Abstract
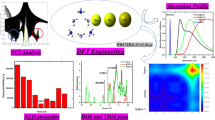
A new complex named HMNd has been basically designed by doping rare-earth neodymium metal inside the hexamine surface HM. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were carried out using B3LYP functional with split basis set GENECP to examine their geometrical, electronic, and non-linear optical properties of newly designed complex HMNd. After getting stable geometry of HMNd, its optoelectronic properties were compared with pure HM surface to check the influence of doping. HMNd revealed the obvious reduction in band gap energies from 8.4 eV (HM) to 1.79 eV (HMNd) as confirmed through DOS analysis. The highest hyperpolarizability and linear isotropic polarizability values of 6.8 × 105 a.u and 262.81 a.u respectively are perceived in HMNd. Electronic and thermodynamic stability of the designed complex has been confirmed through their vertical ionization and interaction energies. As revealed through the UV–visible analysis, doping with neodymium metal (HMNd) shifts the absorption to IR region with λmax of 2699.63 nm which leads towards the production of new materials. These upshots highlight the adequacy of designed complex providing gateway for designing new IR NLO materials in laser frequency conversion technology having usages in versatile fields.
Graphical Abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data will be available if required.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Xue X et al (2018) Photoswitchable nonlinear optical properties of metal complexes. Dalton Trans 47(1):13–22
Mohamed RG et al (2019) Synthesis, characterization, NLO properties, antimicrobial, CT-DNA binding and DFT modeling of Ni (II), Pd (II), Pt (II), Mo (IV) and Ru (I) complexes with NOS Schiff base. J Mol Struct 1176:501–514
Vu TV et al (2018) First-principles DFT calculations of the electronic structure and optical properties of TlInGe2Se6, a prospective NLO material. Mater Chem Phys 219:162–174
Tamer Ö, Avcı D, Atalay Y (2016) Synthesis, X-Ray crystal structure, photophysical characterization and nonlinear optical properties of the unique manganese complex with picolinate and 1, 10 phenantroline: toward the designing of new high NLO response crystal. J Phys Chem Solids 99:124–133
Sivasubramani V et al (2017) Synthesis, crystal growth, physicochemical properties and quantum chemical investigations of a D–π–A type organic single crystal: 2-amino-5-nitropyridinium p-phenolsulfonate (2A5NPP) for nonlinear optical (NLO) applications. CrystEngComm 19(37):5662–5678
Ding S et al (2019) Directly written photo-crosslinked fluorinated polycarbonate photoresist materials for second-order nonlinear optical (NLO) applications. J Mater Chem 7(16):4667–4672
Verbiest T et al (1995) Exceptionally thermally stable polyimides for second-order nonlinear optical applications. Science 268(5217):1604–1606
Dhumane N et al (2008) Influence of glycine on the nonlinear optical (NLO) properties of zinc (tris) thiourea sulfate (ZTS) single crystal. Opt Mater 31(2):328–332
Halasyamani PS, Zhang W (2017) Inorganic materials for UV and deep-UV nonlinear-optical applications. Inorg Chem 56(20):12077–12085
Suresh S, Arivuoli D (2012) Nanomaterials for nonlinear optical (NLO) applications: a review. Rev Adv Mater Sci 30(3):243–253
Panunzi B et al (2019) A new donor-acceptor crosslinkable l-shape chromophore for NLO applications. J Mol Struct 1189:21–27
Kamatchi K et al (2018) Investigation on organic-inorganic hybrid NLO crystal L-valine potassium penta borate octa hydrate (LVPPB) for NLO applications. Optik 172:674–679
Goel S et al (2020) Optical, piezoelectric and mechanical properties of xylenol orange doped ADP single crystals for NLO applications. Arab J Chem 13(1):146–159
Mydlova L et al (2018) Theoretical and experimental investigation of multifunctional highly conjugated organic push-pull ligands for NLO applications. Opt Mater 86:304–310
Mohan B et al (2019) Syntheses, characterizations, crystal structures and efficient NLO applications of new organic compounds bearing 2-methoxy-4-nitrobenzeneamine moiety and copper (II) complex of (E)-N′-(3, 5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzohydrazide. J Mol Struct 1190:54–67
Menezes J et al (2007) Logic gates based in two-and three-modes nonlinear optical fiber couplers. Opt Quant Electron 39(14):1191–1206
Zou G, Ok KM (2020) Novel ultraviolet (UV) nonlinear optical (NLO) materials discovered by chemical substitution-oriented design. Chem Sci 11(21):5404–5409
Muhammad S et al (2017) First principles study for the key electronic, optical and nonlinear optical properties of novel donor-acceptor chalcones. J Mol Graph Model 72:58–69
Liu S et al (2019) Transition metals doped fullerenes: structures–NLO property relationships. Mol Phys 117(6):705–711
Zhu L, Xue K, Hou J (2019) A theoretical study of alkaline-earthides Li (NH3) 4M (M= Be, Mg, Ca) with large first hyperpolarizability. J Mol Model 25(6):1–10
Li X et al (2016) Modification of alkali metals on silicon-based nanoclusters: an enhanced nonlinear optical response. Chem Phys Lett 659:93–99
Irfan A et al (2017) Tuning of optoelectronic and charge transport properties in star shaped anthracenothiophene-pyrimidine derivatives as multifunctional materials. Optik 149:321–331
Irfan A et al (2019) Exploring the effect of electron withdrawing groups on optoelectronic properties of pyrazole derivatives as efficient donor and acceptor materials for photovoltaic devices. Z Phys Chem 233(11):1625–1644
