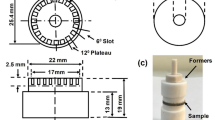
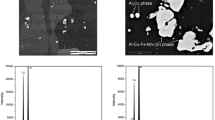
Abstract
The microstructure of AlCu4Mg1 as-cast aluminium alloy was first determined by means of field emission-scanning electron microscope with an integrated electron dispersion spectrometer, secondary ion mass spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. Large precipitates (Al2Cu, Al–Si–Mn–Fe–Cu, oxides) were located at grain boundaries, whereas small particles (aluminium, magnesium and copper) were present in grains. The electrochemical response and pitting susceptibility of sites containing precipitates were then investigated after polishing using the electrochemical microcell technique. After straining, big scattering was observed in the electrochemical response. The most active places corresponded to the sites containing wide microcracks and severe damages in the matrix. In this case, the corrosion potential was around −1,000 mV vs. Ag/AgCl, and the current in the passive domain was five times higher than on the strained matrix. In the absence of severe damage in the matrix or wide microcracks, the corrosion potential was more anodic and the current density in the passive range was around 0.5 mA cm−2. Local polarisation curves carried out in sites containing large precipitates and no defects induced by straining were very close to those obtained in grains far from precipitates.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delmas F, Vivas M, Lours P, Casanove MJ, Couret A, Coujou A (2003) Mater Sci Eng A 340:286
Kobayashi T (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 286:333
Qian L, Toda H, Uesugi K, Ohgaki T, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi T (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 483–484:293
Toda H, Sinclair I, Buffiere JY, Maire E, Khor KH, Gregson P, Kobayashi T (2004) Acta Mater 52:1305
Nisancioglu K (1990) J Electrochem Soc 137:69
Mc.Cafferty E (2003) J Electrochem Soc 150:B238
Searles JL, Gouma PI, Buchheit RG (2001) Metall Mater Trans A 32:2859
Birbilis N, Buchheit RG (2005) J Electrochem Soc 152:B140
Guillaumin V, Mankowski G (1999) Corr Sci 41:421
Campestrini P, van Westing EPM, van Rooijen HW, de wit JHW (2000) Corr Sci 42:1853
Little DA, Connolly BJ, Scully JR (2007) Corr Sci 49:347
Ambat R, Davenport AJ, Scamans GM, Afseth A (2006) Corr Sci 48:3455
Vogt H, Speidel MO (1998) Corr Sci 40:251
Lin CK, Yang ST (1998) Eng Fract Mech 59:779
Dymek S, Dollar M (2003) Mater Chem Phys 81:286
Liu X, Frankel GS, Zoofan B, Rokhlin SI (2004) Corr Sci 46:405
Liu X, Frankel GS (2006) Corr Sci 48:3309
Webb EG, Alkire RC (2002) J Electrochem Soc 149:B280
Jorcin JB, Blanc C, Pebere N, Tribollet B, Vivier V (2008) J Electrochem Soc 155:C46
Lacroix L, Ressier L, Blanc C, Mankowski G (2008) J Electrochem Soc 155:C131
Starink MJ (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 390:260
Kobayashi T (2003) Mater Sci Forum 426:67
Toda H, Kobayashi T, Takahashi A (1999) Alum Trans 1:109
Beck W, Bockris JO’M, McBreen J, Nanis L (1966) Proc R Soc A290:220
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the French–Polish bilateral program Polonium (project no. 17798ZH) and Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education (grant N507 no. 28.28.170.7004). The authors would like to thank Dr. O. Heintz (ICB) for assistance in SIMS experiments and Dr. C. Josse (ICB) for assistance in FE-SEM/EDS observations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krawiec, H., Vignal, V. & Szklarz, Z. Local electrochemical studies of the microstructural corrosion of AlCu4Mg1 as-cast aluminium alloy and influence of applied strain. J Solid State Electrochem 13, 1181–1191 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0638-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0638-8