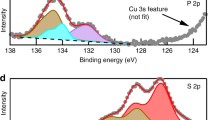
Abstract
The fundamental understanding of the solid electrolyte/electrode interphase during charge and discharge is promising for the development of all-solid-state batteries. Here, we employ a solid-state Li/Li6.4Ga0.2La3Zr2O12/LiFePO4 cell and study in situ the electrolyte/anode and electrolyte/cathode interphase as a function of applied potential under ultra-high vacuum using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. An ultra-thin interfacial passivation layer is formed at the Li/Ga-doped LLZO interphase, which inhibits the Ga-LLZO from being further reduced by Li. During charging, the oxidation reaction of Li with Ga-LLZO still occurs, which is evidenced by the broadening of the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and shifting of the Li 1s peak towards lower binding energies and the increment of Li2O peak intensity in the O 1s range. The Ga-LLZO solid electrolyte/LiFePO4 cathode interphase was also studied by in situ XPS under UHV. The deintercalation of Li+ ion is evidenced by the broadening and shifting of Fe 2p peak during charging. Other components shift by the same values as the applied potential. These results indicate good reversibility of the LiFePO4/Ga-LLZO interphase upon charge/discharge. The long-term stability of the LiFePO4/Ga-LLZO interphase was also examined during charging/discharging for 100 cycles. These insights provide a new perspective for understanding of the solid electrolyte interphase, which enables high energy density, long-term stability, and safety for next-generation batteries.

Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng F, Kotobuki M, Song S, Lai MO, Lu L (2018) Review on solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 389:198–213
Sun C, Liu J, Gong Y, Wilkinson DP, Zhang J (2017) Recent advances in all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. Nano Energy 33:363–386
Quartarone E, Mustarelli P (2011) Electrolytes for solid-state lithium rechargeable batteries: recent advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2525–2540
Thangadurai V, Narayanan S, Pinzaru D (2014) Garnet-type solid-state fast Li ion conductors for Li batteries: critical review. Chem Soc Rev 43(13):4714–4727
Oudenhoven JFM, Baggetto L, Notten PHL (2011) All-solid-state lithium-ion microbatteries: a review of various three-dimensional concepts. Adv Energy Mater 1(1):10–33
Kamaya N, Homma K, Yamakawa Y, Hirayama M, Kanno R, Yonemura M, Kamiyama T, Kato Y, Hama S, Kawamoto K, Mitsui A (2011) A lithium superionic conductor. Nat Mater 10(9):682–686
Bron P, Johansson S, Zick K, Schmedt auf der Günne J, Dehnen S, Roling B (2013) Li10SnP2S12: an affordable lithium superionic conductor. J Am Chem Soc 135(42):15694–15697
Cussen EJ (2010) Structure and ionic conductivity in lithium garnets. J Mater Chem 20(25):5167–5173
Thangadurai V, Kaack H, Weppner WJF (2003) Novel fast Lithiumlion conduction in garnet-type Li5La3M2O12 (M = Nb, Ta). J Am Ceram Soc 86(3):437–440
Percival J, Kendrick E, Smith RI, Slater PR (2009) Cation ordering in Li containing garnets: synthesis and structural characterisation of the tetragonal system, Li7La3Sn2O12. Dalton Trans (26):5177–5181. https://doi.org/10.1039/B907331K
Murugan R, Thangadurai V, Weppner W (2007) Fast lithium ion conduction in garnet-type Li7La3Zr2O12. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(41):7778–7781
Ramzy A, Thangadurai V (2010) Tailor-made development of fast Li ion conducting garnet-like solid electrolytes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(2):385–390
Awaka J, Kijima N, Hayakawa H, Akimoto J (2009) Synthesis and structure analysis of tetragonal Li7La3Zr2O12 with the garnet-related type structure. J Solid State Chem 182(8):2046–2052
Yang SH, Kim MY, Kim DH, Jung HY, Ryu HM, Han JH, Lee MS, Kim H-S (2017) Ionic conductivity of Ga-doped LLZO prepared using Couette–Taylor reactor for all-solid lithium batteries. J Ind Eng Chem 56:422–427
Ohta S, Kobayashi T, Asaoka T (2011) High lithium ionic conductivity in the garnet-type oxide Li7−X La3(Zr2−X, NbX)O12 (X=0–2). J Power Sources 196(6):3342–3345
Li Y, Wang C-A, Xie H, Cheng J, Goodenough JB (2011) High lithium ion conduction in garnet-type Li6La3ZrTaO12. Electrochem Commun 13(12):1289–1292
Kumazaki S, Iriyama Y, Kim K-H, Murugan R, Tanabe K, Yamamoto K, Hirayama T, Ogumi Z (2011) High lithium ion conductive Li7La3Zr2O12 by inclusion of both Al and Si. Electrochem Commun 13(5):509–512
Luntz AC, Voss J, Reuter K (2015) Interfacial challenges in solid-state Li ion batteries. J Phys Chem Lett 6(22):4599–4604
Fu K, Gong Y, Liu B, Zhu Y, Xu S, Yao Y, Luo W, Wang C, Lacey SD, Dai J, Chen Y, Mo Y, Wachsman E, Hu L (2017) Toward garnet electrolyte–based Li metal batteries: an ultrathin, highly effective, artificial solid-state electrolyte/metallic Li interface. Sci Adv 3(4):e1601659
Luo W, Gong Y, Zhu Y, Li Y, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Fu K, Pastel G, Lin C-F, Mo Y, Wachsman ED, Hu L (2017) Reducing interfacial resistance between garnet-structured solid-state electrolyte and Li-metal anode by a germanium layer. Adv Mater 29:1606042
