Abstract
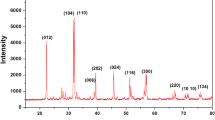
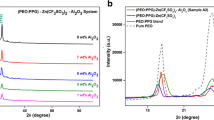
In the present work, the effect of dispersion of Al2O3 nanoparticles on ionic conductivity of non-aqueous PVdF-HFP/PMMA blend-based nanocomposite gel polymer electrolyte system comprising liquid electrolyte of sodium trifluoromethanesulfonate is investigated. The ionic conductivity of the electrolyte increases maximum to ∼ 1.5 × 10−3 S cm−1 for the composition with 6 wt% Al2O3 nanoparticles. The optimized composition retains Vogel-Tamman-Fulcher (VTF) behavior in the temperature range from − 50 to 95 °C. The scanning electron micrography and x-ray diffraction studies reveal the uniform dispersion of Al2O3 nanoparticles in the porous structure of the nanocomposite gel polymer electrolyte and enhanced amorphicity of polymer matrix. The optimized electrolyte composition owns a sufficiently large electrochemical stability window of ~ 3.6 V with good sodium ion transference number. The optimized electrolyte is used in a prototype sodium battery cell, which shows an open circuit potential of ~ 2.5 V and first discharge capacity ~ 400 mA h g−1 followed by a capacity decline with cycling.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan H, Hu YS, Chen L (2013) Room-temperature stationary sodium-ion batteries for large-scale electric energy storage. Energy Environ Sci 6(8):2338–2360
Hwang JY, Myung ST, Sun YK (2017) Sodium-ion batteries: present and future. Chem Soc Rev 46(12):3529–3614
Kubota K, Komaba S (2015) Review—practical issues and future perspective for Na-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 162(14):A2538–A2550
Kumar D, Rajouria SK, Kuhar SB, Kanchan DK (2017) Progress and prospects of sodium-sulfur batteries: a review. Solid State Ionics 312:8–16
Attias R, Salama M, Hirsch B, Goffer Y, Aurbach D (2019) Anode-electrolyte interfaces in secondary magnesium batteries. Joule 3(1):27–52
Muldoon J, Bucur CB, Gregory T (2017) Fervent hype behind magnesium batteries: an open call to synthetic chemists—electrolytes and cathodes needed. Angew Chem Int Ed 56(40):12064–12084
Khor A, Leung P, Mohamed MR, Flox C, Xu Q, An L, Wills RGA, Morante JR, Shah AA (2018) Review of zinc-based hybrid flow batteries: from fundamentals to applications. Mater Today Energy 8:80–108
Chen X, Zhou Z, Karahan HE, Shao Q, Wei L, Chen Y (2018) Recent advances in materials and design of electrochemically rechargeable zinc–air batteries. Small 14(44):1801929
Masese T, Yoshii K, Yamaguchi Y, Okumura T, Huang ZD, Kato M, Kubota K, Furutani J, Orikasa Y, Senoh H, Sakaebe H, Shikano M (2018) Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors. Nat Commun 9(1):3823
Moyer K, Donohue J, Ramanna N, Cohn AP, Muralidharan N, Eaves J, Pint CL (2018) High-rate potassium ion and sodium ion batteries by co-intercalation anodes and open framework cathodes. Nanoscale 10(28):13335–13342
Ponrouch A, Monti D, Boschin A, Steen B, Johansson P, Palacín MR (2015) Non-aqueous electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3(1):22–42
Che H, Chen S, Xie Y, Wang H, Amine K, Liao XZ, Ma ZF (2017) Electrolyte design strategies and research progress for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 10(5):1075–1101
Wu F, Zhu N, Bai Y, Liu L, Zhou H, Wu C (2016) Highly safe ionic liquid electrolytes for sodium-ion battery: wide electrochemical window and good thermal stability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(33):21381–21386
Monti D, Jónsson E, Palacín MR, Johansson P (2014) Ionic liquid based electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries: Na+ solvation and ionic conductivity. J Power Sources 245:630–636
Ngai KS, Ramesh S, Ramesh K, Juan JC (2016) A review of polymer electrolytes: fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics 22(8):1259–1279
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(22):223001 (pp 18)
Cheng X, Pan J, Zhao Y, Liao M, Peng H (2018) Gel polymer electrolytes for electrochemical energy storage. Adv Energy Mater 8(7):1702184
Yadav N, Mishra K, Hashmi SA (2017) Optimization of porous polymer electrolyte for quasi-solid-state electrical double layer supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 235:570–582
