Abstract
Context
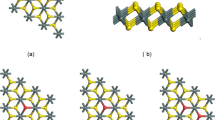
Based on the first principles, the influence of S-atom doping on the electronic and optical properties of stanene is comprehensively examined in this work. The results show that pure stanene is a quasi-metal with zero bandgap. After doping with an S atom, opening the bandgap of pure stanene becomes possible and the state of the stanene is converted from quasi-metal to semiconductor. Analysis of the density of states reveals that the density of states of all doped systems is primarily made of the p-orbital of the Sn. The overlap population analysis showed that charge transfer occurs between S and Sn atoms under different doping concentrations. The charge transfer increases with increasing doping concentration. The charge transfer reaches a maximum at a doping concentration of 9.38%. The increase in doping concentration causes blue-shifting of the absorption and reflection peaks of the doped system as compared to those of pure stanene. It is expected that these studies can provide theoretical guidance for the practical application of stanene in optoelectronic devices.
Methods
All simulations are undertaken with the Cambridge Sequential Total Energy Package (CASTEP) (Wei et al. Physica B: Condensed Matter 545:99, 2018; Bafekry et al. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2021; Zala et al. Appl Surf Sci, 2022; Bafekry et al. Nanotechnology, 2021; Bafekry et al. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2021; Bafekry et al. J Phys: Condens Matter, 2021), which is based on density functional theory (DFT). For the exchange correlation, the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) is implemented with the Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) functional Perdew et al. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 48:4978, 1993. Using the Monkhorst–Pack technique, a specific K-point sample of the Brillouin zone was carried out Monkhorst and Pack Phys Rev B 13:5188, 1976. After the convergence tests, the K-point grid was set to 3 × 3 × 1. The plane-wave truncation energy was set to 400 eV. The residual stress for all atoms was 0.03 eV/Å. The energy convergence criterion was 1.0 × 10−5 eV. To prevent recurring interactions between the layers, a vacuum layer with a thickness of 20 Å was established in the Z-direction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Wei L, Liu G-L, Fan D-Z, Zhang G-Y (2018) Physica B: Condens Matter 545:99
Bafekry A, Faraji M, Fadlallah MM, Hoat DM, Khatibani AB, Sarsari IA, Ghergherehchi M (2021) Effect of adsorption and substitutional B doping at different concentrations on the electronic and magnetic properties of a BeO monolayer: a first-principles study. Phys Chem Chem Phys
Zala VB, Shukla RS, Bafekry A, Gupta SK, Gajjar PN (2022) In silico study of adsorption of oxide gases by MN4 (M = Be, Mg) monolayers. Appl Surf Sci
Bafekry A, Faraji M, Hieu NN, Ang YS, Karbasizadeh S, Abdolhosseini Sarsari I, Ghergherehchi M (2021) Two-dimensional Dirac half-metal in porous carbon nitride C6N7 monolayer via atomic doping. Nanotechnology
Bafekry A, Faraji M, Karbasizadeh S, Khatibani AB, Ziabari AA, Gogova D, Ghergherehchi M (2021) Point defects in two-dimensional BeO monolayer: a first-principles study on electronic and magnetic properties. Phys Chem Chem Phys
Bafekry A, Faraji M, Karbasizadeh S, Jappor HR, Sarsari IA, Ghergherehchi M, Gogova D (2021) Investigation of vacancy defects and substitutional doping in AlSb monolayer with double layer honeycomb structure: a first-principles calculation. J Phys: Condens Matter 34:065701
Perdew JP, Chevary JA, Vosko SH, Jackson KA, Pederson MR, Singh DJ, Fiolhais C (1993) Phys Rev B Condens Matter 48:4978
Monkhorst HJ, Pack JD (1976) Phys Rev B 13:5188
Zhu FF, Chen WJ, Xu Y, Gao CL, Guan DD, Liu CH, Qian D, Zhang SC, Jia JF (2015) Nat Mater 14:1020
