Abstract
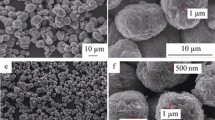
LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 samples with their particle sizes from micro to nano are synthesized via polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)-assisted coprecipitation of nickel and manganese hydroxide. Their morphology, structure, and performance as cathode of high-voltage lithium ion battery are investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and charge/discharge test. The characterizations from SEM and XRD show that the particle size of the resulting LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 is tunable from micro to nano by controlling the concentrations of PVP for the formation of nickel and manganese hydroxide precursor. The results from CV, EIS, and charge/discharge test reveal that reducing the particle size of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 results in its less interfacial resistance for lithium insertion/desertion process, leading to its improved rate capability. Meanwhile, the cyclic stability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 is also improved when its particle size is changed from micro to nano, but too smaller particle size is not beneficial to its cyclic stability, especially at elevated temperature. When evaluated in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Li half cell, the resulting LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 samples of 800, 250, and 125 nm, in average, deliver a 20 C rate capacity of 40, 58, and 71 mAh g−1, while they exhibit a capacity retention of 79, 89, and 82 % after 250 cycles with 0.5 C rate at room temperature and 33, 77, and 64 % after 200 cycles with 1 C rate at 55 °C, respectively. This difference in capacity retention becomes more significant in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite full cells due to the effect of graphite anode.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang W, Tian S, Liu LL, Li L, Zhang HP, Yue YB, Bai Y, Wu YP, Zhu K (2011) Electrochem Commun 13:205–208
Park OK, Cho Y, Lee S, Yoo HC, Song HK, Cho J (2011) Energy Environ Sci 4:1621–1633
Kraytsberg A, Ein-Eli Y (2012) Adv Energy Mater 2:922–939
Wang HL, Xia H, Lai MO, Lu L (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:1539–1542
Li BZ, Xing LD, Xu MQ, Lin HB, Li WS (2013) Electrochem Commun 34:48–51
Fang HS, Li LP, Li GS (2007) J Power Sources 167:223–227
Kunduraci M, Amatucci GG (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:4193–4199
Ma LW, Chen BZ, Shi XC, Zhang W, Zhang K (2010) Colloids Surf A 369:88–94
Yoon T, Park S, Mun J, Ryu JH, Choi W, Kang YS, Park JH, Oh SM (2012) J Power Sources 215:312–316
Zhou L, Zhao D, Lou X (2012) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:239–241
Zhang X, Cheng F, Yang J, Chen J (2013) Nano Lett 13:2822–2825
Lin HB, Zhang YM, Hu JN, Wang YT, Xing LD, Xu MQ, Li XP, Li WS (2014) J Power Sources 257:37–44
Shaju KM, Bruce PG (2008) Dalton Trans 5471–5475
Zhang X, Cheng F, Zhang K, Liang Y, Yang S, Liang J, Chen J (2012) RSC Adv 2:5669–5675
Rho YH, Dokko K, Kanamura K (2006) J Power Sources 157:471–476
Kim DK, Muralidharan P, Lee HW, Ruffo R, Yang Y, Chan CK, Peng H, Huggins RA, Cui Y (2008) Nano Lett 8:3948–3952
Ding YL, Goh BM, Zhang H, Loh KP, Lu L (2013) J Power Sources 236:1–9
Lee HW, Muralidharan P, Mari CM, Ruffo R, Kim DK (2011) J Power Sources 196:10712–10716
Xiang XD, Fu Z, Li WS (2013) J Solid State Electrochem 17:1201–1206
Xiao XC, Lu P, Ahn D (2011) Adv Mater 23:3911–3915
Matsuda K, Taniguchi I (2004) J Power Sources 132:156–160
Amatucci G, Pasquier AD, Blyr A, Zheng T, Tarascon JM (1999) Electrochim Acta 45:255–271
Kim HJ, Choi Y, Yoon S, Cho JJ (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:801–806
Wei GZ, Lu X, Ke FS, Huang L, Li JT, Wang ZX, Zhou ZY, Sun SG (2010) Adv Mater 22:4364–4367
Wang J, Yao XY, Zhou XF, Liu ZP (2011) J Mater Chem 21:2544–2549
Xiang XD, Li XQ, Li WS (2013) J Power Sources 230:89–95
Yi TF, Xie Y, Zhu YR, Ye MF (2012) J Power Sources 211:59–65
Talyosef Y, Markovsky B, Salitra G, Aurbach D, Kim HJ, Choi S (2005) J Power Sources 146:664–669
Chen D, Li B, Liao Y, Lan H, Lin H, Xing L, Wang Y, Li W (2014) J Solid State Electrochem 18:2027–2033
Aklalouch M, Amarilla JM, Saadoune I, Rojo JM (2011) J Power Sources 196:10222–10227
Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM (2008) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 47:2930–2946
Wang Y, Li H, He P, Hosono E, Zhou H (2010) Nanoscale 2:1294–1305
Li B, Wang YQ, Rong HB, Wang YT, Liu JS, Xing LD, Xu MQ, Li WS (2013) J Mater Chem A 1:12954–12961
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported from the joint project of National Natural Science Foundation of China and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. U1134002), the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 21273084), the Natural Science Fund of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 10351063101000001), the key project of Science and Technology in Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2012A010702003), Joint Project of Guangdong Province and Ministry of Education for the Cooperation among Industries, Universities and Institutes (Grant No. 2012B091100332), and the scientific research project of Department of Education of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2013CXZDA013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, L., Li, X., Liao, Y. et al. Effect of particle size on rate capability and cyclic stability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for high-voltage lithium ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 19, 569–576 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2635-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2635-4