Abstract
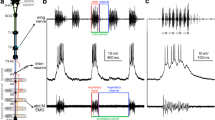
Respiratory abdominal movements during vocalization were measured in awake squirrel monkeys during spontaneous and playback-induced vocal activity. Large vocalization-correlated respiratory movements (VCRM) starting before vocalization were observed during several call types, such as peeping, trilling, cackling and err-chuck. Purring, in contrast, was accompanied by only small VCRM that started late after vocal onset. VCRM during trilling, a call with marked frequency modulation, showed a modulation in the rhythm of the frequency changes. A correlation with amplitude modulation was also present but more variable. As high frequencies need a higher lung pressure for production than low frequencies, the modulation of VCRM seems to serve to optimize the lung pressure in relation to the vocalization frequency. The modulation, furthermore, may act as a mechanism to produce different trill variants. During err-chucks and staccato peeps, which show a large amplitude modulation, a non-modulated VCRM occurred. This indicates the existence of a laryngeal amplitude-controlling mechanism that is independent of respiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Häusler, U. Respiratory movements during vocalization in the squirrel monkey. EBO 1, 1–11 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00898-996-0009-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00898-996-0009-9