Abstract
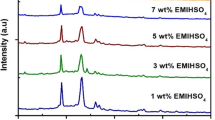
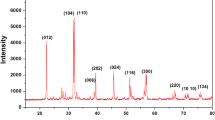
The effect of the dispersion of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles in the zinc ion conducting gel polymer electrolyte is studied. Changes in the morphology/structure of the gel polymer electrolyte with the introduction of ZnO particles are distinctly observed using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The nanocomposites offer ionic conductivity values of >10−3 S cm−1 with good thermal and electrochemical stabilities. The variation of ionic conductivity with temperature follows the Vogel–Tamman–Fulcher behavior. AC impedance spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and transport number measurements have confirmed Zn2+ ion conduction in the gel nanocomposites. An electrochemical stability window from −2.25 to 2.25 V was obtained from voltammetric studies of nanocomposite films. The cationic (i.e., Zn2+ ion) transport number (t +) has been found to be significantly enhanced up to a maximum of 0.55 for the dispersion of 10 wt.% ZnO nanoparticles, indicating substantial enhancement in Zn2+ ion conductivity. The gel polymer electrolyte nanocomposite films with enhanced Zn2+ ion conductivity are useful as separators and electrolytes in Zn rechargeable batteries and other electrochemical applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacCallum JR, Vincent CA (eds) (1987) Polymer electrolyte reviews—I. Elsevier, London
Gray FM (1991) Solid polymer electrolytes—fundamentals and technological applications. VCH, New York
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:223001
Manualstephan A (2006) Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur Polymer J 42:21–42
Michot T, Nishimoto A, Watanabe M (2000) Electrochemical properties of polymer gel electrolytes based on poly (vinylidene fluoride) copolymer and homopolymer. Electrochim Acta 45:1347–1360
Hashmi SA (2004) Supercapacitor: An emerging power source. Nat Acad Sci Lett 27:27–46
Sannier L, Bouchet R, Rosso M, Tarascon J-M (2006) Evaluation of GPE performances in lithium metal battery technology by means of simple polarization tests. J Power Sources 158:564–570
Kumar B (2004) From colloidal to composite electrolytes: properties, peculiarities, and possibilities. J Power Sources 135:215–231
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2009) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with nanosized magnesium oxide. J Power Sources 190:563–572
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ion transport and ion–filler-polymer interaction in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195:5101–5108
Adebahr J, Byrne N, Forsyth M, MacFarlane DR, Jacobson P (2003) Enhancement of ion dynamics in PMMA-based gels with addition of TiO2 nano-particles. Electrochim Acta 48:2099–2103
Saikia D, Chen-Yang YW, Chen YT, Li YK, Lin SI (2009) 7Li NMR spectroscopy and ion conduction mechanism of composite gel polymer electrolyte: a comparative study with variation of salt and plasticizer with filler. Electrochim Acta 54:1218–1227
Ferrari S, Quatarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A, Fagnoni M, Protti S, Gerbaldi C, Spinella A (2010) Lithium ion conducting PVdF-HFP composite gel electrolytes based on N-methoxyethyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)-imide ionic liquid. J Power Sources 195:559–566
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2011) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with fumed silica for rechargeable magnesium battery application. J Solid State Electrochem. doi:10.1007/s10008-010-1240-4
Maier J (1994) Defect chemistry at interfaces. Solid State Ionics 70–71:43–51
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Rand DAJ, Woods R, Dell RM (1998) Batteries for electric vehicles. Wiley, New York
Egashira M, Todo H, Yoshimoto N, Morita M (2008) Lithium ion conduction in ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolyte. J Power Sources 178:729–735
Aurbach D, Lu Z, Schechter A, Gofer Y, Gizbar H, Turgeman R, Cohen Y, Moshkovich M, Levi E (2000) Prototype systems for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Nature 407:724–727
Noto VD, Paolo D, Vittadello M, Dall’Igna R, Boella F (2003) Potentiometric sensors with liquid polymer electrolytes based on poly ethylene glycol 400, LiCl and δ-MgCl2. Electrochim Acta 48:2329–2342
Vittadello M, Biscazzo S, Lavina S, Fauri M, Noto VD (2002) Vibrational studies of the ion–polymer interactions in α-hydro-ω-oligo (oxyethylene) hydroxy-poly [oligo (oxyethylene) oxydimethylsililene]/δ-MgCl2. Solid State Ionics 147:341–347
Biscazzo S, Vittadello M, Lavina S, Noto VD (2002) Synthesis and structure of electrolytic complexes based on α-hydro-ω-oligo (oxyethylene) hydroxy-poly [oligo (oxyethylene) oxydimethylsililene] and δ-MgCl2. Solid State Ionics 147:377–382
