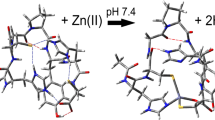
Abstract
Understanding the role that metal ions play in biological and material processes is critical to addressing a number of diseases and problems facing society today. There have been a number of studies that have begun to approach this concern from a myriad of different perspectives. However, there is still a considerable lack of understanding concerning the mechanisms and structures of metal-related problems, specifically biological and medical-related issues. Understanding the mechanism of ingestion and uptake of metals into the human body is critical to addressing many diseases such as Alzheimer’s and certain types of cancers. Using computational techniques, this work adds to the overall understanding of metal interactions with proteins by focusing on metal ion interactions with the amino acid, histidine, one of the most common sites of metal attachment. In this work, the geometries of single and dual histidines attached to Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ ions at B3LYP/6-311G(d) are presented. The results show stable octahedral complexes associated with each of the metal ions. Free energy calculations suggest that all three complexes are spontaneous in the formation of the dual histidine-metal complexes. Nickel and copper are spontaneous in the formation of the single histidine complex, although the copper complex undergoes slight geometric changes. Zinc is found to be nonspontaneous in forming the single histidine complex. Finally, the reduction potential of the single histidine-metal complex is presented. All of the complexes show positive reduction potentials. However, the nickel and copper complexes undergo geometrical changes to adopt a square planar conformation.

The impact of metal ions in biological systems is of great importance to understanding a diverse number of diseases. By understanding the fundamentals of select ions complexed with histidines, greater understanding of the mechanisms of actions these ions play in health may be elucidated. This work presents initial structures and thermodynamics of histidine complexes with nickel, copper, and zinc metal ions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farkas E, Sovago I Metal complexes of amino acids and peptides. In: Ryadnov M, Hudecz F (eds) Amino acids, peptides and proteins, vol 412017, pp 100–151
Belal AAM, El-Deen IM, Farid NY, Zakaria R, Refat MS (2015) Synthesis, spectroscopic, coordination and biological activities of some transition metal complexes containing ONO tridentate Schiff base ligand. Spectrochim Acta A 149:771–787
Bieske EJ, Dopfer O (2000) High-resolution spectroscopy of cluster ions. Chem Rev 100:3963–3998
Care A, Bergquist PL, Sunna A (2015) Solid-binding peptides: smart tools for nanobiotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 33:259–268
Hashimoto Y, Yoshinari N, Matsushita N, Konno T (2014) Close correlation between metal oxidation states and molecular structures in a cobalt-gold multinuclear coordination system with mixed D-penicillaminate and tripodal triphosphine. Eur J Inorg Chem:3474–3478
Abdel-Rahman LH, El-Khatib RM, Nassr LAE, Abu-Dief AM, Ismael M, Seleem AA (2014) Metal based pharmacologically active agents: synthesis, structural characterization, molecular modeling, CT-DNA binding studies and in vitro antimicrobial screening of iron (II) bromosalicylidene amino acid chelates. Spectrochim Acta A 117:366–378
Gutierrez A, Gracia-Fleta L, Marzo I, Cativiela C, Laguna A, Gimeno MC (2014) Gold(I) thiolates containing amino acid moieties. Cytotoxicity and structure-activity relationship studies. Dalton Trans 43:17054–17066
Moustafa EM, Korany M, Mohamed NA, Shoeib T (2014) Carnosine complexes and binding energies to some biologically relevant metals and platinum containing anticancer drugs. Inorg Chim Acta 421:123–135
Guo CX, Li P, Pei MS, Zhang GY (2015) A new polythiophene derivative-based fluorescent sensor for Co2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and its complex with Cu2+ for sensing homocysteine and glutathione. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:1223–1228
Arun TR, Raman N (2014) Antimicrobial efficacy of phenanthrenequinone based Schiff base complexes incorporating methionine amino acid: structural elucidation and in vitro bio assay. Spectrochim Acta A 127:292–302
Ding XZ, Hua YF, Chen YM, Zhang CM, Kong XZ (2015) Heavy metal complexation of thiol-containing peptides from soy glycinin hydrolysates. Int J Mol Sci 16:8040–8058
Ghosh C, Seal M, Mukherjee S, Dey SG (2015) Alzheimer’s disease: a heme-A beta perspective. Acc Chem Res 48:2556–2564
Grasso G, Bonnet S (2014) Metal complexes and metalloproteases: targeting conformational diseases. Metallomics 6:1346–1357
Hussien MA, Nawar N, Radwan FM, Hosny NM (2015) Spectral characterization, optical band gap calculations and DNA binding of some binuclear Schiff-base metal complexes derived from 2-amino-ethanoic acid and acetylacetone. J Mol Struct 1080:162–168
Ali-Torres J, Mirats A, Marechal JD, Rodriguez-Santiago L, Sodupe M (2014) 3D structures and redox potentials of Cu2+-A beta(1-16) complexes at different pH: a computational study. J Phys Chem B 118:4840–4850
Breivogel A, Kreitner C, Heinze K (2014) Redox and photochemistry of bis (terpyridine) ruthenium (II) amino acids and their amide conjugates-from understanding to applications. Eur J Inorg Chem:5468–5490
