Abstract
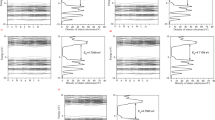
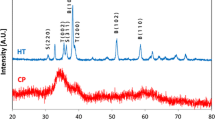
Recently, high oxide ion conduction has been observed in the apatite-type systems La9.33+x (Si/Ge)6O26+x/2, with conductivities approaching and even exceeding that of yttria-stabilized zirconia. The Ge-based phases have been reported to suffer from Ge loss and undergo irreversible structural changes on sintering at the high temperatures required to obtain dense pellets. In this paper we discuss doping studies (Ba, Bi for La) aimed at stabilizing the hexagonal apatite lattice to high temperature, and/or lowering the synthesis and sintering temperatures. The results show that doping with Ba helps to stabilize the hexagonal lattice at high temperatures, although Ge loss appears to still be a problem. Conductivity data show that, as previously reported for the Si-based systems, non-stoichiometry in the form of cation vacancies and/or oxygen excess is required to achieve high oxide ion conduction in these Ge-based systems. Neutron diffraction structural data for the fully stoichiometric phase La8Ba2Ge6O26 shows that the channel oxygen atoms show little anisotropy in their thermal displacement parameters, consistent with the low oxide ion conductivity of this phase. Bi doping is shown to lower the synthesis and sintering temperatures, although the presence of Bi means that these samples are not stable at high temperatures under reducing conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakayama S, Aono H, Sadaoka Y (1995) Chem Lett 431
Nakayama S, Sakamoto M (1998) J Eur Ceram Soc 18:1413
Nakayama S, Sakamoto M, Higuchi M, Kodaira K, Sato M, Kakita S, Suzuki T, Itoh K (1999) J Eur Ceram Soc 19:507
Tao S, Irvine JTS (2001) Mater Res Bull 36:1245
Sansom JEH, Richings D, Slater PR (2001) Solid State Ionics 139:205
Abram EJ, Sinclair DC, West AR (2001) J Mater Chem 11:1978
Arikawa H, Nishiguchi H, Ishihara T, Takita Y (2000) Solid State Ionics 136–137:31
Ishihara T, Arikawa H, Akbay T, Nishiguchi H, Takita Y (2001) J Am Chem Soc 123:203
McFarlane J, Barth S, Swaffer M, Sansom JEH, Slater PR (2002) Ionics 8:149
Sansom JEH, Hildebrandt L, Slater PR (2002) Ionics 8:155
Slater PR, Sansom JEH (2003) Solid State Phenom 90–91:195
Nakayama S, Sakamoto M (2001) J Mater Sci Lett 20:1627
Berastegui P, Hull S, Garcia Garcia FJ, Grins J (2002) J Solid State Chem 168:294
Islam MS, Tolchard JR, Slater JR (2003) Chem Commun 1486
Tolchard JR, Islam MS, Slater PR (2003) J Mater Chem 13:1956
Sansom JEH, Tolchard JR, Slater PR, Islam MS (2004) Solid State Ionics (in press)
Sansom JEH, Slater PR (2004) Solid State Ionics (in press)
Larson AC, Von Dreele RB (1987) Los Alamos National Laboratory, report no LA-UR-86-748
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank EPSRC and Merck Ltd for funding. We would also like to thank ISIS, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, for the provision of neutron diffraction facilities, and R. Smith for help with the collection of neutron powder diffraction data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented at the OSSEP Workshop “Ionic and Mixed Conductors: Methods and Processes”, Aveiro, Portugal, April 10–12, 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolchard, J.R., Sansom, J.E.H., Slater, P.R. et al. Effect of Ba and Bi doping on the synthesis and sintering of Ge-based apatite phases. J Solid State Electrochem 8, 668–673 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-003-0492-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-003-0492-7