Abstract
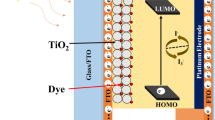
Hierarchically nano-structured ZnO microspheres have been synthesized solvothermally at variable reaction times (6, 12, 36, and 48 h) by using ethylene glycol as a solvent, zinc acetate as precursor, and hexamethylene triamine (HMT) as structure directing agent. The study also focused on the mechanism of time-dependant growth of hierarchical ZnO microspheres and their deployment in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) as photoanode. Longer reaction times lead to formation of nearly spherical ZnO microspheres. The structural and morphological analysis reveals the formation of a wurtzite hexagonal crystalline structure having a microsphere-like morphology. ZnO hierarchical microspheres synthesized at different reaction times have been used as photoanode in DSSCs which show enhanced light-harvesting properties than the commercial ZnO powders. ZnO microspheres synthesized at 48 h show maximum current density and cell efficiency of 8.51 mA/cm2 and 3.31%, respectively. This enhancement in photovoltaic parameters could be due to highly porous microspheres which provide more specific surface area for dye loading, retardation of recombination, and better charge transport.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Regan B, Gratzel M (1991) A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 353:737–740
Zhang Q, Cao G (2011) Nanostructured photoelectrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Today 6:91–109
Hagfeldt A, Grätzel M (1995) Light-induced redox reactions in nanocrystalline systems. J Chem Rev 95:49–68
Grätzel M (2005) Solar energy conversion by dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells. J Inorg Chem 44:6841e51
Zhang Q, Dandeneau CS, Zhou X, Cao G (2009) ZnO nanostructures for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv Mater 21:4087–4108
Xu F, Sun L (2011) Solution-derived ZnO nanostructures for photoanodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ Sci 4:818–841
Meulenkamp EA (1998) Synthesis and growth of ZnO nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 102:5566–5572
Chou TP, Zhang Q, Fryxell GE, Cao G (2007) Hierarchically structured ZnO film for dye-sensitized solar cells with enhanced energy conversion efficiency. Adv Mater 19:2588–2592
Saito N, Haneda H (2011) Hierarchical structures of ZnO spherical particles synthesized solvothermally. Sci Technol Adv Mater 12:064707
Ashoka S, Nagaraju G, Tharamani CN, Chandrapp GT (2009) Ethylene glycol assisted hydrothermal synthesis of flower like ZnO architectures. Mater Lett 63:873–876
Wang LB, Fan YP, Bala H, Sun G (2011) Controllable synthesis of hierarchical ZnO microstructures via a hydrothermal route. Micro Nano Lett 6:741–744
Xiao X (2009) Synthesis and characterization of 3D ZnO superstructures via a template-free hydrothermal method. Powder Technol 189:103–107
Matsumoto K, Saito N, Mitate T, Hojo J, Inada M, Haneda H (2009) Surface polarity determination of ZnO spherical particles synthesized via solvothermal route. Cryst Growth Des 9:5014–5016
Xiong J, Wang Y, Xue Q, Wu X (2011) Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using L-ascorbic acid. Green Chem 13:900–904
Chekin F, Ghasemi S (2014) Silver nanoparticles prepared in presence of ascorbic acid and gelatin, and their electrocatalytic application. Bull Mater Sci 37:1433–1437
Sampath M, Vijayan R, Tamilarasu E, Tamilselvan A, Sengottuvelan B (2014) Green synthesis of novel jasmine bud-shaped copper nanoparticles. J Nanotechnol 2014:626523
Ding K (2009) Hydrothermal synthesis of leaf-shaped ferric oxide particles onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and its catalysis for the electrooxidation of ascorbic acid. Int J Electrochem Sci 4:943–953
Ihara T, Wagata H, Kogure T, Katsumata K, Okada K, Matsushita N (2014) Template-free solvothermal preparation of ZnO hollow microspheres covered with c planes. RSC Adv 4:25148–25154
Govender K, Boyle DS, Kenway PB, O’Brien P (2004) Understanding the factors that govern the deposition and morphology of thin films of ZnO from aqueous solution. J Mater Chem 14:2575–2591
Parawee SKN, Tonto P, Mekasuwandumrong O, Pavarajarn V, Praserthdam P (2006) Solvothermal synthesis of ZnO with various aspect ratios using organic solvents. Cryst Growth Des 6:2446–2450
Zhang AQ, Lu Zhang L, Sui L, Qian DJ, Chen M (2013) Morphology-controllable synthesis of ZnO nano−/microstructures by a solvothermal process in ethanol solution Cryst. Res Technol 11:947–955
Deng H, Li XL, Peng Q, Wang X, Chen JP, Li YD (2005) Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 117:2842–2845
Tian S, Li N, Zeng D, Li H, Tang G, Pang A, Xie C, Zhao X (2015) Hierarchical ZnO hollow microspheres with exposed (001) facets as promising catalysts for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Cryst Eng Comm 17:8689–8696
Hu P, Zhang X, Han N, Xiang WC, Cao YB, Yuan FL (2011) Solution-controlled self-assembly of ZnO nanorods into hollow microspheres. Cryst Growth Des 11:1520–1526
Chauhan R, Shinde M, Kumar A, Gosavi S, Amalnerkar DP (2016) Hierarchical zinc oxide pomegranate and hollow sphere structures as efficient photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 226:201–208
Umar AA, Rahman MYA, Taslim R, Salleh MM, Oyama M (2012) Effect of the thickness of quasi one-dimensional zine oxide nanorods synthesized via multiple growth process under ammonia assisted hydrolysis technique on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cell. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:8384–8393
Pang S, Xie T, Zhang Y, Wei X, Yang M, Wang D, Du Z (2007) Research on the effect of different sizes of ZnO nanorods on the efficiency of TiO2-based dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C 111:18417–18422
Lin J, Heo YU, Nattestad A, Sun Z, Wang L, Kim JH, Dou SX (2014) 3D hierarchical rutile TiO2 and metal-free organic sensitizer producing dye-sensitized solar cells 8.6% conversion efficiency. Sci Rep 4:5769
Wang Q, Moser JE, Gratzel M (2005) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic analysis of dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem B 109:14945–14953
Wu W, Yang J, Hua J, Tang J, Zhang L, Long Y (2010) Efficient and stable dye sensitized solar cells based on phenothiazine sensitizers with thiophene units. J Mater Chem 20:1772–1779
Naveen KE, Jose R, Archana PS, Vijila C, Yusoff MM, Ramakrishna S (2012) High performance dye-sensitized solar cells with record open circuit voltage using tin oxide nano flowers developed by electrospinning. Energy Environ Sci 5:5401–5407
Qian J, Liu P, Xiao Y, Jiang Y, Cao Y, Ai X, Yang H (2009) TiO2-coated multilayered SnO2 hollow microspheres for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv Mater 21:3663–3667
Kim YJ, Lee MH, Kim HJ, Lim G, Choi YS, Park NG, Kim LWI (2009) Formation of highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells by hierarchical pore generation with nanoporous TiO2 spheres. Adv Mater 21:3668–3673
Acknowledgment
The authors RC and YW are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, Project No. (IFA12-CH-34), for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waghadkar, Y., Shinde, M., Ballal, R. et al. Time-varied synthesis of hierarchical ZnO microspheres and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Solid State Electrochem 21, 1797–1804 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3554-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3554-y