Noto VD, Vittadello M (2002) Mechanism of ionic conductivity in poly (ethylene glycol 400)/(MgCl2)x polymer electrolytes: studies based on electrical spectroscopy. Solid State Ionics 147:309–316
Noto VD, Munchow V, Vittadello M, Collet JC, Lavina S (2002) Synthesis and characterization of lithium and magnesium complexes based on [EDTA][PEG400]2 and [EDTA]3[PEG400]7. Macromol Chem Phys 203:1211–1227
Noto VD, Vittadello M, Pace G, Biscazzo S, Lavina S (2002) Synthesis and characterization of [PEG400-alt-DEOS]/(δ-MgCl2)0.2597 complex. Macromol Chem Phys 203:1201–1210
Noto VD, Lavina S, Longo D, Vidali M (1998) A novel electrolytic complex based on δ-MgCl2 and poly(ethylene glycol) 400. Electrochim Acta 43:1225–1237
Pandey GP, Hashmi SA (2009) Experimental investigations of an ionic-liquid-based, magnesium ion conducting, polymer gel electrolyte. J Power Sources 187:627–634
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ionic liquid based sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 181:416–423
Kumar GG, Sampath S (2003) Electrochemical characterization of poly (vinylidenefluoride)-zinc triflate gel polymer electrolyte and its application in solid-state zinc batteries. Solid State Ionics 160:289–300
Kumar GG, Sampath S (2005) Electrochemical and spectroscopic investigations of a gel polymer electrolyte of poly (methylmethacrylate) and zinc triflate. Solid State Ionics 176:773–780
Ye H, John Xu J (2007) Zinc ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on oligomeric polyether/PVDF-HFP blends. J Power Sources 165:500–508
Ikeda S, Mori Y, Furuhashi Y, Masuda H (1999) Multivalent cation conductive solid polymer electrolytes using photo-cross-linked polymers: II. magnesium and zinc trifluoromethanesulfonate systems. Solid State Ionics 121:329–333
Chang W, Choi J-W, Im J-C, Lee JK (2010) Effects of ZnO coating on electrochemical performance and thermal stability of LiCoO2 as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:320–326
Wu C-G, Lu M-I, Tsai C-C, Chuang H-J (2006) PVdF-HFP/metal oxide nanocomposites: the matrices for high-conducting, low-leakage porous polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 159:295–300
Fan L, Dang Z, Wei G, Nan C-W, Li M (2003) Effect of nanosized ZnO on the electrical properties of (PEO)16LiClO4 electrolytes. Mater Sci Eng B 99:340–343
Zhang Y, Sun X, Pan L, Li H, Sun Z, Sun C, Tay BK (2009) Carbon nanotube–zinc oxide electrode and gel polymer electrolyte for electrochemical supercapacitors. J Alloys and Compds 480:L17–L19
Chandra A, Singh PK, Chandra S (2002) Semiconductor-dispersed polymer electrolyte composites. Solid State Ionics 154–155:15–20
Kloster GM, Thomas JA, Brazis PW, Kannewurf CR, Shriver DF (1996) Synthesis, characterization, and transport properties of new mixed ionic−electronic conducting V2O5−polymer electrolyte xerogel nanocomposites. Chem Mater 8:2418–2420
Hashmi SA, Chandra S (1995) Experimental investigations on a sodium-ion-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (ethylene oxide) complexed with NaPF6. Mater Sci Eng B 34:18–26
Evans J, Vincent CA, Bruce PG (1987) Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 28:2324–2328
Wang K, Lee H, Cooper R, Liang H (2009) Time-resolved, stress-induced, and anisotropic phase transformation of a piezoelectric polymer. Appl Phys A 95:435–441
Simoes RD, Job AE, Chilanglia DL, Zucolotto V, Camargo-Filho JC, Alves N, Giacometti JA, Oliveira ON Jr, Constantino CJL (2005) Structural characterization of blends containing both PVDF and natural rubber latex. J Raman Spectrosc 36:1118–1124
Nunes SC, de Zea BV, Ostrovskii D, Carlos LD (2006) FT-IR and Raman spectroscopic study of di-urea cross-linked poly(oxyethylene)/siloxane ormolytes doped with Zn2+ ions. Vib Spectrosc 40:278–288
Liu Y, Lee JY, Hong L (2003) Morphology, crystallinity, and electrochemical properties of in situ formed poly(ethylene oxide)/TiO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Appl Polym Sci 89:2815–2822
Maier J (1995) Ionic conduction in space charge regions. Prog Solid State Chem 23:171–263
Fujinaga T, Sakamoto I (1976) Electrochemical studies of sulfonates in non-aqeous solvents. Part II. polarographic reductions of some alkaline earth and transition metal ions with sulfonate supporting electrolyte in N, N-Dimethylformamide and acetonitrile. J Electroanal Chem 73:235–246
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support received from the Department of Science & Technology, New Delhi, and University of Delhi (under the Scheme to Strengthen R&D Doctoral Research Programme providing funds to University faculty, 11-17 Research Fund).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sellam, Hashmi, S.A. Enhanced zinc ion transport in gel polymer electrolyte: effect of nano-sized ZnO dispersion. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 3105–3114 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1733-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1733-4