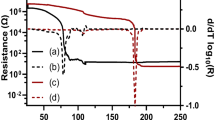
Abstract
Nanocrystalline gold is electrodeposited from a stable nontoxic bath, in which Au+ is stabilized by complex formation with 3-mercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt. Nanoscaling is achieved by pulse techniques. The crystallite size is strongly dependent on physical and chemical process parameters, such as pulse duration, current density, bath temperature, type, and amount of additives; especially, we observe a decrease of the crystallite size down to 16 nm by the proper choice of current density and temperature, and down to 7 nm by the use of additives. The thermal stability of nanocrystalline gold is investigated by in situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction; nanogold exhibits a thermal stability up to 673 K. An activation energy of 37 kJ mol−1 is determined for the grain-growth kinetics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Popov KI, Pavlovic MG (1993) Mod Aspects Electrochem 24:299
Robertson A, Erb U, Palumbo G (1999) Nanostruct Mater 12:1035
Natter H, Hempelmann R (2003) Electrochim Acta 49:51
Dinan TE, Cheh HY (1992) J Electrochem Soc 139:2
Harman GG (1991) Reliability and yield problems of wire bonding in microelectronics. ISHM, Reston
http://www.palomartechnologies.com/resources/whitepapers/makingconnection.htm
Li YG, Lasia A (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:6
Osaka T, Kodera A, Misato T, Homma T, Okinaka Y (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:10
Green TA, Liew MJ, Roy S (2003) J Electrochem Soc 150:3
Simon F (2000) Galvanotechnik 54:10
Puippe JC, Leaman F (eds) (1986) Theory and practise of pulse plating, Amer Electroplaters Soc, Florida
Bockris JO’M, Razumney GA (1967) Fundamental aspects of electrocrystallization. Plenum, New York
Kashchiev D (2000) Nucleation basic theory with applications. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Budevski, Staikov G, Lorenz WJ (1996) Electrochemical phase formation and growth. VCH, Weinheim
Warren BE, Averbach LE (1950) J Appl Phys 21:536
Warren BE, Averbach LE (1952) J Appl Phys 23:497
Warren BE (1990) X-ray diffraction. Dover, New York
Natter H, Hempelmann R (1996) J Phys Chem 100:19525
Natter H, Schmelzer M, Loffler MS, Krill CE, Fitch A, Hempelmann R (2000) J Phys Chem 104:2467
Holleman-Wiberg (1985) Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin
Lin K, Weil R (1986) J Electrochem Soc 133:4
Shunk FA (1969) Constitution of binary alloys, second supplement. McGraw-Hill, New York
Carotenuto G, Nicolais L (2003) J Mater Chem 13
Michels A, Krill CE, Erhardt H, Birringer R, Wu DT (1999) Acta Mater 47:2143
Landolt-Boernstein (1990) Numerical data and functional relationships in science and technology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p. 640
Acknowledgments
The present work is initiated and performed at the Universität des Saarlandes (Germany) in the framework of the Sonderforschungsbereich 277 (Grenzflächenbestimmte Materialien). For experimental assistance, we thank S. Kuhn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yevtushenko, O., Natter, H. & Hempelmann, R. Influence of bath composition and deposition parameters on nanostructure and thermal stability of gold. J Solid State Electrochem 11, 138–143 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-006-0212-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-006-0212-1