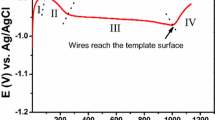
Abstract
ZnO nanowire arrays were grown by potentiostatic cathodic electrodeposition on aluminum anodic oxide template (AAO) from dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solutions containing zinc chloride and molecular oxygen as precursors. The nanowires presented high aspect ratio and exhibited a very high crystallinity with a wurtzite crystal structure with preferential orientation along the (0001) crystallographic axis. Chronoamperometric experiments were performed on gold bulk electrodes in order to model this preferential mode growth of ZnO nanowires, which has not been previously reported for similar precursors in DMSO solution. The analysis of the corresponding chronoamperograms revealed that chloride ions influence the oxide nucleation and growth mechanism. It was found that in the absence of KCl as a supporting electrolyte, the data fitted an instantaneous three-dimensional diffusion-controlled (IN-3D)diff nucleation and growth mechanism (NGM). The presence of KCl, instead favored a progressive three-dimensional (PN-3D)diff NGM. With these results, a model for the more complex nanowire’s growth inside the pores of the AAO template is proposed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cobden DH (2001) Molecular electronics—nanowires begin to shine. Nature 409(6816):32–33
Jie JS, Wang GZ, Han XH, Yu QX, Liao Y, Li GP, Hou JG (2004) Indium-doped zinc oxide nanobelts. Chem Phys Lett 387(4–6):466–470
Cui Y, Lieber CM (2001) Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science 291(5505):851–853
Jie JS, Wang GZ, Han XH, Hou JG (2004) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO: in nanowires with superlattice structure. J Phys Chem B 108(44):17027–17031
Prinz GA (1998) Device physics—magnetoelectronics. Science 282(5394):1660–1663
Whitney TM, Jiang JS, Searson PC, Chien CL (1993) Fabrication and magnetic-properties of arrays of metallic nanowires. Science 261(5126):1316–1319
Li FY, Metzger RM, Doyle WD (1997) Influence of particle size on the magnetic viscosity and activation volume of alpha-Fe nanowires in alumite films. IEEE Trans Magn 33(5):3715–3717
Saito N, Haneda H, Sekiguchi T, Ohashi N, Sakaguchi I, Koumoto K (2002) Low-temperature fabrication of light-emitting zinc oxide micropatterns using self-assembled monolayers. Adv Mater 14(6):418–421
Huang MH, Mao S, Feick H, Yan HQ, Wu YY, Kind H, Weber E, Russo R, Yang PD (2001) Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 292(5523):1897–1899
Lee JY, Choi YS, Kim JH, Park MO, Im S (2002) Optimizing n-ZnnO/p-Si heterojunctions for photodiode applications. Thin Solid Films 403:553–557
Liang S, Sheng H, Liu Y, Huo Z, Lu Y, Shen H (2001) ZnO Schottky ultraviolet photodetectors. J Cryst Growth 225(2–4):110–113
Liu CH, Zapien JA, Yao Y, Meng XM, Lee CS, Fan SS, Lifshitz Y, Lee ST (2003) High-density, ordered ultraviolet light-emitting ZnO nanowire arrays. Adv Mater 15(10):838–841
Li Y, Meng GW, Zhang LD, Phillipp F (2000) Ordered semiconductor ZnO nanowire arrays and their photoluminescence properties. Appl Phys Lett 76(15):2011–2013
Ramanathan S, Patibandla S, Bandyopadhyay S, Edwards JD, Anderson J (2006) Fluorescence and infrared spectroscopy of electrochemically self assembled ZnO nanowires: evidence of the quantum confined Stark effect. J Mater Sci Mater El 17(9):651–655
Ramirez D, Pauporte T, Gomez H, Lincot D (2008) Electrochemical growth of ZnO nanowires inside nanoporous alumina templates. A comparison with metallic Zn nanowires growth. Phys Status Solidi A 205(10):2371–2375
Wu MZ, Yao LZ, Cai WL, Jiang GW, Li XG, Yao Z (2004) Preparation and photoluminescence of ordered ZnO nanowire arrays. J Mater Sci Technol 20(1):11–13
Yuldashev SU, Choi SW, Kang TW, Nosova LA (2003) Growth of ZnO nanowires by electrochemical deposition into porous alumina on silicon substrates. J Korean Phys Soc 42:S216–S218
Zheng MJ, Zhang LD, Li GH, Shen WZ (2002) Fabrication and optical properties of large-scale uniform zinc oxide nanowire arrays by one-step electrochemical deposition technique. Chem Phys Lett 363(1–2):123–128
Peulon S, Lincot D (1998) Mechanistic study of cathodic electrodeposition of zinc oxide and zinc hydroxychloride films from oxygenated aqueous zinc chloride solutions. J Electrochem Soc 145(3):864–874
Gal D, Hodes G, Lincot D, Schock HW (2000) Electrochemical deposition of zinc oxide films from non-aqueous solution: a new buffer/window process for thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 361–362:79–83
Jayakrishnan R, Hodes G (2003) Non-aqueous electrodeposition of ZnO and CdO films. Thin Solid Films 440(1–2):19–25
