Abstract
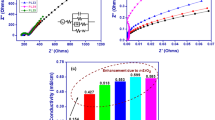
Solid composite polymer electrolytes consisting of polyethylene oxide (PEO), LiClO4, and porous inorganic–organic hybrid poly (cyclotriphosphazene-co-4, 4′-sulfonyldiphenol) (PZS) nanotubes were prepared using the solvent casting method. Differential scanning calorimetry and scanning electron microscopy were used to determine the characteristics of the composite polymer electrolytes. The ionic conductivity, lithium ion transference number, and electrochemical stability window can be enhanced after the addition of PZS nanotubes. The electrochemical impedance showed that the conductivity was improved significantly. Maximum ionic conductivity values of 1.5 × 10−5 S cm−1 at ambient temperature and 7.8 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 80 °C were obtained with 10 wt.% content of PZS nanotubes, and the lithium ion transference number was 0.35. The good electrochemical properties of the solid-state composite polymer electrolytes suggested that the porous inorganic–organic hybrid polyphosphazene nanotubes had a promising use as fillers in SPEs and the PEO10–LiClO4–PZS nanotube solid composite polymer electrolyte might be used as a candidate material for lithium polymer batteries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray FM (1997) Polymer electrolytes. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Dias FB, Plomp L, Veldhuis JBJ (2000) J Power Sources 88:169–191
Croce F, Appetechi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1995) Nature 373:557–558
Croce F, Fiory FS, Persi L, Scrosati B (2001) Electrochem Solid State Lett 4:A121–A123
Kumar B, Scanlon LG (2000) J Electroceram 5:127–139
Kim J, Ji K, Lee J, Park J (2003) J Power Sources 119:415–421
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nature 394:456–458
Yang YWC, Chen SY, Yuan CY, Yan DP (2005) Macromolecules 38:2710–2715
Wang ZX, Huang XJ, Chen LQ (2003) Electrochem Solid State Lett 6:E40–E44
Xiong HM, Zhao KK, Zhao X (2003) Solid State Ionics 159:89–95
Xi JY, Mao SJ, Tang XZ (2004) Macromolecules 37:8592–8598
Xi J, Qiu XP, Zhu WT (2006) Micropor Mesopor Mater 88:1–7
Nan CW, Fan LZ, Lin YH (2003) Phys Rev Lett 91:266104
Wieczorek W, Stevens JR, Florjanczyk Z (1996) Solid State Ionics 85:67–72
Croce F, Persi L, Scrosati B, Fiory FS, Plichta E, Hendrickson MA (2001) Electrochim Acta 46:2457–2461
Chung SH, Wang Y, Persi L, Croce F, Greenbaum SG, Scrosati B, Plichta E (2001) J Power Sources 97:644–648
Allcock HR (2004) Phosphorus Sulfur 179:661–671
Singh A, Krogman NR, Sethuraman S, Nair LS, Sturgeon JL, Brown PW, Laurencin CT, Allcock HR (2006) Biomacromolecules 7:914–918
Zhu L, Xu YY, Yuan WZ, Xi JY, Huang XB, Tang XZ, Zheng SX (2006) Adv Mater 18:2997–3000
Fu JW, Huang XB, Zhu L, Tang XZ (2008) Scr Mater 58:1047–1049
Jaeger RD, Gleria M (1998) Prog Polym Sci 23:179–276
Xi J, Qiu XP, Cui MZ, Tang XZ, Zhu WT, Chen LQ (2006) J Power Sources 156:581–588
Bruce PG, Vincent CA (1987) J Electroanal Chem 225:1–17
Evans J, Vincent CA, Bruce PG (1987) Polymer 28:2324–2328
Riley M, Fedkiw PS, Khan SA (2002) J Electrochem Soc 149:A667–A674
Heitner KL (2000) J Power Sources 89:128–131
Luther TA, Stewart F, Budzien JL, LaViolette RA, Bauer WF, Harrup MK, Allen CW, Elayan A (2003) J Phys Chem 107:3168–3176
Li X, Hsu SL (1984) J Poly Sci Polym Phys Ed 22:1331–1342
Kim S, Park SJ (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:3477–3484
Gray FM (1991) Solid polymer electrolytes—fundamentals and technical applications. VCH, Wenheim
Salomon M, Xu M, Eyring EM, Petrucci S (1994) J Phys Chem 98:8234–8244
Nan CW, Smith DM (1991) Mater Sci Eng B 10:99–106
Nan CW (1993) Prog Mater Sci 37:1–116
Wieczorek W, Raducha D, Zalewska A (1998) J Phys Chem B 102:8725–8731
Wieczorek W, Zalewska A, Raducha D, Florjanczyk Z, Stevens JR (1996) Macromolecules 29:143–155
Maier J (1995) Prog Solid State Chem 23:171–263
Sata N, Eberman K, Eberl K, Maier J (2000) Nature 408:946–949
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Shanghai Science and Technology Grant No. 10ZR1416100 and Shanghai-Applied Materials Collaborative Research Program No. 09520714400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Huang, X., Wei, H. et al. Enhanced electrochemical properties of polyethylene oxide-based composite solid polymer electrolytes with porous inorganic–organic hybrid polyphosphazene nanotubes as fillers. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 101–107 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1278-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1278-3