Ullah F et al (2020) Alkaline earth metal decorated phosphide nanoclusters for potential applications as high performance NLO materials; a first principle study. Physica E 118:113906
Iqbal J, Ayub K (2016) Enhanced electronic and non-linear optical properties of alkali metal (Li, Na, K) doped boron nitride nano-cages. J Alloy Compd 687:976–983
Muhammad S (2018) Quantum chemical design of triple hybrid organic, inorganic and organometallic materials: an efficient two-dimensional second-order nonlinear optical material. Mater Chem Phys 220:286–292
Venkatesh G et al (2016) Molecular structure, vibrational spectral assignments (FT-IR and FT-RAMAN), NMR, NBO, HOMO–LUMO and NLO properties of 2-nitroacetophenone based on DFT calculations. J Theor Comput Chem 15(01):1650007
Papadopoulos MG, Sadlej AJ, Leszczynski J (2006) Non-linear optical properties of matter. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–676
Dalton LR, Thomson J, Nalwa HS (1987) The role of extensively delocalized π-electrons in electrical conductivity, nonlinear optical properties and physical properties of polymers. Polymer 28(4):543–552
Meng X et al (2003) Novel Pb and Zn coordination polymers: synthesis, molecular structures, and third-order nonlinear optical properties. Inorg Chem 42(4):1306–1315
Delaire JA, Nakatani K (2000) Linear and nonlinear optical properties of photochromic molecules and materials. Chem Rev 100(5):1817–1846
Sun W-M et al (2015) A theoretical study on novel alkaline earth-based excess electron compounds: unique alkalides with considerable nonlinear optical responses. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(6):4524–4532
Shehzad RA et al (2021) Enhanced linear and nonlinear optical response of superhalogen (Al7) doped graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4). Optik 226:165923
Muhammad S et al (2012) Halide ion complexes of decaborane (B10H14) and their derivatives: noncovalent charge transfer effect on second-order nonlinear optical properties. J Phys Chem A 116(5):1417–1424
Muhammad S et al (2009) A theoretical investigation of intermolecular interaction of a phthalimide based “on–off” sensor with different halide ions: tuning its efficiency and electro-optical properties. Theoret Chem Acc 122(1):77–86
Muhammad S, Janjua MRSA, Su Z (2009) Investigation of dibenzoboroles having π-electrons: toward a new type of two-dimensional NLO molecular switch? J Phys Chem 113(28):12551–12557
Fonseca Guerra C et al (2004) Voronoi deformation density (VDD) charges: assessment of the Mulliken, Bader, Hirshfeld, Weinhold, and VDD methods for charge analysis. J Comput Chem 25(2):189–210
Asif A, Maqsood N, Tamam N, Ayub K, Ans M, Iqbal J, ..., Alrowaili ZA (2022) DFT study of transition metals doped calix-4-pyrrole with excellent electronic and non-linear optical properties. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 1214:113767
Ans M et al (2020) Designing alkoxy-induced based high performance near infrared sensitive small molecule acceptors for organic solar cells. J Mol Liq 305:112829
Arshad MN et al (2022) Donor moieties with D–π–a framing modulated electronic and nonlinear optical properties for non-fullerene-based chromophores. RSC Adv 12(7):4209–4223
Ahmed S, Kalita DJ (2020) End-capped group manipulation of non-fullerene acceptors for efficient organic photovoltaic solar cells: a DFT study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22(41):23586–23596
Hachi M et al (2020) New small organic molecules based on thieno [2, 3-b] indole for efficient bulk heterojunction organic solar cells: a computational study. Mol Phys 118(8):e1662956
Zahid S et al (2021) Quantum chemical approach of donor− π–acceptor based arylborane–arylamine macrocycles with outstanding photovoltaic properties toward high-performance organic solar cells. Energy Fuels 35(18):15018–15032
Johnson ER et al (2010) Revealing noncovalent interactions. J Am Chem Soc 132(18):6498–6506
Contreras-García J et al (2011) NCIPLOT: a program for plotting noncovalent interaction regions. J Chem Theory Comput 7(3):625–632
Funding
Funding acquisition from the University of Agriculture Faisalabad (UAF), Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed efficiently and dedicatedly to this manuscript and their credit to this manuscript is summarized as follows.
Shanza Hameed, Investigation; formal analysis; validation; visualization; writing—original draft
Shehla Gul, Visualization; data curation; validation; writing—review & editing.
Muhammad Ans, Supervision; resources; software; interpretation of data; visualization; data curation; validation; revision; writing—review & editing.
Ijaz Ahmed Bhatti, Revision; visualization; data curation; validation; writing—review & editing.
Khurshid Ayub, Visualization; data curation; validation; writing—review & editing.
Javed Iqbal, Supervision; resources; software; interpretation of data; visualization; data curation; validation; revision; writing—review & editing.
Rasheed Ahmad Khera, Methodology; supervision; resources; software; interpretation of data; visualization; data curation; validation; writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We approved all ethics.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hameed, S., Gul, S., Ans, M. et al. Designing neodymium-doped hexamine complexant as novel IR NLO material with extremely large non-linear optical behavior. J Mol Model 28, 381 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05364-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05364-9