Abstract
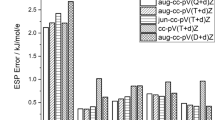
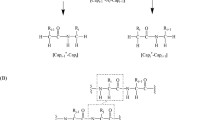
VESPA, an improved semiempirical method for the calculation of electrostatic potential-derived atomic charges has been tested. It is shown that this approach is even less dependent upon molecular orientation than "high density" CHELPG ab initio ESP-derived charges. The conformational dependence of VESPA charges has been investigated for rotation around the C-N bond in formamide and 11 different conformers of glycerolphosphorylcholine. The results obtained are also compared to the corresponding ab initio values. Finally, VESPA is used to calculate electrostatic potential-derived charges for bioorganic molecules. We discuss the abilities and the limitations of ESP charges in this area.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 October 1995/ Accepted: 20 October 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, B., Clark, T. & Glen, R. A Detailed Study of VESPA Electrostatic Potential-Derived Atomic Charges. J Mol Model 1, 176–187 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/s008940050014
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s008940050014