Abstract
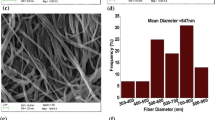
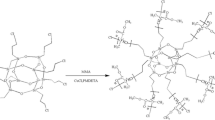
Composite polymer electrolyte membranes composed of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) {P(VdF-HFP)} blends, dedoped (insulating) polyaniline (PAni) nanofibers, and LiClO4 as salt have been synthesized with varying fraction of dedoped PAni nanofibers (from 2 to 10 wt.%). The ionic conductivity of PEO–P(VdF-HFP)–LiClO4 electrolyte system increases with increase in the fraction of dedoped polyaniline nanofibers. This could be attributed to the incorporation of nanofibers (aspect ratio >50), which may provide high ion conducting path along the interface due to Lewis acid–base interactions between Li+ ions and lone pair of electrons of nitrogen atom of polyaniline. However, at higher fraction (>6 wt.%), the nanofibers get phase separated from the polymer matrix and form domain-like structures, which may act as physical barrier to the conduction of Li+ ions resulting in decreased ionic conductivity. Electrochemical potential window and interfacial stability of nanofibers dispersed polymer electrolyte membranes are also better than that of nanofibers free membranes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature (London) 414:359–367
Ahn J-H, Wang GX, Liu HK, Dou SX (2003) Nanoparticle-dispersed PEO polymer electrolytes for Li batteries. J Power Sources 119–121:422–426
Algamir M, Abraham KM (1994) Lithium batteries, new materials, development and prospectives. In: Pistoia G (ed) Industrial chemistry library, vol 5. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 93–136
Abraham KM (1993) Highly conductive polymer electrolytes. In: Scrosati B (ed) Applications of electroactive polymers. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 75–112
Kovac M, Gaberscek M, Grdadolnik J (1998) The effect of plasticizer on the microstructural and electrochemical properties of a (PEO)nLiAl(SO3 Cl)4 system. Electrochim Acta 44:863–870
Armand MB, Chabagno JM, Duclot MJ (1997) Fast ion transport in solids. In: Vashista P, Shenoy GK (eds) Elsevier. North-Holland, New York, pp 131–136
Jacob MME, Hackett E, Giannelis EP (2003) From nanocomposite to nanogel polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem 13:1–5
Song JY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1999) Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 77:183–197
Fan LZ, Nan C-W, Zhau SJ (2003) Effect of modified SiO2 on the properties of PEO-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion 164:81–86
Zhang S, Lee JY, Hong L (2004) Visualization of particle distribution in composite polymer electrolyte systems. J Power Sources 126:125–133
Nookala M, Kumar B, Rodrigues S (2002) Ionic conductivity and ambient temperature Li electrode reaction in composite polymer electrolytes containing nano-size alumina. J Power Sources 111:165–172
Qian XM, Gu NY, Cheng ZL, Yang XR, Wang EK, Dong SJ (2001) Impedance study of (PEO)10LiClO4–Al2O3 composite polymer electrolyte with blocking electrodes. Electrochim Acta 46:1829–1836
Liu Y, Lee JY, Hong L (2003) Morphology, crystallinity, and electrochemical properties of in situ formed poly(ethylene oxide)/TiO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Appl Polym Sci 89:2815–2822
Croce F, Persi L, Scrosati B (2000) Impedance spectroscopy study of PEO-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 147:1718–1721
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Curini R, Martinelli A, Persi L, Ronci F, Scrosati B, Caminiti R (1999) Physical and chemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 103:10632–10638
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 394:456–458
Tang M, Liau WR (2000) Solvent effect on the miscibility of poly(4-hydroxystyrene)–poly(ethylene oxide) blends. Eur Polym J 36:2597–2603
Pielichowski K, Hamerton I (2000) Compatible poly(vinyl chloride)/chlorinated polyurethane blends: thermal characteristics. Eur Polym J 36:171–181
Rocco AM, Pereira RP, Felisberti MI (2001) Miscibility, crystallinity and morphological behavior of binary blends of poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(methyl vinyl ether–maleic acid). Polymer 42:5199–5205
Choi N-S, Lee Y-G, Park J-K, Ko J-M (2001) Preparation and electrochemcial characteristics of plasticized polymer electrolytes based upon a P(VdF-co-HFP)/PVAc blend. Electrochim Acta 46:1581–1586
Choi BK, Kim YW, Shin HK (2000) Ionic conduction in PEO–PAN blend polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 45:1371–1374
Jacob MME, Prabaharan SRS, Radhakrishna S (1997) Effect of PEO addition on the electrolytic and thermal properties of PVDF-LiClO4 polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion 104:267–276
Fan L, Dang Z, Nan C-W, Li M (2002) Thermal electrical and mechanical properties of plasticized polymer electrolytes based on PEO/P(VDF-HFP) blends. Electrochim Acta 48:205–209
Arvindan V, Vickraman P (2007) Polyvinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes (NCPE) complexed with LiPF3 (CF3 CF2)3. Eur Polym J 43:5121–5127
