Abstract
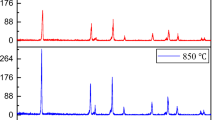
A submicron LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode was synthesized via the pyrolysis of polyacrylate salts as precursor polymerized by reaction of the metal salts with acrylate acid. The structure and morphology of the resulting compound was characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results reveal that the prepared LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material has a pure cubic spinel structure \(({\rm Fd}\ifmmode\expandafter\bar\else\expandafter\=\fi{3}\,{\rm m})\) and submicron-sized morphology even if calcined at 900 °C and quenched to room temperature. The LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 electrodes exhibited promising high-rate characteristics and delivered stable discharge capacity (90 mAh/g) with excellent retention capacity at the current density of 50 mA/g between 3.5 and 4.9 V. The capacity of the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 electrodes remains stable even after 30 cycles at low or high current density. This polymer-pyrolysis method is simple and particularly suitable for preparation of the spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material compared to the conventional synthesis techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amine K, Tukamoto H, Yasuda H, Fujita Y (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143:1607
Zhong Q, Bonakdarpour A, Zhang M, Gao Y, Dahn JR (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:205
Ohzuku T, Takeda S, Iwanaga M (1999) J Power Sources 81:90
Lee YS, Todorov YM, Konishi T, Yoshio M (2001) ITE Lett 1:1
Sigala C, Guyomard D, Verbaere A, Piffard Y, Toumoux M (1995) Solid State Ionics 81:167
Gao Y, Myrtle K, Zhang M, Reimers JN, Dahn JR (1996) Phys Rev B 54:16670
Ohzuku T, Ariyoshi K, Takeda S, Sakai Y (2001) Electrochim Acta 46:2327
Ein-Eli Y, Vaughey JT, Thackeray MM, Mukerjee S, Yang XQ, McBreen J (1999) J Electrochem Soc 146:908
Kawai H, Nagata M, Tukamoto H, West AR (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:67
Shigemura H, Sakaebe H, Kageyama H, Kobayashi H, West AR, Kanno R, Morimoto S, Nasu S, Tabuchi M (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:A730
West AR, Kawai H, Kageyama H, Tabuchi M, Nagata M, Tukamoto H (2001) J Mater Chem 11:1662
Guohua L, Ikuta H, Uchida T, Wakihara M (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143:178
Sun YK, Lee YS, Yoshio M, Amine K (2002) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 5:A99
Alcantara R, Jaraba M, Lavela P, Tirado JL (2002) Electrochem Acta 47:1829
Amine K, Tukamoto H, Yasuda H, Fujita Y (1997) J Power Sources 68:604
Yu LH, Yang HX, Ai XP, Cao YL (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:1148
Kim JH, Myung ST, Sun YK (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:219
Lee YS, Sun YK, Ota S, Miyashita T, Yoshio M (2002) Electrochem Commun 4:989
Ohzuku T, Kitagawa M, Hirai T (1990) J Electrochem Soc 137:769
Caballero A, Cruz M, Hernan L, Melero M, Morales J, Castellon ER (2005) J Electrochem Soc 152 (3):A552
Markovsky B, Talyossef Y, Salitra G, Aurbach D, Kim HJ, Choi S (2004) Electrochem Commun 6:821
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely acknowledge the financial support by the 973 Program, China (Grant No. 2002CB211800) and the technical assistance in TEM work by the Center for Electron Microscopy, Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Cao, Y., Yang, H. et al. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 electrode material for Li-ion batteries by the polymer-pyrolysis method. J Solid State Electrochem 10, 283–287 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-005-0695-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-005-0695-1