Gao YP, Wang YY, Liu WX (2015) Redox activity of the mini-alpha A-crystallin-Cu (II) complex and its biological relevance. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:6302–6311
Kepp KP (2012) Bioinorganic chemistry of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Rev 112:5193–5239
Chen WT, Liao YH, Yu HM, Cheng IH, Chen YR (2011) Distinct effects of Zn2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Al3+ on amyloid-beta stability, oligomerization, and aggregation. J Biol Chem 286:9646–9656
Bush AI, Pettingell WH, Multhaup G, Paradis MD, Vonsattel JP, Gusella JF, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Tanzi RE (1994) Rapid induction of Alzheimer A-beta amyloid formation by zinc. Science 265:1464–1467
Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2006) A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 314:777–781
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) Medicine-the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Grenacs A, Sanna D, Sovago I (2015) Copper (II) and nickel (II) binding sites of peptide containing adjacent histidyl residues. J Inorg Biochem 151:87–93
Guilloreau L, Damian L, Coppel Y, Mazarguil H, Winterhalter M, Faller P (2006) Structural and thermodynamical properties of Cu-II amyloid-beta 16/28 complexes associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Inorg Chem 11:1024–1038
Mantyh PW, Ghilardi JR, Rogers S, Demaster E, Allen CJ, Stimson ER, Maggio JE (1993) Aluminum, iron, and zinc ions promote aggregation of physiological concentrations of beta-amyloid peptide. J Neurochem 61:1171–1174
Nunomura A, Perry G, Aliev G, Hirai K, Takeda A, Balraj EK, Jones PK, Ghanbari H, Wataya T, Shimohama S, Chiba S, Atwood CS, Petersen RB, Smith MA (2001) Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:759–767
Huang XD, Atwood CS, Hartshorn MA, Multhaup G, Goldstein LE, Scarpa RC, Cuajungco MP, Gray DN, Lim J, Moir RD, Tanzi RE, Bush AI (1999) The A beta peptide of Alzheimer’s disease directly produces hydrogen peroxide through metal ion reduction. Biochemistry 38:7609–7616
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82:4245–4249
Kong XT, Zhao Z, Lei X, Zhang BB, Dai DX, Jiang L (2015) Interaction of metal ions with the His13-His14 sequence relevant to Alzheimer’s disease. J Phys Chem A 119:3528–3534
Pushie MJ, Nienaber KH, McDonald A, Millhauser GL, George GN (2014) Combined EXAFS and DFT structure calculations provide structural insights into the 1:1 multi-histidine complexes of Cu-II, Cu-I, and Zn-II with the tandem octarepeats of the mammalian prion protein. Chem Eur J 20:9770–9783
Han GC, Ferranco A, Feng XZ, Chen ZC, Kraatz HB (2014) Synthesis, characterization of some ferrocenoyl cysteine and histidine conjugates, and their interactions with some metal ions. Eur J Inorg Chem:5337–5347
Potocki S, Valensin D, Kozlowski H (2014) The specificity of interaction of Zn2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ ions with the histidine-rich domain of the TjZNT1 ZIP family transporter. Dalton Trans 43:10215–10223
Umadevi P, Senthilkumar L (2014) Influence of metal ions (Zn2+, Cu2+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Na+) on the water coordinated neutral and zwitterionic L-histidine dimer. RSC Adv 4:49040–49052
Gorboletova GG, Metlin AA (2014) Thermodynamics of the formation of nickel (II) complexes with L-histidine in aqueous solutions. Russ J Phys Chem A 88:1514–1518
Chen LT, Liu T, Ma C (2010) Metal complexation and biodegradation of EDTA and S,S-EDDS: a density functional theory study. J Phys Chem A 114:443–454
Sillanpaa AJ, Aksela R, Laasonen K (2003) Density functional complexation study of metal ions with (amino) polycarboxylic acid ligands. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5:3382–3393
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Li X, Caricato M, Marenich AV, Bloino J, Janesko BG, Gomperts R, Mennucci B, Hratchian HP, Ortiz JV, Izmaylov AF, Sonnenberg JL, Williams FD, Lipparini F, Egidi F, Goings J, Peng B, Petrone A, Henderson T, Ranasinghe D, Zakrzewski VG, Gao J, Rega N, Zheng G, Liang W, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Throssell K, Montgomery Jr JA, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark MJ, Heyd JJ, Brothers EN, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith TA, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell AP, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Millam JM, Klene M, Adamo C, Cammi R, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Fox DJ (2016) Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01, Wallingford, CT
Becke AD (1993) Density-functional thermochemistry. 3. The role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys 98:5648–5652
Lee CT, Yang WT, Parr RG (1988) Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B 37:785–789
Roy Dennington TAK, Millam JM (2016) GaussView, version 6.1. Semichem Inc., Shawnee Mission, KS
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J Phys Chem B 113:6378–6396
Funding
The authors wish to recognize the support of the National Science Foundation HRD 1547754 and DMR 1826886.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franklin, L.M., Walker, S.M. & Hill, G. A DFT study of isolated histidine interactions with metal ions (Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+) in a six-coordinated octahedral complex. J Mol Model 26, 116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-04389-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-04389-2