Yang YQ, Chang Z, Li MX, Wang XW, Wu YP (2015) A sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 269:1–7
Xue Y, Quesnel DJ (2016) Synthesis and electrochemical study of sodium ion transport polymer gel electrolytes. RSC Adv 6(9):7504–7510
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ion transport and ion–filler-polymer interaction in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195(15):5101–5108
Hashmi SA, Bhat MY, Singh MK, Sundaram NTK, Raghupathy BPC, Tanaka H (2016) Ionic liquid-based sodium ion-conducting composite gel polymer electrolytes: effect of active and passive fillers. J Solid State Electrochem 20(10):2817–2826
Vignarooban K, Badami P, Dissanayake MAKL, Ravirajan P, Kannan AM (2017) Poly-acrylonitrile-based gel-polymer electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. Ionics 23(10):2817–2822
Edmondson CA, Wintersgill MG, Fontanella JJ, Gerace F, Scrosati B, Greenbaum SG (1996) High pressure NMR and electrical conductivity studies of gel electrolytes based on poly(acrylonitrile). Solid State Ionics 85(1-4):173–179
He Z, Cao Q, Jing B, Wang X, Deng Y (2017) Gel electrolytes based on poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)/thermoplastic polyurethane/poly(methyl methacrylate) with in situ SiO2 for polymer lithium batteries. RSC Adv 7(6):3240–3248
Gebreyesus MA, Purushotham Y, Kumar JS (2016) Preparation and characterization of lithium ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on a blend of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) and poly(methyl methacrylate). Heliyon 2(7):e00134
Jacob MME, Hackett E, Giannelis EP (2003) From nanocomposite to nanogel polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem 13(1):1–5
Scrosati B, Corce F, Persi L (2000) Impedance spectroscopy study of PEO-based nanocomposite polymer electrolyte. J Electrochem Soc 147(5):1718–1721
Mishra K, Garg A, Sharma R, Gautam R, Pundir SS (2019) Effect of blending of PMMA on PVdF-HFP+ NaCF3SO3-EC-PC gel polymer electrolyte. Mater Today Proc 12:621–627
Mishra K, Hashmi SA, Rai DK (2013) Nanocomposite blend gel polymer electrolyte for proton battery application. J Solid State Electrochem 17(3):785–793
Pundir SS, Mishra K, Rai DK (2018) Ion transport studies in nanocomposite polymer electrolyte membrane of PVA–[C4C1Im][HSO4]–SiO2. J Solid State Electrochem 22:1201–1215
Kumar B (2004) From colloidal to composite electrolytes: properties, peculiarities, and possibilities. J. Power Sources 135(1-2):215–231
Saito Y, Kataoka H, Quartarone E, Mustarelli P (2002) Carrier migration mechanism of physically cross-linked polymer gel electrolytes based on PVDF membranes. J Phys Chem B 106(29):7200–7204
Mishra K, Hashmi SA, Rai DK (2014) Protic ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte: evidence of proton conduction and performance studies of proton battery. J Solid State Electrochem 18(8):2255–2266
Adelhelm P, Hartmann P, Bender CL, Busche M, Eufinger C, Janek J (2015) From lithium to sodium: cell chemistry of room temperature sodium–air and sodium–sulfur batteries. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 6:1016–1055
Wang YX, Zhang B, Lai W, Xu Y, Chou SL, Liu HK, Dou SX (2017) Room temperature sodium-sulfur batteries: a comprehensive review on research progress and cell chemistry. Adv Energy Mater 7(24):1602829
Kumar D, Kanchan DK, Kumar S, Mishra K (2019) Recent trends on tailoring cathodes for room-temperature Na-S batteries. Mater Sci Energy Technol 2:117–129
Acknowledgments
One of us (DK) thanks and acknowledges the encouragement and motivation received from Electronics and Mechanical Engineering School, Corps of Electronics and Mechanical Engineers, Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board, a statutory body of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (File No: YSS/2015/001234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, K., Arif, T., Kumar, R. et al. Effect of Al2O3 nanoparticles on ionic conductivity of PVdF-HFP/PMMA blend-based Na+-ion conducting nanocomposite gel polymer electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 2401–2409 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04348-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04348-9