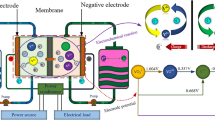
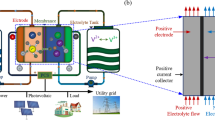
Abstract
In this paper, a flow frame with multi-distribution channels is designed. The electrolyte flow distribution in the graphite felt electrode is simulated to be uniform at some degree with the tool of a commercial computational fluid dynamics (CFD) package of Star-CCM+. A 5 kW-class vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) stack composed of 40 single cells is assembled. The electrochemical performance of the VRB stack is investigated. Under the applied current density of 60 mA cm−2 during the charge and discharge processes, the current and energy efficiencies are delivered to be 93.9 and 80.8 %, respectively. A higher average output power of 7.2 kW can be achieved at the current density of 80 mA cm−2 with a lower energy efficiency of 78.4 %. The studies of kW-class VRB stack can be beneficial to the development of large-scale energy storage.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Z, Zhang J, Kintner-Meyer MCW, Lu X, Choi D, Lemmon JP, Liu J (2011) Electrochemical energy storage for green grid. Chem Rev 111(5):3577–3613
Weber AZ, Mench MM, Meyers JP, Ross PN, Gostick JT, Liu Q (2011) Redox flow batteries: a review. J Appl Electrochem 41(10):1137–1164
Moncada A, Mistretta MC, Randazzo S, Piazza S, Sunseri C, Inguanta R (2014) High-performance of PbO2 nanowire electrodes for lead-acid battery. J Power Sources 256:72–79
Waag W, Fleischer C, Sauer DU (2014) Critical review of the methods for monitoring of lithium-ion batteries in electric and hybrid vehicles. J Power Sources 258:321–339
Wang XW, Wang FX, Wang LY, Li MX, Wang YF, Chen BW, Zhu YS, Fu LJ, Zha LS, Zhang LX, Wu YP, Huang W (2016) An aqueous rechargeable Zn//Co3O4 battery with high energy density and good cycling behavior. Advanced Materials. 28:4904--4911
Tang W, Hou Y, Wang F, Liu L, Wu Y, Zhu K (2013) LiMn2O4 nanotube as cathode material of second-level charge capability for aqueous rechargeable batteries. Nano Lett 13(5):2036–2040
Sum E, Rychcik M, Skyllas-Kazacos M (1985) Investigation of the V(V)/V(IV) system for use in the positive half-cell of a redox battery. J Power Sources 16(2):85–95
Sum E, Skyllas-Kazacos M (1985) A study of the V(II)/V(III) redox couple for redox flow cell applications. J Power Sources 15(2):179–190
Alotto P, Guarnieri M, Moro F (2014) Redox flow batteries for the storage of renewable energy: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 29:325–335
Schreiber M, Harrer M, Whitehead A, Bucsich H, Dragschitz M, Seifert E, Tymciw P (2012) Practical and commercial issues in the design and manufacture of vanadium flow batteries. J Power Sources 206:483–489
Park M, Y-j J, Kim J, Lee HI, Cho J (2013) Synergistic effect of carbon nanofiber/nanotube composite catalyst on carbon felt electrode for high-performance all-vanadium redox flow battery. Nano Lett 13(10):4833–4839
Li B, Gu M, Nie Z, Wei X, Wang C, Sprenkle V, Wang W (2013) Nanorod niobium oxide as powerful catalysts for an all vanadium redox flow battery. Nano Lett 14(1):158–165
Kim KJ, Park M-S, Kim J-H, Hwang U, Lee NJ, Jeong G, Kim Y-J (2012) Novel catalytic effects of Mn3O4 for all vanadium redox flow batteries. Chem Commun 48(44):5455–5457
Li L, Kim S, Wang W, Vijayakumar M, Nie Z, Chen B, Zhang J, Xia G, Hu J, Graff G (2011) A stable vanadium redox-flow battery with high energy density for large-scale energy storage. Adv Energy Mater 1(3):394–400
Li B, Gu M, Nie Z, Shao Y, Luo Q, Wei X, Li X, Xiao J, Wang C, Sprenkle V (2013) Bismuth nanoparticle decorating graphite felt as a high-performance electrode for an all-vanadium redox flow battery. Nano Lett 13(3):1330–1335
Wu XW, Liu J, Xiang X, Zhang J, Hu JP, Wu YP (2014) Electrolytes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Pure Appl Chem 86(5):661–669
Li X, Zhang H, Mai Z, Zhang H, Vankelecom I (2011) Ion exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) applications. Energy & Environmental Science 4(4):1147–1160