Huang J (2006) Syntheses and applications of conducting polymer polyaniline nanofibers. Pure Appl Chem 78:15–27
Deka M, Nath AK, Kumar A (2009) Effect of dedoped (insulating) polyaniline nanofibers on the ionic transport and interfacial stability of poly(vinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene) based composite polymer electrolyte membranes. J Membr Sci 327:188–194
Saikia D, Kumar A (2004) Ionic conduction in P(VDF-HFP)/PVDF-(PC + DEC)-LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 49:2581–2589
Leo CJ, Rao GVS, Chowdari BVR (2002) Studies on plasticized PEO–lithium triflate-ceramic filler composite electrolyte system. Solid State Ion 148:159–171
Saikia D, Hussain AMP, Kumar A, Singh F, Avasthi DK (2006) Ionic conduction studies in Li3+ ion irradiated (PVDF-HFP)-(PC + DEC)-LiCF3SO3 gel polymer electrolytes. NIMB 244:230–234
Scrosati B, Croce F, Panero S (2001) Progress in lithium polymer battery R&D. J Power Sources 100:93–100
Stephan AM, Thirunakaran R, Renganathan NG, Sundaram V, Pitchumani S, Muniyandi N, Gangadharan R, Ramamoorthy P (1997) A study on polymer blend electrolyte based on PVC/PMMA with lithium salt. J Power Sources 81–82:752–758
Deka M, Kumar A (2010) Enhanced electrical and electrochemical properties of PMMA–clay nanocomposite gel polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 55:1836–1842
Rajendran S, Uma T (2000) Conductivity studies on PVC/PMMA polymer blend electrolyte. Mater Lett 44:242–247
Croce F, Persi L, Scrosati B, Serraino-Fiory F, Plichta E, Hendrickson MA (2001) Role of the ceramic fillers in enhancing the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 46:2457–2461
Chung SH, Wang Y, Persi L, Croce F, Greenbaum SG, Scrosati B, Plichta E (2001) Enhancement of ion transport in polymer electrolytes by addition of nano-scale inorganic oxides. J Power Sources 97–98:644–648
Stephan AM, Nahm KS (2006) Review on composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Polymer 47:5952–5964
Wieczorek W, Zalewska A, Raducha D, Florjańczyk Z, Stevens JR (1996) Polyether, poly(N, N-dimethylacrylamide), and LiClO4 composite polymeric electrolytes. Macromolecules 29:143–155
Kumar B, Scanlon LG (1994) Polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes. J Power Sources 52:261–268
Kim S, Park S-J (2007) Preparation and electrochemical behaviors of polymeric composite electrolytes containing mesoporous silicate fillers. Electrochim Acta 52:3477–3484
Kurian M, Galvin ME, Trapa PE, Sadoway DR, Mayes AM (2005) Single-ion conducting polymer–silicate nanocomposite electrolytes for lithium battery applications. Electrochim Acta 50:2125–2134
Li ZH, Su GY, Wang XY, Gao DS (2005) Micro-porous P(VDF-HFP)-based polymer electrolyte filled with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Solid State Ion 176:1903–1908
Christie AM, Lilly SJ, Staunton E, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2005) Increasing the conductivity of crystalline polymer electrolytes. Nature 433:500–553
Rhoo H-J, Kim H-T, Park J-K, Hwang T-S (1997) Ionic conduction in plasticized PVC/PMMA blend polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 42:1571–1579
Saikia D, Kumar A (2005) Ionic transport in P(VDF-HFP)-PMMA-LiCF3SO3-(PC + DEC)-SiO2 composite gel polymer electrolyte. Eur Polym J 41:563–568
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS (2001) Introduction to spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Harcourt College Publ, USA
Kim CS, Oh SM (2000) Importance of donor number in determining solvating ability of polymers and transport properties in gel-type polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 45:2101–2109
Yang G, Hou W, Sun Z, Yan Q (2005) A novel inorganic–organic polymer electrolyte with a high conductivity: insertion of poly(ethylene) oxide into LiV3O8 in one step. J Mater Chem 15:1369–1374
Zhou W, Ma L, Lu K (2007) Facile Synthesis of polyaniline nanofibers in the presence of polyethylene glycol. J Polym Res 14:1–4
Kim D-W, Park J-K, Bae J-S, Pyun S-I (1996) Electrochemical characteristics of blended polymer electrolytes containing lithium salts. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 34:2127–2137
Li Q, Sun HY, Takeda Y, Imanishi N, Yang J, Yamamoto O (2001) Interface properties between a lithium metal electrode and a poly(ethylene oxide) based composite polymer electrolyte. J Power Sources 94:201–205
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Mr. A.K. Nath and Mr. Somik Banerjee, Department of Physics, Tezpur University, for their help in synthesis and making measurements during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Deka, M. PEO/P(VdF-HFP) blend based Li+ ion-conducting composite polymer electrolytes dispersed with dedoped (insulating) polyaniline nanofibers. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 35–44 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1271-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1271-x