Abstract
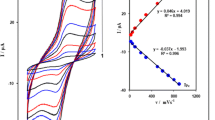
In the present paper, the use of a novel carbon paste electrode modified by N,N′(2,3-dihydroxybenzylidene)-1,4-phenylene diamine (DHBPD) and TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by a simple and rapid method for the determination of hydrazine (HZ) was described. In the first part of the work, cyclic voltammetry was used to investigate the redox properties of this modified electrode at various solution pH values and at various scan rates. A linear segment was found with a slope value of about 48 mV/pH in the pH range 2.0–12.0. The apparent charge transfer rate constant (k s) and transfer coefficient (α) for electron transfer between DHBPD and TiO2 nanoparticles-modified carbon paste electrode were calculated. In the second part of the work, the mediated oxidation of HZ at the modified electrode was described. It has been found that under optimum condition (pH 8.0) in cyclic voltammetry, a high decrease in overpotential occurs for oxidation of HZ at the modified electrode. The values of electron transfer coefficients (α) and diffusion coefficient (D) were calculated for HZ, using electrochemical approaches. Differential pulse voltammetry exhibited a linear dynamic range from 1.0 × 10−8 to 4.0 × 10−6 M and a detection limit (3σ) of 9.15 nM for HZ. Finally, this method was used for the determination of HZ in water samples, using standard addition method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Welch CM, Compton RG (2006) Anal Bioanal Chem 384:601–619
Morales GR, Silva TR, Galicia L (2003) J Solid State Electrochem 7:355–360
Beitollahi H, Mazloum Ardakani M, Ganjipour B, Naeimi H (2008) Biosens Bioelectron 24:362–368
Katz E, Willner I, Wang J (2004) Electroanalysis 16:19–44
Mazloum Ardakani M, Talebi A, Naeimi H, Nejati Barzoky M, Taghavinia N (2009) J Solid State Electrochem 13:1433–1440
Schessl HW (1995) Encyclopedia of chemical technology, 4th edn. Wiley/Interscience, New York
US Environmental protection Agency (1999) Integrated risk information system (iris) on hydrazine/hydrazine sulfate. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development, Washington
Budavari S, O’Neil MJ, Smith A (1989) The Merck index: an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs and biologicals, 11th edn. Merck and Co. Inc.
Pingarron JM, Ortiz Hernandez I, Gonalez-Cores A, Yez-Sendeno P (2001) Anal Chim Acta 439:281–290
US Department of Health and Human Services (1993) Hazardous substances data bank (HDBS, online database). National Toxicology Information Program, National Library of Medicine, Bethesda, MD
Sitting M (1985) Handbook of toxic and hazardous chemical and carcinogens, 2nd edn. Noyes Publications, Park Ridge
World Health Organization (1987) Environmental Health Criteria 68: Hydrazine, Geneva, Switzerland
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (1974) IARC monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to man: some aromatic amines, hydrazine and related substances, N-nitroso compounds and miscellaneous alkylating agents, vol 4. World Health Organization, Lyon
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (1997) Toxicological profile for hydrazines. Public Health Service. US Department of Health and Human Services, Atlanta
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) (1997) Pocket guide to chemical hazards. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cincinnati
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) (1998) Occupational Safety and Health Standards, Toxic and Hazardous Substances, Code of Federal Regulations, 29 CFR
Duarte JC, Luz RCS, Damos FS, Oliveira AB, Kubota LT (2007) J Solid State Electrochem 11:631–638
Yang M, Li HL (2001) Talanta 55:479–484
Mori M, Tanaka K, Xu Q, Ikedo M, Taoda H, Hu W (2004) J Chromatogr A 1039:135–139
Afkhami A, Zarei AR (2004) Talanta 62:559–565
Ensafi AA, Naderi B (1997) Microchem J 56:269–272
Safavi A, Karimi MA (2002) Talanta 58:785–792
Beitollahi H, Mazloum Ardakani M, Naeimi H, Ganjipour B (2009) J Solid State Electrochem 13:353–363
Mazloum-Ardakani M, Beitollahi H, Sheikh Mohseni MA, Benvidi A, Naeimi H, Nejati-Barzoki M, Taghavinia N (2010) Colloids, Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 76:82–87
Abbaspour A, Shamsipur M, Siroueinejad A, Kia R, Raithby PR (2009) Electrochim Acta 54:2916–2923
Zhenga L, Songa JF (2009) Talanta 79:319–326
Abbaspour A (2009) J Electroanal Chem 631:52–57
Zheng L, Song JF (2009) Sens Actuators B 135:650–655
Quintino MSM, Araki K, Toma HE, Angnes L (2008) Talanta 74:730–735
Richard Prabakar SJ, Sriman Narayanan S (2008) J Electroanal Chem 617:111–120
Ojani R, Raoof JB, Norouzi B (2008) Electroanalysis 20:1378–1382
Nassef HM, Radi AE, O’Sullivan CK (2006) J Electroanal Chem 592:139–146
Li J, Lin X (2007) Sens Actuators B 126:527–535
Abbaspour A, Kamyabi MA (2005) J Electroanal Chem 576:73–83
Raoof JB, Ojani R, Ramine M (2007) Electroanalysis 19:597–603
Zheng J, Sheng Q, Li L, Shen Y (2007) J Electroanal Chem 611:155–161
Jayasri D (2007) Sriman Narayanan S. J Hazard Mater 144:348–354
Wang G, Gu A, Wang W, Wei Y, Wu J, Wang G, Zhang X, Fang B (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:631–634
Mazloum Ardakani M, Ebrahimi karami P, Rahimi P, Zare HR, Naeimi H (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:6118–6124
Laviron E (1979) J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Galus Z (1976) Fundamentals of electrochemical analysis. Ellis Horwood, New York
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Nima Taghavinia, Yazd University Research Council and IUT Research Council and Excellence in Sensors for financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazloum-Ardakani, M., Rajabi, H., Mirjalili, B.B.F. et al. Nanomolar determination of hydrazine by TiO2 nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 14, 2285–2292 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1060-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1060-6