Castro Neto AH, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2009) The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys 81:109
Hoi BD, Yarmohammadi M, Mirabbaszadeh K, Habibiyan H (2018) Spin- and valley-dependent electrical conductivity of ferromagnetic group-IV 2D sheets in the topological insulator phase. Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct 97:340
Kumar V, Shukla S, Saxena S (2019) Quantum conductance in edge functionalized stanene nanoribbons: A first-principle study. Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct 114:113595
Chen J, Wang Z, Dai X, Xiao J, Long M, Chen T (2020) The effects of transition metal adatoms on the electronic properties of stanene. Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct 124:114365
Araidai M, Kurosawa M, Ohta A, Shiraishi K (2017)First-principles study on adsorption structure and electronic state of stanene on α-alumina surface. Jpn J Appl Phys 56:095701
Eltinge S, Ismail-Beigi S (2022) Phys Rev Mater 6:014007
Jingjin C, Kexin M, Jianrong X, Liang X, Xueqiong D, Zhiyong W (2022) Results Phys 34:105252
Karimi N, Sardroodi JJ, Rastkar AE (2022) J Mol Model 28:290
Ma K, Chen J, Dai X, Xiao J, Wang L, Xu L, Wang Z (2021) Results Phys 28:104617
Mahmud S, Haque MM, Alam MK (2022) Phys Status Solidi Rapid Res Lett 16:2200106
Mao Y, Long L, Xu C, Yuan J (2018) Mater Res Express 5:065023
Mortazavi B, Rahaman O, Makaremi M, Dianat A, Cuniberti G, Rabczuk T (2017) Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct 87:228
Wang T, Zhao R, Zhao M, Zhao X, An Y, Dai X, Xia C (2017) J Mater Sci 52:5083
Zhao J, Liu G, Wei L, Jiao G, Chen Y, Zhang G (2023) Comput Theor Chem 1225:114142
Bechstedt F, Gori P, Pulci O (2021) Prog Surf Sci 96:100615
Lyu JK, Zhang SF, Zhang CW, Wang PJ (2019) Ann Phys 531:1900017
Wu S-C, Shan G, Yan B (2014) Phys Rev Lett 113:256401
Cherukara MJ, Narayanan B, Kinaci A, Sasikumar K, Gray SK, Chan MK, Sankaranarayanan SK (2016) J Phys Chem Lett 7:3752
Navid IA, Subrina S (2018) RSC Adv 8:31690
Noshin M, Khan AI, Subrina S (2018) Nanotechnology 29:185706
Bachra ME, Zaari H, Benyoussef A, Kenz AE, Hachimi AGE (2017) J Supercond Nov Magn 31:2579
Wang J, Xu Y, Zhang S-C (2014) Phys Rev B 90:054503
Zhao C-X, Jia J-F (2020) Front Phys 15:53201
Yang Y, Zhang H, Song L, Liu Z (2020) Appl Surf Sci 512:145727
Zhang A, Yang H, Liu Q, Li W, Wang Y (2020) Synth Met 266:116441
Zhou J, Liu D, Wu F, Yang L, Xiong Y, Abbasi A (2020) Theor Chem Acc 139:46
He C, Cheng M, Zhang W (2018) Mater Res Express 5:065059
Qingxiao Z, Li W, Weiwei J, Huanyu M, Shiyang Y, Yijia L (2022) Chem Phys Lett 808:140123
Pamungkas MA, Sari VKR, Irwansyah, Putra SA, Abdurrouf, Nurhuda M (2021) Coatings 11:47
Shaidu Y, Akin-Ojo O (2016) Comput Mater Sci 118:11
Abbasi A, Sardroodi JJ (2018) Appl Surf Sci 456:290
Barhoumi M, Sfina N, Lazaar K, Said M (2020) Solid State Commun 321:114016
He J, Liu G, Li X, Wang H, Zhang G (2022) First-principles study of strain on BN-doped arsenene. J Mol Model 28
Ren C-C, Ji W-X, Zhang C-W, Li P, Wang P-J (2016) Mater Res Express 3:105008
Fadaie M, Shahtahmassebi N, Roknabad MR, Gulseren O (2018) Phys Lett A 382:180
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51371049), and the Department of Education Foundation of Liaoning Provincial (Grant No. LQGD2020008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mengting Ma: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Guili Liu: Software, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision. Xuewen Gao: Writing—review &; editing. Guoying Zhang: Writing—review &; editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, M., Liu, G., Gao, X. et al. First-principles study of the effect of S-atom doping on the optoelectronic properties of stanene. J Mol Model 30, 115 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-024-05905-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-024-05905-4