Abstract
Novel two-stage pulse electrodeposition was used to fabricate TiO2-NTs@Sb-SnO2 electrodes. At the first pulse stage, a compact Sb-SnO2-coating TiO2-NTs interlayer was realized; at the second, various morphologies of apparent layers including flower-like, hierarchical, and dendritic morphologies were realized through regulating pulse parameters. Morphology-dependent electrode activities were investigated. Electrochemical experiment results show that dendritic-morphology electrode has the lowest charge transfer impedance (27.5 Ω vs. 43.2, 38.1, and 37.5 Ω) in comparison with other electrodes, and chronopotentiometry tests show a higher accelerated service lifetime of dendritic electrode (23 h vs. 17.8, 17.4, and 13.9 h), indicating the optimal electrochemical activity. The electrocatalytic methyl orange decolorization processes show that dendritic electrode possesses a higher first-order kinetics rate constant than other two electrodes (51.7 × 10−3 min−1 vs. 32.5 × 10−3, 39.7 × 10−3, and 35.5 × 10−3 min−1). These results demonstrate that the dendritic electrode possesses the most efficient catalytic performance.

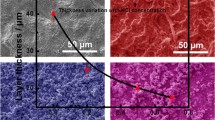
Various morphologies on electrodes were realized, and experimental results reveal the morphology-dependent activities of electrodes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng M, Zeng G, Huang D, Lai C, Xu P, Zhang C, Liu Y (2016) Hydroxyl radicals based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for remediation of soils contaminated with organic compounds: a review. Chem Eng J 284:582–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.001
Antonopoulou M, Evgenidou E, Lambropoulou D, Konstantinou I (2014) A review on advanced oxidation processes for the removal of taste and odor compounds from aqueous media. Water Res 53:215–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.01.028
Martínez-Huitle CA, Rodrigo MA, Sires I, Scialdone O (2015) Single and coupled electrochemical processes and reactors for the abatement of organic water pollutants: a critical review. Chem Rev 115(24):13362–13407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00361
Ganzenko O, Huguenot D, Hullebusch ED, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation and biological processes for wastewater treatment: a review of the combined approaches. Environ Sci Pollut R 21(14):8493–8524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2770-6
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA, Rodrigo MA, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(14):8336–8367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Trasatti S (2000) Electrocatalysis: understanding the success of DSA. Electrochim Acta 45(15-16):2377–2385. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(00)00338-8
Chen G (2004) Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 38(1):11–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2003.10.006
Martínez-Huitle CA, Ferro S (2006) Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes. Chem Soc Rev 35(12):1324–1340. https://doi.org/10.1039/B517632H
Chaplin BP (2014) Critical review of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for water treatment applications. Environ Sci Proc Impacts 16(6):1182–1203. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00679D
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B-Environ 166-167:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem Rev 109(12):6541–6569. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr9001319
Bagastyo AY, Batstone DJ, Rabaey K, Radjenovic J (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of electrodialysed reverse osmosis concentrate on Ti/Pt-IrO2, Ti/SnO2-Sb and boron-doped diamond electrodes. Water Res 47(1):242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.10.001
Lin H, Niu J, Ding S, Zhang L (2012) Electrochemical degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by Ti/SnO2-Sb, Ti/SnO2-Sb/PbO2 and Ti/SnO2–Sb/MnO2 anodes. Water Res 46(7):2281–2289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.053
Lin H, Niu J, Xu J, Huang H, Li D, Yue Z, Feng C (2013) Highly efficient and mild electrochemical mineralization of long-chain perfluorocarboxylic acids (C9-C10) by Ti/SnO2-Sb-Ce, Ti/SnO2-Sb/Ce-PbO2, and Ti/BDD electrodes. Environ Sci Technol 47(22):13039–13046. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4034414