Xu W, Li X, Cao J, Zhang H, Zhang H (2014) Membranes with well-defined ions transport channels fabricated via solvent-responsive layer-by-layer assembly method for vanadium flow battery. Scientific reports 4
Wu XW, Hu JP, Liu J, Zhou QM, Zhou W, Li H, Wu YP (2014) Ion exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Pure Appl Chem 86(5):633–649
Caglar B, Fischer P, Kauranen P, Karttunen M, Elsner P (2014) Development of carbon nanotube and graphite filled polyphenylene sulfide based bipolar plates for all-vanadium redox flow batteries. J Power Sources 256:88–95
Kim S, Thomsen E, Xia G, Nie Z, Bao J, Recknagle K, Wang W, Viswanathan V, Luo Q, Wei X (2013) 1 kW/1 kWh advanced vanadium redox flow battery utilizing mixed acid electrolytes. J Power Sources 237:300–309
Aaron DS, Liu Q, Tang Z, Grim GM, Papandrew AB, Turhan A, Zawodzinski TA, Mench MM (2012) Dramatic performance gains in vanadium redox flow batteries through modified cell architecture. J Power Sources 206:450–453
Liu QH, Grim GM, Papandrew AB, Turhan A, Zawodzinski TA, Mench MM (2012) High performance vanadium redox flow batteries with optimized electrode configuration and membrane selection. J Electrochem Soc 159(8):A1246–A1252
Xu Q, Zhao TS, Leung PK (2013) Numerical investigations of flow field designs for vanadium redox flow batteries. Appl Energy 105:301–306
“CFD studies on mass transport in redox flow batteries”, https://etd.ohiolink.edu
Zhu SQ, Chen JQ, Wang BG (2007) Influence of electrolyte flow patterns on the performance of all vanadium redox flow battery [J]. Battery Bimonthly 3:016
Zhu SQ, Chen JQ, Wang Q, Wang BG (2008) Influence of flow channel structure and electrolyte flow state on the performance of VRB. Battery Bimonthly 5:005
Ke XY, Alexander ID, Prahl JM, Savinell RF (2014) Flow distribution and maximum current density studies in redox flow batteries with a single passage of the serpentine flow channel. J Power Sources 270:646–657
Latha TJ, Jayanti S (2014) Ex-situ experimental studies on serpentine flow field design for redox flow battery systems. J Power Sources 248:140–146
Knudsen E, Albertus P, Cho KT, Weber AZ (2015) Kojic A. Flow simulation and analysis of high-power flow batteries Journal of Power Sources 299:617–628
Ke XY, Alexander ID, Prahl JM, Savinell RF (2015) A simple analytical model of coupled single flow channel over porous electrode in vanadium redox flow battery with serpentine flow channel. J Power Sources 288:308–313
Ma XK, Zhang HM, Xing F, Sun CX (2012) Simulation and optimization of flow field of all vanadium redox flow battery. Chinese J Power Sources 36:1647–1650
Zhao P, Zhang H, Zhou H, Chen J, Gao S, Yi B (2006) Characteristics and performance of 10 kW class all-vanadium redox-flow battery stack. J Power Sources 162(2):1416–1420
He Z, Su A, Gao C, Zhou Z, Pan C, Liu S (2013) Carbon paper modified by hydrothermal ammoniated treatment for vanadium redox battery. Ionics 19(7):1021–1026
Skyllas-Kazacos M, Kasherman D, Hong DR, Kazacos M (1991) Characteristics and performance of 1 kW UNSW vanadium redox battery. J Power Sources 35(4):399–404
Tang A, McCann J, Bao J, Skyllas-Kazacos M (2013) Investigation of the effect of shunt current on battery efficiency and stack temperature in vanadium redox flow battery. J Power Sources 242:349–356
Xing F, Zhang H, Ma X (2011) Shunt current loss of the vanadium redox flow battery. J Power Sources 196(24):10753–10757
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2015JJ3074), Science and Technology project of Changsha (KL403147-11) and postdoctoral fund of Hunan Agricultural University (129263).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Contribution to Symposium A: “Advances in Energy Storage Systems: Lithium Batteries, Supercapacitors and Beyond”, during ICMAT 2015, June 28 - July 3, Singapore.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Yuan, X., Wang, Z. et al. Electrochemical performance of 5 kW all-vanadium redox flow battery stack with a flow frame of multi-distribution channels. J Solid State Electrochem 21, 429–435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3361-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-016-3361-x