Abstract
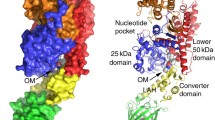
Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA (NMMHC IIA, gene code: MYH9) plays a critical role in physiological and pathological functions. A homology model of NMMHC IIA was constructed based on the crystal structure of smooth muscle myosin II. Blebbistatin, a myosin II ATPase inhibitor, had been found to bind to NMMHC IIA with Leu228 as the important amino acid residue and van der Waals contacts as the main force of the interaction. The final complex demonstrated that the destruction of the salt bridge occurred between the Arg204 and Glu427 residues when blebbistatin was present. Molecular dynamic simulation of the complex showed that the binding affinity of blebbistatin to NMMHC IIA was strongly sensitive to the nucleotide binding region and actin binding region. The disturbance of the two regions increased the enhancement of the binding cavity with blebbistatin and resulted in a slightly more expanded conformation in the nucleotide binding region and actin binding region. A combined pharmacophore- and docking-based virtual screening was performed to identify several saponins as potential inhibitors for NMMHC IIA. These findings introduce new insights on the binding mode of blebbistatin and NMMHC IIA and novel leading compounds from natural products for NMMHC IIA-related diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song JX, Kou JP, Yu BY (2009) Recent advances of NMHCIIA in physiological and pathological functions. Prog Mod Biomed 9:3964–3979. doi:cnki:sun:swcx.0.2009-20-050
Clark K, Middelbeek J, Dorovkov MV, Figdor CG, Ryazanov AG, Lasonder E, van Leeuwen FN (2008) The alpha-kinases TRPM6 and TRPM7, but not eEF-2 kinase, phosphorylate the assembly domain of myosinIIA, IIB and IIC. FEBS Lett 582:2993–2997. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.07.043
Manzanares MV, Ma XF, Adelstein RS, Horwitz AR (2009) Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:778–790. doi:10.1038/nrm2786
Conti MA, Even-Ram S, Liu C, Yamada KM, Adelstein RS (2004) Defects in cell adhesion and the visceral endoderm following ablation of nonmuscle myosin heavy chain II-A in mice. J Biol Chem 279:41263–41266. doi:10.1074/jbc.C400352200
Leon C, Eckly A, Hechler B, Aleil B, Freund M, Ravanat C, Jourdain M, Nonne C, Weber J, Tiedt R, Gratacap MP, Severin S, Cazenave JP, Lanza F, Skoda R, Gachet C (2007) Megakaryocyte-restricted MYH9 inactivation dramatically affects hemostasis while preserving platelet aggregation and secretion. Blood 110:3183–3191. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-080184
Arii J, Goto H, Suenaga T, Oyama M, Kozuka-Hata H, Imai T, Minowa A, Akashi H, Arase H, Kawaoka Y, Kawaguchi Y (2010) Non-muscle myosin IIA is a functional entry receptor for herpes simplex virus-1. Nature 467:859–864. doi:10.1038/nature09420
Liang SL, He LJ, Zhao XD, Miao Y, Gu Y, Guo CC, Xue ZF, Dou WJ, Hu FR, Wu KC, Nie YZ, Fan DM (2011) MicroRNA let-7f inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting MYH9 in human gastric cancer. PLoS One 6:e18409. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018409
Wrighton KH (2011) Autophagy: myosin II moves in on autophagosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:77. doi:10.1038/nrm3053
Yu BY, Kou JP, Huang YL, Jiang WW, Liu JH, A target of control inflammation associated with cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases and its inhibitor drug target. China patent authorization ZL 200710024810
Duxbury MS, Ashley SW, Whang EE (2004) Inhibition of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cellular invasiveness by blebbistatin: a novel myosin II inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:992–997. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.12.031
Kovacs M, Toth J, Hetenyi C, Malnasi-Csizmadia A, Sellers JR (2004) Mechanism of blebbistatin inhibition of myosin II. J Biol Chem 279:35557–35563. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405319200
Gu BJ, Rathsam C, Stokes L, McGeachie AB, Wiley JS (2009) Extracellular ATP dissociates nonmuscle myosin from P2X7 complex: this dissociation regulates P2X7 pore formation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:430–439. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00079.2009
Gu BJ, Saunders BM, Jursik C, Wiley JS (2010) The P2X7-nonmuscle myosin membrane complex regulates phagocytosis of nonopsonized particles and bacteria by a pathway attenuated by extracellular ATP. Blood 115:1621–1631. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-11-251744
