Abstract
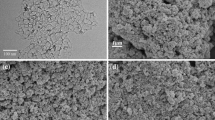
Superfine and uniform La2NiO4+δ powder was synthesized by a polyaminocarboxylate complex precursor method. La2NiO4+δ layers were screen-printed on dense Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 electrolyte substrates and sintered at 900–1,100 °C. The microstructure and electrochemical properties of the resulting porous electrodes were investigated with respect to sintering temperature. The results indicate a significant effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and electrode polarization. It was found that elevating sintering temperature was favorable to the charge transfer process whereas undesired for the oxygen surface exchange process due to an increase of the grain size. Sintering at 900 °C was determined to be preferred in terms of the polarization resistance of the electrode. The porous electrode sintered at the temperature showed a fine-grained microstructure (about 200 nm) and a relatively low polarization resistance of 0.28 Ω cm2 at 800 °C. This work suggests that preparing the electrode from superfine starting powder is contributive to modifying the polarization properties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kharton VV, Viskup AP, Naumovich EN, Marques FMB (1999) J Mater Chem 9(10):2623–2629
Skinner SJ, Kilner JA (2000) Solid State Ionics 135(1–4):709–712
Lalanne C, Mauvy F, Siebert E, Fontaine ML, Bassat JM, Ansart F, Stevens P, Grenier JC (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27(13–15):4195–4198
Amow G, Davidson IJ, Skinner SJ (2006) Solid State Ionics 177(13–14):1205–1210
Mauvy F, Lalanne C, Fourcade S, Bassat JM, Grenier JC (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27(13–15):3731–3734
Aguadero A, Escudero MJ, Perez M, Alonso JA, Daza L (2007) J Fuel Cell Sci Technol 4(3):294–298
Pérez-Coll D, Aguadero A, Escudero MJ, Núñez P, Daza L (2008) J Power Sources 178(1):151–162
Kammer K (2009) Ionics 15(3):325–328
Kharton VV, Tsipis EV, Yaremchenko AA, Frade JR (2004) Solid State Ionics 166(3–4):327–337
Mauvy F, Lalanne C, Bassat JM, Grenier JC, Zhao H, Dordor P, Stevens P (2005) J Eur Ceram Soc 25(12):2669–2672
Mauvy F, Lalanne C, Bassat J-M, Grenier J-C, Zhao H, Huo L, Stevens P (2006) J Electrochem Soc 153(8):A1547–A1553
Li Q, Fan Y, Zhao H, Sun L-P, Huo L-H (2007) J Power Sources 167(1):64–68
Escudero MJ, Aguadero A, Alonso JA, Daza L (2007) J Electroanal Chem 611(1–2):107–116
Zhao H, Mauvy F, Lalanne C, Bassat JM, Fourcade S, Grenier JC (2008) Solid State Ionics 179(35–36):2000–2005
Pérez-Coll D, Aguadero A, Escudero MJ, Daza L (2009) J Power Sources 192(1):2–13
Lin Y, Barnett SA (2008) Solid State Ionics 179(11–12):420–427
Qiang F, Sun K, Zhang N, Le S, Zhu X, Piao J (2009) J Solid State Electrochem 13(3):455–467
Huang D-p, Xu Q, Zhang F, Chen W, Liu H-x, Zhou J (2006) Mater Lett 60(15):1892–1895
Chen M, Kim BH, Xu Q, Ahn BK, Kang WJ, Huang Dp (2009) Ceram Int 35(4):1335–1343
Choy KL, Charojrochkul S, Steele BCH (1997) Solid State Ionics 96(1–2):49–54
Chen D, Ran R, Zhang K, Wang J, Shao Z (2009) J Power Sources 188(1):96–105
Baumann FS, Fleig J, Habermeier H-U, Maier J (2006) Solid State Ionics 177(11–12):1071–1081
Adler SB, Lane JA, Steele BCH (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143(11):3554–3564
Hart NT, Brandon NP, Day MJ, Lapeña-Rey N (2002) J Power Sources 106(1–2):42–50
Dusastre V, Kilner JA (1999) Solid State Ionics 126(1–2):163–174
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (50572079 and A3 Foresight Program-50821140308), Ministry of Education (200804971002), Wuhan Science and Technology Bureau (200851430485), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2010-ZY-CL-060). The authors are grateful to the International Collaborative Research Program of Jeonbuk National University (2009) for supporting the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, K., Xu, Q., Huang, DP. et al. Microstructure and electrochemical properties of porous La2NiO4+δ electrode screen-printed on Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 9–16 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1270-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1270-y