Lu X-H, Wang D, Li G-R, Su C-Y, Kuang D-B, Tong Y-X (2009) Controllable electrochemical synthesis of hierarchical ZnO nanostructures on FTO glass. J Phys Chem C 113(31):13574–13582
Wang Q, Wang G, Xu B, Jie J, Han X, Li G, Li Q, Hou JG (2005) Non-aqueous cathodic electrodeposition of large-scale uniform ZnO nanowire arrays embedded in anodic alumina membrane. Mater Lett 59(11):1378–1382
Cortés A, Riveros G, Palma JL, Denardin JC, Marotti RE, Dalchiele EA, Gómez H (2009) Single-crystal growth of nickel nanowires: influence of deposition conditions on structural and magnetic properties. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:1992–2000
Green S, Badán JA, Gilles M, Cortes A, Riveros G, Ramírez D, Gómez H, Quagliata E, Dalchiele EA, Marotti RE (2007) Optical properties of nanoporous Al2O3 obtained by aluminium anodization. Phys Status Solidi C 4(2):618–621
Henriquez R, Froment M, Riveros G, Dalchiele EA, Gomez H, Grez P, Lincot D (2007) Electrodeposition of polyphasic films of zinc oxi sulfide from DMSO onto n-InP(100) and n-InP(111) single crystals in the presence of zinc salt, thiourea, and dissolved molecular oxygen. J Phys Chem C 111(16):6017–6023
Henriquez R, Gomez H, Grez P, Lincot D, Froment M, Dalchiele EA, Riveros G (2007) One-step electrodeposition of ZnO2-ZnS thin-film mixtures onto n-InP(111) and n-InP(100) substrates. Electrochem Solid State Lett 10(11):D134–D138
Riveros G, Gomez H, Cortes A, Marotti RE, Dalchiele EA (2005) Crystallographically-oriented single-crystalline copper nanowire arrays electrochemically grown into nanoporous anodic alumina templates. Appl Phys A 81(1):17–24
Schonenberger C, vander Zande BMI, Fokkink LGJ, Henny M, Schmid C, Kruger M, Bachtold A, Huber R, Birk H, Staufer U (1997) Template synthesis of nanowires in porous polycarbonate membranes: electrochemistry and morphology. J Phys Chem B 101(28):5497–5505
Toimil-Molares ME, Buschmann V, Dobrev D, Neumann R, Scholz R, Schuchert IU, Vetter J (2001) Single-crystalline copper nanowires produced by electrochemical deposition in polymeric ion track membranes. Adv Mater 13(1):62–65
Valizadeh S, George JM, Leisner P, Hultman L (2002) Electrochemical synthesis of Ag/Co multilayered nanowires in porous polycarbonate membranes. Thin Solid Films 402(1–2):262–271
PD Joint Committee for Powder Diffraction Studies (JCPDS) File No. JCPDS 5-0664 (hexagonal wurtzite ZnO)
Elias J, Tena-Zaera R, Levy-Clement C (2008) Electrochemical deposition of ZnO nanowire arrays with tailored dimensions. J Electroanal Chem 621(2):171–177
Chen J, Ae L, Aichele C, Lux-Steiner MC (2008) High internal quantum efficiency ZnO nanorods prepared at low temperature. Appl Phys Lett 92(16):161906
Inamdar AI, Mujawar SH, Barman SR, Bhosale PN, Patil PS (2008) The effect of bath temperature on the electrodeposition of zinc oxide thin films via an acetate medium. Semicond Sci Technol 23(8):085013
Tena-Zaera R, Elias J, Wang G, Levy-Clement C (2007) Role of chloride ions on electrochemical deposition of ZnO nanowire Arrays from O-2 reduction. J Phys Chem C 111(45):16706–16711
Riveros G, Green S, Cortes A, Gomez H, Marotti RE, Dalchiele EA (2006) Silver nanowire arrays electrochemically grown into nanoporous anodic alumina templates. Nanotechnology 17(2):561–570
Zhang XY, Zhang LD, Lei Y, Zhao LX, Mao YQ (2001) Fabrication and characterization of highly ordered Au nanowire arrays. J Mater Chem 11(6):1732–1734
Schuchert IU, Toimil-Molares ME, Dobrev D, Vetter J, Neumann R, Martin M (2003) Electrochemical copper deposition in etched ion track membranes—experimental results and a qualitative kinetic model. J Electrochem Soc 150(4):C189–C194
Arudi RL, Allen OA, Bielski HJB (1981) Some observations on the chemistry of KO2—DMSO solutions. FEBS Lett 135(2):265–267
Fujinaga T, Izutsu K, Adachi T (1969) Polarographic studies of dissolved oxygen in DMSO–water mixtures. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 42:140–145
Scharifker B, Hills G (1983) Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation. Electrochim Acta 28(7):879–889
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FONDECYT (Chile) project 1080195 and DII, PUCV, project 037.108/2008. D. Ramirez thanks MECESUP UVA0604. EAD thanks PEDECIBA-Física and CSIC-UDELAR, Uruguay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez, H., Riveros, G., Ramirez, D. et al. Growth and characterization of ZnO nanowire arrays electrodeposited into anodic alumina templates in DMSO solution. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 197–204 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1309-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1309-8