Tsai C-L, Roddatis V, Chandran CV, Ma Q, Uhlenbruck S, Bram M, Heitjans P, Guillon O (2016) Li7La3Zr2O12 interface modification for Li dendrite prevention. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(16):10617–10626
Zhou W, Wang S, Li Y, Xin S, Manthiram A, Goodenough JB (2016) Plating a dendrite-free lithium anode with a polymer/ceramic/polymer sandwich electrolyte. J Am Chem Soc 138(30):9385–9388
Wu X, Villevieille C, Novák P, El Kazzi M (2018) Monitoring the chemical and electronic properties of electrolyte–electrode interfaces in all-solid-state batteries using operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 20(16):11123–11129
Koerver R, Walther F, Aygün I, Sann J, Dietrich C, Zeier WG, Janek J (2017) Redox-active cathode interphases in solid-state batteries. J Mater Chem A 5(43):22750–22760
Wood KN, Teeter G (2018) XPS on Li-battery-related compounds: analysis of inorganic SEI phases and a methodology for charge correction. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1(9):4493–4504
Tonti D, Pettenkofer C, Jaegermann W (2004) Origin of the electrochemical potential in intercalation electrodes: experimental estimation of the electronic and ionic contributions for Na intercalated into TiS2. J Phys Chem B 108(41):16093–16099
Wolfenstine J, Ratchford J, Rangasamy E, Sakamoto J, Allen JL (2012) Synthesis and high Li-ion conductivity of Ga-stabilized cubic Li7La3Zr2O12. Mater Chem Phys 134(2-3):571–575
Wu J-F, Chen E-Y, Yu Y, Liu L, Wu Y, Pang WK, Peterson VK, Guo X (2017) Gallium-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 garnet-type electrolytes with high lithium-ion conductivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(2):1542–1552
Rettenwander D, Redhammer G, Preishuber-Pflügl F, Cheng L, Miara L, Wagner R, Welzl A, Suard E, Doeff MM, Wilkening M, Fleig J, Amthauer G (2016) Structural and electrochemical consequences of Al and Ga cosubstitution in Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolytes. Chem Mater 28(7):2384–2392
Bernuy-Lopez C, Manalastas W, Lopez del Amo JM, Aguadero A, Aguesse F, Kilner JA (2014) Atmosphere controlled processing of Ga-substituted garnets for high Li-ion conductivity ceramics. Chem Mater 26(12):3610–3617
Sharafi A, Yu S, Naguib M, Lee M, Ma C, Meyer HM, Nanda J, Chi M, Siegel DJ, Sakamoto J (2017) Impact of air exposure and surface chemistry on Li–Li7La3Zr2O12 interfacial resistance. J Mater Chem A 5(26):13475–13487
Cheng L, Crumlin EJ, Chen W, Qiao R, Hou H, Franz Lux S, Zorba V, Russo R, Kostecki R, Liu Z, Persson K, Yang W, Cabana J, Richardson T, Chen G, Doeff M (2014) The origin of high electrolyte–electrode interfacial resistances in lithium cells containing garnet type solid electrolytes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16(34):18294–18300
Biesinger MC, Payne BP, Grosvenor AP, Lau LWM, Gerson AR, Smart RSC (2011) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl Surf Sci 257(7):2717–2730
Rho Y-H, Nazar LF, Perry L, Ryan D (2007) Surface chemistry of LiFePO4 studied by Mössbauer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and its effect on electrochemical properties. J Electrochem Soc 154(4):A283–A289
Castro L, Dedryvère R, El Khalifi M, Lippens PE, Bréger J, Tessier C, Gonbeau D (2010) The spin-polarized electronic structure of LiFePO4 and FePO4 evidenced by in-lab XPS. J Phys Chem C 114(41):17995–18000
Yao KPC, Kwabi DG, Quinlan RA, Mansour AN, Grimaud A, Lee Y-L, Lu Y-C, Shao-Horn Y (2013) Thermal stability of Li2O2 and Li2O for Li-air batteries: in situ XRD and XPS studies. J Electrochem Soc 160(6):A824–A831
Ma C, Cheng Y, Yin K, Luo J, Sharafi A, Sakamoto J, Li J, More KL, Dudney NJ, Chi M (2016) Interfacial stability of Li metal–solid electrolyte elucidated via in situ electron microscopy. Nano Lett 16(11):7030–7036
Dedryvère R, Maccario M, Croguennec L, Le Cras F, Delmas C, Gonbeau D (2008) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy investigations of carbon-coated LixFePO4 materials. Chem Mater 20(22):7164–7170
Castro L, Dedryvère R, Ledeuil J-B, Bréger J, Tessier C, Gonbeau D (2012) Aging mechanisms of LiFePO4 // graphite cells studied by XPS: redox reaction and electrode/electrolyte interfaces. J Electrochem Soc 159(4):A357–A363
Miara LJ, Richards WD, Wang YE, Ceder G (2015) First-principles studies on cation dopants and electrolyte|cathode interphases for lithium garnets. Chem Mater 27(11):4040–4047
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank a joint project funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (EN 370/28-1) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51761135123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 547 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Li, G., Borodin, A. et al. In situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy investigation of the solid electrolyte interphase in a Li/Li6.4Ga0.2La3Zr2O12/LiFePO4 all-solid-state battery. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 2107–2117 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04296-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04296-4