Valero D, García-García V, Expósito E, Aldaz A, Montiel V (2014) Electrochemical treatment of wastewater from almond industry using DSA-type anodes: direct connection to a PV generator. Sep Purif Technol 123:15–22
Rao ANS, Venkatarangaiah VT (2014) Metal oxide-coated anodes in wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:3197–3217
Wu W, Huang Z-H, Lim T-T (2014) Recent development of mixed metal oxide anodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants in water. App Catal A-Gen 480:58–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.04.035
Yang SY, Kim D, Park H (2014) Shift of the reactive species in the Sb-SnO2-electrocatalyzed inactivation of E. coli and degradation of phenol: effects of nickel doping and electrolytes. Environ Sci Technol 48:2877–2884
Yang SY, Choi W, Park H (2015) TiO2 nanotube array photoelectrocatalyst and Ni-Sb-SnO2 electrocatalyst bifacial electrodes: a new type of bifunctional hybrid platform for water treatment. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(3):1907–1914. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5076748
Liu L, Liu H, Zhao Y-P, Wang Y, Duan Y, Gao G, Ge M, Chen W (2008) Directed synthesis of hierarchical nanostructured TiO2 catalysts and their morphology-dependent photocatalysis for phenol degradation. Environ Sci Technol 42(7):2342–2348. https://doi.org/10.1021/es070980o
Li Y, Shen W (2014) Morphology-dependent nanocatalysts: rod-shaped oxides. Chem Soc Rev 43(5):1543–1574. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60296F
Xia Y, Xiong Y, Lim B, Skrabalak SE (2009) Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: simple chemistry meets complex physics? Angew Chem Int Edit 48(1):60–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200802248
Montilla F, Morallón E, Vázqueza JL (2005) Evaluation of the electrocatalytic activity of antimony-doped tin dioxide anodes toward the oxidation of phenol in aqueous solutions. J Electrochem Soc 152:B421–B427
Adams B, Tian M, Chen A (2009) Design and electrochemical study of SnO2-based mixed oxide electrodes. Electrochim Acta 54:1491–1498
Christensen PA, Zakaria K, Christensen H, Yonard T (2013) The effect of Ni and Sb oxide precursors, and of Ni composition, synthesis conditions and operating parameters on the activity, selectivity and durability of Sb-doped SnO2 anodes modified with Ni. J Electrochem Soc 160(8):H405–H413. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.023308jes
Sun Z, Zhang H, Wei X, Du R, Hu X (2015) Fabrication and electrochemical properties of a SnO2-Sb anode doped with Ni-Nd for phenol oxidation. J Electrochem Soc 162(9):H590–H596. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0221509jes
Fan CM, Hu B, Wang Y, Liang ZH, Hao XG, Liu SB, Sun YP (2009) Preparation of Ti/SnO2-Sb2O4 photoanode by electrodeposition and dip coating for PEC oxidations. Desalination 249(2):736–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.01.035
Chen Y, Li H, Liu W, Tu Y, Zhang Y, Han W, Wang L (2014) Electrochemical degradation of nitrobenzene by anodic oxidation on the constructed TiO2-NTs/SnO2-Sb/PbO2 electrode. Chemosphere 113:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.122
Hu F, Dong Z, Cui X, Chen W (2011) Improved SnO2-Sb2O4 based anode modified with Cr3C2 and CNT for phenol oxidation. Electrochim Acta 56(3):1576–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.10.037
Chen Z, Li S, Zhang W (2013) Pulse electrodeposition of ZnO/SnO2 composite films: growth mechanism, structural and optical studies. J Alloy Compd 557:274–278
Lai M, Lim J-H, Mubeen S, Rheem Y, Mulchandani A, Deshusses MA, Myung NV (2009) Size-controlled electrochemical synthesis and properties of SnO2 nanotubes. Nanotechnology 20(18):185602–185607. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/18/185602
Moura DCD, Cerro-López M, Quiroz MA, Silva DRD, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Large disk electrodes of Ti/TiO2-nanotubes/PbO2 for environmental applications. RSC Adv 5(40):31454–31459. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA16723F
Cerro-Lopez M, Meas-Vong Y, Méndez-Rojas MA, Martínez-Huitle CA, Quiroz MA (2014) Formation and growth of PbO2 inside TiO2 nanotubes for environmental applications. Appl Catal B-Environ 144:174–181
