Abstract
Aim
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF) as a socket plug with or without use of Plaster of Paris (POP) as bone substitute to preserve the alveolar ridge post-extraction.
Material and methods
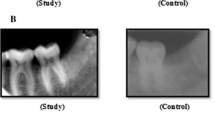
A prospective randomised single blind controlled study, was conducted for 18 months from November 2014 to May 2016 on 48 patients requiring extraction. All teeth were extracted atraumatically using periotomes and luxators without raising mucoperiosteal flap. Sockets were randomly allotted to groups A, B and C. Group A sockets were chosen as control, where figure of eight suture was placed. In group B sockets, PRF obtained by centrifugation was used as a socket plug and stabilised with figure of eight suture. Group C sockets were filled with POP and then covered with PRF. The socket was then closed with a figure of eight suture. Patients were informed of need for 6 months follow-up.
Results
Ninety sockets in 48 patients were subjected to our study. We found that results in the sockets where we have grafted POP showed better ridge preservation and post-operative comfort even though the difference in ridge resorption between the three groups was not statistically significant. Powered by Editorial Manager® and ProduXion Manager® from the Aries Systems Corporation.
Conclusion
Atraumatic extraction may minimise the post-operative pain and discomfort to patient as well as the post-extraction alveolar height and width changes. The use of PRF and/or bone substitute even though clinically contributes to better post-operative healing and minimal loss of alveolar width and height, the values were not statistically significant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Irinakis T (2006) Rationale for socket preservation after extraction of a single rooted tooth when planning for future implant placement. J Can Dent Assoc 72(10):917–922
Kubilius M, Kubilis R, Gleiznys A (2012) The preservation of alveolar bone ridge during tooth extraction. Stomatologija 14:3–11
Abadzhiev M. Ridge preservation technique. Journal of IMAB–Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2009;(book)2:58–60
Pagini G, Pellegrini G, Giannobile WV, Rasperini G (2012) Postextraction alveolar ridge preservation: biological basis and treatments. Int J Dentistry:1–13
Casey DM, Lauciello FR (1980) A review of the submerged root concept. J Prosthet Dent 43(2):128–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3913(80)90174-2
Von Wowern N, Winther S (1980) Submergence of roots for alveolar ridge augmentation: a failure (4-year follow-up study). Int J Oral Surg 10:247–250
Anson D (1996) Calcium sulfate: a 4-year observation of its use as a resorbable barrier in guided tissue regeneration of periodontal defects. Compend Contin Educ Dent 17:895–899
Vance GS, Greenwell H, Miller RL, Hill M, Johnston H, Scheetz JP (2004) Comparison of an allograft in an experimental putty carrier and a bovine-derived xenograft used in ridge preservation: a clinical and histologic study in humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19:491–497
Kim S-G, Chug C-H, Kim YK, Park JC, Lim SC (2002) The use of particulate dentin-plaster of Paris combination with/without platelet rich plasma in the treatment of bone defects around implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 17(1):86–94
Ricci J, Alexander H, Nadkarni P et al (2000) Biological mechanisms of calcium sulfate replacement by bone. Toronto, Em squared Inc
Walsh WR, Morberg P, Yu Y, Yang JL, Haggard W, Sheath PC, Svehla M, Bruce WJM (2003) Response of a calcium sulfate bone graft substitute in a confined cancellous defect. Clin Orthop Relat Res 406:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200301000-00033
David DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan A, Mouhyi J et al (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second generation platelet concentrate. Part 1: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101(3):e 45–e 50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.009
Donald D. Price. The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 1983;17(Elsevier):45–56
Celio-Mariano R, de Melo WM, Carneiro-Avelino C (2012) Comparative radiographic evaluation of alveolar bone healing associated with autologous platelet rich plasma after impacted mandibular third molar surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2011.03.028
Madras N, D’Aiuto F, Mezzomo L, Arzoumanidi M, Donos N (2011) Radiographic alveolar bone changes following ridge preservation with two different biomaterials. Clin Oral Implants Res 22(4):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02154.x
Van der Weijden F, Acqua FD, Slot DE (2009) Alveolar bone dimensional changes post-extraction sockets in humans: a systemic review. J Clin Periodontol 36(12):1048–1058. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2009.01482.x
