Abstract
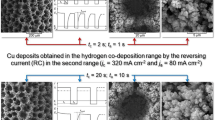
The effect of the regime of pulsating current (PC) on copper electrodeposition in the hydrogen co-deposition range was examined by the techniques of scanning electron and optical microscopes. The quantities of evolved hydrogen and morphologies of electrodeposited copper strongly depended on the applied parameters of square waves PC, such as the current density amplitude (or the amplitude of the cathodic current density), deposition pulse, and pause duration. The increase of the current density amplitude led to intensification of hydrogen evolution reaction, and the change of morphology of electrodeposited copper from dendrites and shallow holes to dish-like holes was observed. For the constant pause duration, the prolonging deposition pulses intensify hydrogen evolution reaction leading to the formation of the honeycomb-like structures. The set of modified equations considering the effect of hydrogen generated during metal electrodeposition processes by the pulsating current regime is also presented. The concept of “effective overpotential amplitude” was proposed to explain the change of copper surface morphology with the intensification of hydrogen evolution reaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nikolić ND, Popov KI (2010) Hydrogen co-deposition effects on the structure of electrodeposited copper. In: Djokić SS (ed) Modern aspects of electrochemistry, electrodeposition: theory and practice, vol 48. Springer, New York, pp 1–70
Shin HC, Dong J, Liu M (2003) Adv Mater 15:1610–1614
Nikolić ND, Popov KI, Pavlović LjJ, Pavlović MG (2006) J Electroanal Chem 588:88–98
Li Y, Jia W-Z, Song Y-Y, Xia X-H (2007) Chem Mater 19:5758–5764
Nikolić ND, Pavlović LjJ, Pavlović MG, Popov KI (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:8096–8104
Nikolić ND, Branković G, Pavlović MG, Popov KI (2008) J Electroanal Chem 621:13–21
Shin HC, Liu M (2005) Adv Funct Mater 15:582–586
Kim R, Han D, Nam D, Kim J, Kwon H (2010) J Electrochem Soc 157:D269–D273
Yin J, Jia J, Zhu L (2008) Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:7444–7447
Ortiz GF, Hanzu I, Knauth P, Lavela P, Tirado JL, Djenizian T (2009) Electrochim Acta 54:4262–4268
Ortiz GF, Hanzu I, Lavela P, Knauth P, Tirado JL, Djenizian T (2010) Chem Mater 22:1926–1932
Nikolić ND, Popov KI, Pavlović LjJ, Pavlović MG (2007) J Solid State Electrochem 11:667–675
Nikolić ND, Popov KI, Pavlović LjJ, Pavlović MG (2007) Sensors 7:1–15
Marozzi CA, Chialvo AC (2000) Electrochim Acta 45:2111–2120
Cherevko S, Xing X, Chung C-H (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:467–470
Cherevko S, Chung C-H (2010) Electrochim Acta 55:6383–6390
Nikolić ND, Maksimović VM, Pavlović MG, Popov KI (2009) J Serb Chem Soc 74:689–696
Nikolić ND, Branković G, Pavlović MG, Popov KI (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:421–424
Nikolić ND, Branković G, Maksimović VM, Pavlović MG, Popov KI (2009) J Electroanal Chem 635:111–119
Nikolić ND, Branković G, Maksimović VM, Pavlović MG, Popov KI (2010) J Solid State Electrochem 14:331–338
Nikolić ND, Branković G, Popov KI (2011) Mater Chem Phys 125:587–594
Shin HC, Liu M (2004) Chem Mater 16:5460–5464
Kim J-H, Kim R-H, H-Sang K (2008) Electrochem Commun 10:1148–1151
Popov KI, Maksimović MD (1989) Theory of the effect of electrodeposition at a periodically changing rate on the morphology of metal deposits. In: Conway BE, Bockris JO’M, White RE (eds) Modern aspects of electrochemistry, vol 19. Plenum, New York, pp 193–250
Chandrasekar MS, Pushpavanam M (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:3313–3322
Nikolić ND, Branković G (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:740–744
Popov KI, Pavlović MG (1993) Electrodeposition of metal powders with controlled grain size and morphology. In: White RE, Bockris JO’M, Conway BE (eds) Modern aspects of electrochemistry, vol 24. Plenum, New York
Popov KI, Djokić SS, Grgur BN (2002) Fundamental aspects of electrometallurgy. Kluwer Academic, New York
Pavlović MG, Nikolić ND, Popov KI (2003) J Serb Chem Soc 68:649–656
Dima GE, De Vooys ACA, Koper MTM (2003) J Electroanal Chem 554–555:15–23
Ko W-Y, Chen W-H, Cheng C-Y, Lin K-J (2009) Sens Actuators B 137:437–441
Pletcher D, Poorbedi Z (1979) Electrochim Acta 24:1253–1256
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to Prof. Dr. Konstantin I. Popov for helpful discussion during the preparation of this paper. The work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia under the research project: “Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of nanostructured functional materials for application in new technologies” (No. 172046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolić, N.D., Branković, G. & Maksimović, V.M. Morphology and internal structure of copper deposits electrodeposited by the pulsating current regime in the hydrogen co-deposition range. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 321–328 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1331-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1331-x