Jacobelli J, Chmura SA, Buxton DB, Davis MM, Krummel MF (2004) A single class II myosin modulates T cell motility and stopping, but not synapse formation. Nat Immunol 5:531–538. doi:10.1038/ni1065
Jacobelli J, Bennett FC, Pandurangi P, Tooley AJ, Krummel MF (2009) Myosin-IIA and ICAM-1 regulate the interchange between two distinct modes of T cell migration. J Immunol 182:2041–2050. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803267
Dou Y, Arlock P, Arner A (2007) Blebbistatin specifically inhibits actin-myosin interaction in mouse cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:1148–1153. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00551.2006
Allingham JS, Smith R, Rayment I (2005) The structural basis of blebbistatin inhibition and specificity for myosin II. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:378–379. doi:10.1038/nsmb908
Nicola G, Smith CA, Lucumi E, Kuo MR, Karagyozov L, Fidock DA, Sacchettini JC, Abagyan R (2007) Discovery of novel inhibitors targeting enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase in plasmodium falciparum by structure based virtual screening. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358:686–691. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.113
Koppole S, Smith JC, Fischer S (2006) Simulations of the myosin II motor reveal a nucleotide-state sensing element that controls the recovery stroke. J Mol Biol 361:604–616. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.022
Woo HJ (2007) Exploration of the conformational space of myosin recovery stroke via molecular dynamics. Biophys Chem 125:127–137. doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2006.07.001
Yamanaka K, Okimoto N, Neya S, Hata M, Hoshino T (2006) Behavior of water molecules in ATPase pocket of myosin. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 758:97–105. doi:10.1016/j.theochem.2005.10.019
Kawakubo T, Okada O, Minami T (2005) Molecular dynamics simulations of evolved collective motions of atoms in the myosin motor domain upon perturbation of the ATPase pocket. Biophys Chem 115:77–85. doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2004.12.049
Alamo L, Wriggers W, Pinto A, Bartoli F, Salazar L, Zhao FQ, Craig R, Padron R (2008) Three-dimensional reconstruction of tarantula myosin filaments suggests how phosphorylation may regulate myosin activity. J Mol Biol 384:780–797. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.013
Zoghbi ME, Woodhead JL, Moss RL, Craig R (2008) Three-dimensional structure of vertebrate cardiac muscle myosin filaments. PNAS 105:2386–2390
Onishi H, Ohki N, Morales MF (2004) On the myosin catalysis of ATP hydrolysis. Biochemistry 43:3757–3763. doi:10.1006/jsbi.1999.4207
Smith CA, Rayment I (1996) X-ray structure of the magnesium(II) · ADP · Vanadate complex of the Dictyostelium discoideum myosin motor domain to 1.9 Å resolution. Biochemistry 35:5404–5417. doi:10.1021/bi00028a005
Tang S, Liao JC, Dunn AR, Altman RB, Spudich JA, Schmidt JP (2007) Predicting allosteric communication in myosin via a pathway of conserved residues. J Mol Biol 373:1361–1373. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.059
Kawakubo T, Okada O, Minami T (2009) Dynamic conformational changes due to the ATP hydrolysis in the motor domain of myosin:10-ns molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys Chem 141:75–86. doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2008.12.014
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of this work from the laboratory of molecular design and drug discovery, China pharmaceutical university, and helpful discussions with Dr. Yadong Chen. The present research was supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (No. 2006BAI08B05-08), the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 90713042), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-07-849), a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, the Project Program of the State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, China Pharmaceutical University (No. JKGZ201107), and graduate student scientific research innovation plan of jiangsu higher education institutions (CXZZ11_0795).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1838 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Lu, S., Lu, T. et al. Homology model of nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA and binding mode analysis with its inhibitor blebbistatin. J Mol Model 19, 1801–1810 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1750-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1750-3