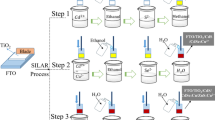
Abstract
We report on the interfacial passivation mechanism in CdSe quantum dot-sensitized ZnO nanocrystalline thin film, where different sulfide semiconductors (such as ZnS and CdS) and sulfide ions are used to modify ZnO nanocrystalline thin film before deposition of CdSe quantum dots (QDs). It is noticed that the highest light-to-electric conversion efficiency of CdSe quantum dot-sensitized ZnO nanocrystalline thin film solar cell is attained up to 4.18 % after CdS interfacial modification. Meanwhile, a simple treatment of ZnO nanocrystalline thin film in Na2S solution can also increase the conversion efficiency of CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cell up to 3.45 %. The electron transfer and recombination processes occurred in the interface of QD-sensitized nanocrystalline thin films with and without the different interfacial modifications are detected by measuring intensity modulated photovoltage spectroscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of solar cells. These results indicate that adsorption of S2− ions on the surface active sites of ZnO nanoparticles is the main reason for the conversion efficiency improvement due to the interfacial passivation of sulfide semiconductors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sambur JB, Novet T, Parkinson BA (2010) Multiple exciton collection in a sensitized photovoltaic system. Science 330:63–66
Robel I, Subramanian V, Kuno M, Kamat PV (2006) Quantum dot solar cells. Harvesting light energy with CdSe nanocrystals molecularly linked to mesoscopic TiO2 films. J Am Chem Soc 128:2385–2393
Yella A, Lee HW, Tsao HN, Yi CY, Chandiran AK, Nazeeruddin MK, Diau EWG, Yeh CY, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M (2011) Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)-based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 334:629–634
Mora-Seró I, Giménez S, Fabregat-Santiago F, Gómez R, Shen Q, Toyoda T, Bisquert J (2009) Recombination in quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Acc Chem Res 42:1848–1857
Lee H, Wang M, Chen P, Gamelin DR, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M, Nazeeruddin MK (2009) Efficient CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells prepared by an improved successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction process. Nano Lett 9:4221–4227
Barea EM, Shalom M, Giménez S, Hod I, Mora-Seró I, Zaban A, Bisquert J (2010) Design of injection and recombination in quantum dot sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 132:6834–6839
Zhang J, Sun C, Bai S, Luo R, Chen A, Sun L, Lin Y (2013) Interfacial passivation of CdS layer to CdSe quantum dots-sensitized electrodeposited ZnO nanowire thin films. Electrochim Acta 106:121–126
Roelofs KE, Brennan TP, Bent SF (2014) Interface engineering in inorganic-absorber nanostructured solar cells. J Phys Chem Lett 5:348–360
Zhao F, Tang G, Zhang J, Lin Y (2012) Improved performance of CdSe quantum dot-sensitized TiO2 thin film by surface treatment with TiCl4. Electrochim Acta 62:396–401
Chan WCW, Nie S (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016–2018
Chen SG, Chappel S, Diamant Y, Zaban A (2001) Preparation of Nb2O5 coated TiO2 nanoporous electrodes and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Mater 13:4629–4634
Roelofs KE, Brennan TP, Dominguez JC, Bailie CD, Margulis GY, Hoke ET, McGehee MD, Bent SF (2013) Effect of Al2O3 recombination barrier layers deposited by atomic layer deposition in solid-state CdS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C 117:5584–5592
Li TC, Goes MS, Fabregat-Santiago F, Bisquert J, Bueno PR, Prasittichai C, Hupp JT, Marks TJ (2009) Surface passivation of nanoporous TiO2 via atomic layer deposition of ZrO2 for solid-state dye-sensitized solar cell applications. J Phys Chem C 113:18385–18390
Hossain MA, Jennings JR, Shen C, Pan JH, Koh ZY, Mathewsb N, Wang Q (2012) CdSe-sensitized mesoscopic TiO2 solar cells exhibiting >5 % efficiency: redundancy of CdS buffer layer. J Mater Chem 22:16235–16242
Hachiya S, Shen Q, Toyoda T (2012) Effect of ZnS coatings on the enhancement of the photovoltaic properties of PbS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Appl Phys 111:104315
Kim SK, Son MK, Park S, Jeong MS, Prabakar K, Kim HJ (2014) Surface modification on TiO2 nanoparticles in CdS/CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cell. Electrochim Acta 118:118–123
Jin H, Choi S, Velu R, Kim S, Lee HJ (2012) Preparation of multilayered CdSe quantum dot sensitizers by electrostatic layer-by-layer assembly and a series of post-treatments toward efficient quantum dot-sensitized mesoporous TiO2 solar cells. Langmuir 28:5417–5426
Chi CF, Chen P, Lee YL, Liu IP, Chou SC, Zhang XL, Bach U (2011) Surface modifications of CdS/CdSe co-sensitized TiO2 photoelectrodes for solid-state quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem 21:17534–17540
Li WX, Zhang JB, Cao YY, Lin Y (2015) Double dyes cubic-sensitized solar cell based on Förster resonant energy transfer. RSC Adv 5:10026–10032
Guijarro N, Lana-Villarreal T, Lutz T, Haque SA, Gomez R (2012) Sensitization of TiO2 with PbSe quantum dots by SILAR: how mercaptophenol improves charge separation. J Phys Chem Lett 3:3367–3372
Gorer S, Hodes G (1994) Quantum size effects in the study of chemical solution deposition mechanisms of semiconductor films. J Phys Chem 98:5338–5346
Zhang JB, Zhao FY, Tang GS, Lin Y (2013) Influence of highly efficient PbS counter electrode on photovoltaic performance of CdSe quantum dots-sensitized solar cells. J Solid State Electrochem 17:2909–2915
Tachan Z, Shalom M, Hod I, Rühle S, Tirosh S, Zaban A (2011) PbS as a highly catalytic counter electrode for polysulfide-based quantum dot solar cells. J Phys Chem C 115:6162–6166
Zhang JB, Li P, Yang H, Zhao FY, Tang GS, Sun LN, Lin Y (2014) Preparation of highly efficient PbS electrode and its application in quantum dots-sensitized solar cells. Acta Phys -Chim Sin 30:1495–1500
Liu P, Li W, Zhang JB (2009) Electrodeposition and photocatalytic selectivity of ZnO/methyl blue hybrid thin films. J Phys Chem C 113:14279–14284
Yang H, Li P, Zhang JB, Lin Y (2014) TiO2 compact layer for dye-sensitized SnO2 nanocrystalline thin film. Electrochim Acta 147:366–370
Shen Q, Kobayashi J, Diguna LJ, Toyoda T (2008) Effect of ZnS coating on the photovoltaic properties of CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Appl Phys 103:084304
Nag A, Kovalenko MV, Lee JS, Liu W, Spokoyny B, Talapin DV (2011) Metal-free inorganic ligands for colloidal nanocrystals: S2−, HS−, Se2−, HSe−, Te2−, HTe−, TeS3 2−, OH−, and NH2 − as surface ligands. J Am Chem Soc 133:10612–10620
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21273160, 21172173, and 20873162), the Nature Science Foundation of Tianjin (Grant No. 14JCYBJC18000), and the Program for Innovative Research Team in the University of Tianjin (TD12-5038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Sun, C., Li, Y. et al. Interfacial passivation mechanism of sulfide towards quantum dot-sensitized nanocrystalline thin films. J Solid State Electrochem 21, 883–889 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3438-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3438-6