Abstract
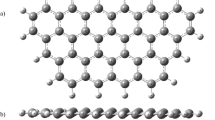
In this work, the influence of competitive adsorption and the change of charge transfer for simultaneous adsorption removal of SO2, NO, and Hg0 over graphene were investigated using density functional theory method. The results showed that all the adsorptive effect of SO2, NO, and Hg0 were caused by physical interaction. The adsorptive energy of SO2 was the highest, and the adsorptive energy of Hg0 was the lowest. SO2 could be preferentially adsorbed and removed. NO/SO2 and Hg0 had the mutual promotion effect for simultaneous adsorption over graphene surface. SO2 and NO had the mutual inhibition effect for simultaneous adsorption over graphene surface. Compared with single molecular adsorption, the adsorption type of bi-molecular adsorption did not change. However, the simultaneous adsorption changed the adsorption type of Hg0 + SO2 + NO to chemical adsorption due to the interaction among Hg0, SO2, and NO. As such, this study provides a theoretical insight for future application and development.

NO/SO2 and Hg0 had the mutual promotion effect for simultaneous adsorption. SO2 and NO had the mutual inhibition effect for simultaneous adsorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang S, Wang D, Liu H, Liu C, Xie X, Xu Z, Liu Z (2019) Highly stable activated carbon composite material to selectively capture gas-phase elemental mercury from smelting flue gas: copper polysulfide modification. Chem. Eng. J. 358:1235–1242
Quan Z, Huang W, Liao Y, Liu W, Xu H, Yan N, Qu Z (2019) Study on the regenerable sulfur-resistant sorbent for mercury removal from nonferrous metal smelting flue gas. Fuel 241:451–458
Liu W, Xu H, Liao Y, Quan Z, Li S, Zhao S, Qu Z, Yan N (2019) Recyclable CuS sorbent with large mercury adsorption capacity in the presence of SO2 from non-ferrous metal smelting flue gas. Fuel 235:847–854
Sun Y, Ren S, Hou Y, Zhang K, Wu W (2018) Absorption of nitric oxide in simulated flue gas by a metallic functional ionic liquid. Fuel Process. Technol. 178:7–12
Díaz-de-Mera Y, Aranda A, Martínez E, Rodríguez AA, Rodríguez D, Rodríguez A (2017) Formation of secondary aerosols from the ozonolysis of styrene: effect of SO2 and H2O. Atmos. Environ. 171:25–31
Nava Núñez MY, Martínez-de la Cruz A (2018) Nitric oxide removal by action of ZnO photocatalyst hydrothermally synthesized in presence of EDTA. Mat Sci Semicon Proc 81:94–101
He F, Deng X, Chen M (2017) Nitric oxide removal by combined urea and FeIIEDTA reaction systems. Chemosphere 168:623–629
Zhou J, Cao L, Wang Q, Tariq M, Xue Y, Zhou Z, Sun W, Yang J (2019) Enhanced Hg0 removal via α-MnO2 anchored to MIL-96(Al). Appl. Surf. Sci. 483:252–259
Liu Z, Adewuyi YG, Shi S, Chen H, Li Y, Liu D, Liu Y (2019) Removal of gaseous Hg0 using novel seaweed biomass-based activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 366:41–49
Yu X, Hao J, Xi Z, Liu T, Lin Y, Xu B (2019) Investigation of low concentration SO2 adsorption performance on different amine-modified Merrifield resins. Atmos Pollut Res 10:404–411
Chinh ND, Hien TT, Do Van L, Hieu NM, Quang ND, Lee SM, Kim C, Kim D (2019) Adsorption/desorption kinetics of nitric oxide on zinc oxide nano film sensor enhanced by light irradiation and gold-nanoparticles decoration. Sensors Actuat B 281:262–272
Luo J, Niu Q, Jin M, Cao Y, Ye L, Du R (2019) Study on the effects of oxygen-containing functional groups on Hg0 adsorption in simulated flue gas by XAFS and XPS analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 376:21–28
Yang Y, Xu W, Wang J, Zhu T (2019) New insight into simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 on CeO2-modified V2O5/TiO2 catalyst: a new modification strategy. Fuel 249:178–187
Fang Z, Yu X, Tu ST (2019) Catalytic oxidation of NO on activated carbons. Energy Procedia 158:2366–2371
Qing M, Su S, Wang L, Liu L, Xu K, He L, Jun X, Hu S, Wang Y, Xiang J (2019) Getting insight into the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts: reaction mechanism and effects of NO and NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 361:1215–1224
Yang Y, Liu J, Liu F, Wang Z, Ding J, Huang H (2019) Reaction mechanism for NH3-SCR of NOx over CuMn2O4 catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 361:578–587
Chen L, Wang X, Cong Q, Ma H, Li S, Li W (2019) Design of a hierarchical Fe-ZSM-5@CeO2 catalyst and the enhanced performances for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 369:957–967
Kwon DW, Kim J, Ha HP (2019) Establishment of surface/bulk-like species functionalization by controlling the sulfation temperature of Sb/V/Ce/Ti for NH3-SCR. Appl. Surf. Sci. 481:1503–1514
Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Yin Y, Pan J, Zhang J, Wang Q (2018) Simultaneous absorption of SO2 and NO from flue gas using ultrasound/Fe2+/heat coactivated persulfate system. J. Hazard. Mater. 342:326–334
Wu Q, Sun C, Wang H, Wang T, Wang Y, Wu Z (2018) The role and mechanism of triethanolamine in simultaneous absorption of NOx and SO2 by magnesia slurry combined with ozone gas-phase oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 341:157–163
Hao R, Mao Y, Mao X, Wang Z, Gong Y, Zhang Z, Zhao Y (2019) Cooperative removal of SO2 and NO by using a method of UV-heat/H2O2 oxidation combined with NH4OH-(NH4)2SO3 dual-area absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 365:282–290
Wang H, You C (2018) Photocatalytic oxidation of SO2 on TiO2 and the catalyst deactivation: a kinetic study. Chem. Eng. J. 350:268–277
Wang H, You C, Tan Z (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of SO2 on TiO2 surface by Na2CO3 modification. Chem. Eng. J. 350:89–99
Zhang AC, Zhang ZH, Shi JM, Chen GY, Zhou CS, Sun LS (2015) Effect of preparation methods on the performance of MnOx-TiO2 adsorbents for Hg0 removal and SO2 resistance. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 43:1258–1266
Gao L, Li C, Li S, Zhang W, Du X, Huang L, Zhu Y, Zhai Y, Zeng G (2019) Superior performance and resistance to SO2 and H2O over CoOx-modified MnOx/biomass activated carbons for simultaneous Hg0 and NO removal. Chem. Eng. J. 371:781–795
Chiu CH, Kuo TH, Chang TC, Lin SF, Lin HP, Hsi HC (2017) Multipollutant removal of Hg0/SO2/NO from simulated coal-combustion flue gases using metal oxide/mesoporous SiO2 composites. Int. J. Coal Geol. 170:60–68
Li B, Ma C (2018) Study on the mechanism of SO2 removal by activated carbon. Energy Procedia 153:471–477
Wang Z, Jin H, Wang K, Xie Y, Ning J, Tu Y, Chen Y, Liu H, Zeng H (2019) A two-step method for the integrated removal of HCl, SO2 and NO at low temperature using viscose-based activated carbon fibers modified by nitric acid. Fuel 239:272–281
Delley B (1990) An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 92:508–517
Song X, Ning P, Li K, Sun X, Wang C, Sun L (2018) Hydrogen transfer effect and reaction mechanism for catalytic hydrolysis of HCN in ionic liquids: a density functional theory study. Chem. Eng. J. 348:630–636
Song X, Ning P, Wang C, Li K, Tang L, Sun X (2017) Catalytic hydrolysis of COS over CeO2 (110) surface: a density functional theory study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 414:345–352
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77:3865–3868
Delley B (2000) From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J. Chem. Phys. 113:7756–7764
Song X, Wang C, Gasem KAM, Li K, Sun X, Ning P, Gong W, Wang T, Fan M, Sun L (2019) New insight into the reaction mechanism of carbon disulfide hydrolysis and the impact of H2S with density functional modeling. New J. Chem. 43:2347–2352
Li K, Song X, Zhu T, Wang C, Sun X, Ning P, Tang L (2018) Mechanistic and kinetic study on the catalytic hydrolysis of COS in small clusters of sulfuric acid. Environ. Pollut. 232:615–623
Song X, Sun L, Ning P, Wang C, Sun X, Li K, Fan M (2019) Catalytic synthesis of non-carbon fuel NH3 from easily available N2 and H2O over FeO(100) surface: study of reaction mechanism using the density functional theory. New J. Chem. 43:10066–10072
Song X, Sun L, Guo H, Li K, Sun X, Wang C, Ning P (2019) Experimental and theoretical studies on the influence of carrier gas for COS catalytic hydrolysis over MgAlCe composite oxides. ACS Omega 4:7122–7127
Ning P, Song X, Li K, Wang C, Tang L, Sun X (2017) Catalytic hydrolysis of carbonyl sulphide and carbon disulphide over Fe2O3 cluster: competitive adsorption and reaction mechanism. Sci. Rep. 7:14452
Cottrell TL (1958) The strengths of chemical bondssecond edn. Butterworths Scientific Publications, London
U.S. Dept. of Commerce (1970) National standard reference data series. National Bureau of Standards, Washington
Abbasi A, Sardroodi JJ (2019) Adsorption of O3, SO2 and SO3 gas molecules on MoS2 monolayers: a computational investigation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 469:781–791
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51568067, 21667015, 41807373 and 51708266), Applied Basic Research Fund Project of Yunnan Province (2016FB100), National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0213400) and the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Li, K., Ning, P. et al. Theoretical study on simultaneous removal of SO2, NO, and Hg0 over graphene: competitive adsorption and adsorption type change. J Mol Model 25, 364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-019-4254-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-019-4254-6