Moura DCD, Quiroz MA, Silva DRD, Salazar R, Martínez-Huitle CA (2016) Electrochemical degradation of acid blue 113 dye using TiO2-nanotubes decorated with PbO2 as anode. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management 5:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2015.11.001
Chen A, Nigro S (2003) Influence of a nanoscale gold thin layer on Ti/SnO2-Sb2O5 electrodes. J Phys Chem B 107(48):13341–13348. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp036138w
Fernandes A, Santos D, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2014) Nitrogen and organic load removal from sanitary landfill leachates by anodic oxidation at Ti/Pt/PbO2, Ti/Pt/SnO2-Sb2O4 and Si/BDD. Appl Catal B Environ 148-149:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.060
Cui X, Zhao G, Lei Y, Li H, Li P, Liu M (2009) Novel vertically aligned TiO2 nanotubes embedded with Sb-doped SnO2 electrode with high oxygen evolution potential and long service time. Mater Chem Phys 113(1):314–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.07.087
Zhao G, Cui X, Liu M, Li P, Zhang Y, Cao T, Li H, Lei Y, Liu L, Li D (2009) Electrochemical degradation of refractory pollutant using a novel microstructured TiO2 nanotubes/Sb-doped SnO2 electrode. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1480–1486. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802155p
Wu T, Zhao G, Lei Y, Li P (2011) Distinctive tin dioxide anode fabricated by pulse electrodeposition: high oxygen evolution potential and efficient electrochemical degradation of fluorobenzene. J Phys Chem C 115(10):3888–3898. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp110149v
Wang Q, Jin T, Hu Z, Zhou L, Zhou M (2013) TiO2-NTs/SnO2-Sb anode for efficient electrocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants: effect of TiO2-NTs architecture. Sep Purif Technol 102:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.10.006
Guo Y, Duan T, Chen Y, Wen Q (2015) Solvothermal fabrication of three-dimensionally sphere-stacking Sb-SnO2 electrode based on TiO2 nanotube arrays. Ceram Int 41(7):8723–8729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.03.092
Jara CC, Salazar-Banda GR, Arratia RS, Campino JS, Aguilera MI (2011) Improving the stability of Sb doped Sn oxides electrode thermally synthesized by using an acid ionic liquid as solvent. Chem Eng J 171:1253–1262
Santos TÉS, Silva RS, Meneses CT, Martínez-Huitle CA, Eguiluz KIB, Salazar-Banda GR (2016) Unexpected enhancement of electrocatalytic nature of Ti/(RuO2)x-(Sb2O5)y anodes prepared by the ionic liquid-thermal decomposition method. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(11):3182–3187. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b04690
Duan T, Chen Y, Wen Q, Duan Y, Qi L (2016) Component-controlled synthesis of gradient electrode for efficient electrocatalytic dye decolorization. J Electrochem Soc 163:H499–H507
Duan T, Chen Y, Wen Q, Duan Y (2015) Different mechanisms and electrocatalytic activities of Ce ion or CeO2 modified Ti/Sb-SnO2 electrodes fabricated by one-step pulse electro-codeposition. RSC Adv 5(25):19601–19612. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01876E
Ourya A, Kirchev A, Bultel Y (2012) Oxygen evolution on alpha-lead dioxide electrodes in methanesulfonic acid. Electrochim Acta 63:28–33
Yao Y, Zhao C, Zhao M, Wang X (2013) Electrocatalytic degradation of methylene blue on PbO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite electrodes prepared by pulse electrodeposition. J Hazard Mater 263:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.10.038
Hamza M, Abdelhedi R, Brillas E, Sirés I (2009) Comparative electrochemical degradation of the triphenylmethane dye methyl violet with boron-doped diamond and Pt anodes. J Electroanal Chem 627(1-2):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2008.12.017
Zhou M, Särkkä H, Sillanpää M (2011) A comparative experimental study on methyl orange degradation by electrochemical oxidation on BDD and MMO electrodes. Sep Purif Technol 78:290–297
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by High-technology Ship Research Project of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, T., Ma, L., Chen, Y. et al. Morphology-dependent activities of TiO2-NTs@Sb-SnO2 electrodes for efficient electrocatalytic methyl orange decolorization. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 1871–1879 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3895-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3895-1