Mardas N, Chadha V, Donos N (2010) Alveolar ridge preservation with guided bone regeneration and a synthetic bone substitute or a bovine-derived xenograft: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 21(7):688–698. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.01918.x
Ashman A (2000) Post-extraction ridge preservation using a synthetic alloplasts. Implant Dent 9(2):168–176
Babbush CA (2007) A new atraumatic system for tooth removal and immediate implant restoration. Implant Dent 16(2):139–145. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0b013e3180581656
Adriaens PA, Van der Stede N (1998) Alveolar bone protection of extraction sites with a resorbable bilayer GBR membranes. J Dent Res 77:777–790
Kotsakis G, Markou N, Chrepa V, Krompa V, Kotsakis A (2012) Alveolar ridge preservation utilizing the socket plug technique. Int J Oral Implantol Clin Res 3(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1060
Diss J, Ling H, Ye L, Xiulian H, Zhang Y, Wu H (2009) A comparative study of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108:707–713
Geurs N, Nitounis A, Vassilopoulos P, Velden UV, Loos BG, Reddy M (2014) Using growth factors in human extraction sockets: a histological and histomorphometric evaluation of short term healing. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 29(2):485–496. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.3408
David MD, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Gogly B (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second generation platelet concentrate. Part 2: platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:e45–e50
Becker W, Clockie C, Sennerby L, Urist MR, Becker BE (1998) Histological findings after implantation of different grafting materials and titanium microscrews into extraction sockets: case reports. J Periodontol 69(4):414–421. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1998.69.4.414
Froum S, Cho S-C, Rosenberg E, Rohrer M, Tarnow D (2002) Histological comparison of healing extraction sockets implanted with bioactive glass or demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft: a pilot study. J Periodontol 73(1):94–102
Froum S, Cho SC, Elian N, Rosenberg E, Rohrer M, Tarnow D (2004) Extraction sockets and implantation of hydroxyapatites with membrane barriers: a histologic study. Implant Dent 13(2):153–164. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ID.0000127524.98819.FF
Guarnieri R, Pecora G, Fini M, Aldini N′N, Giardino R, Orsini G, Piattelli A (2004) Medical grade calcium sulphate hemihydrates in healing of human extraction sockets: clinical and histological observations at 3 months. J Periodontol 75(5):902–908. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2004.75.6.902
Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L, Karring T (2003) Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 23:313–323
Barone A, Ricci M, Tonelli P, Santini S, Covani U (2013) Tissue changes of extraction sockets in humans: a comparison of spontaneous healing vs. ridge preservation with secondary soft tissue healing. Clin Oral Implants Res 24(11):1231–1237
Camargo PM, Lekovic V, Weinlaender M et al (2000) Influence of bioactive glass on changes in alveolar process dimensions after exodontia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 90:581–586
Nevins M, Camelo M, De Paoli S, Friedland B, Schenk RK, Parma-Benfenati S, Simion M, Tinti C, Wagenberg B (2006) A study of the fate of the buccal wall of extraction sockets of teeth with prominent roots. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 26(1):19–29
Crespi R, Cappare P, Gherlone E (2009) Magnesium-enriched hydroxyapatite compared to calcium sulfate in the healing of human extraction sockets: radiographic and histomorphometric evaluation at 3 months. J Periodontol 80:210–218
Pinho MN, Roroz VL, Novaes AB Jr (2006) Titanium membranes in preservation of alveolar collapse after tooth extraction. Implant Dent 15(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.id.0000202596.18254.e1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Please state whether Ethical Approval was given, by whom and the relevant Judgement’s reference number
Yes, ethical approval had been taken from Ethical Committee of Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girish Kumar, N., Chaudhary, R., Kumar, I. et al. To assess the efficacy of socket plug technique using platelet rich fibrin with or without the use of bone substitute in alveolar ridge preservation: a prospective randomised controlled study. Oral Maxillofac Surg 22, 135–142 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-018-0680-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-018-0680-3