cofactor-dependent enzymatic ligation reaction with self-cleaving DNAzyme-amplified electrochemical detection. Biosens Bioelectron 63:14–20
Zhou Q, Lin Y, Lin Y, Wei Q, Chen G, Tang D (2016) In situ amplified electrochemical aptasensing for sensitive detection of adenosine triphosphate by coupling target-induced hybridization chain reaction with the assembly of silver nanotags. Talanta:23–28
Li X, Yang J, Xie J, Jiang B, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2018) Cascaded signal amplification via target-triggered formation of aptazyme for sensitive electrochemical detection of ATP. Biosens Bioelectron 102:296–300
Coolen EJ, Arts IC, Swennen EL, Bast A, Stuart MA, Dagnelie PCJ (2008) Simultaneous determination of adenosine triphosphate and its metabolites in human whole blood by RP-HPLC and UV-detection. Chromatogr B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 864(1-2):43–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Lv, M., Pan, Q. et al. An electrochemical aptasensor based on bifunctional Fe3O4@Au nanocomposites for adenosine triphosphate assay. J Solid State Electrochem 25, 1073–1081 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-020-04887-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-020-04887-6