Abstract
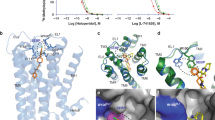
Interest in structure-based G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) ligand discovery is huge, given that almost 30 % of all approved drugs belong to this category of active compounds. The GPCR family includes the dopamine receptor subtype D2 (D2DR), but unfortunately—as is true of most GPCRs—no experimental structures are available for these receptors. In this publication, we present the molecular model of D2DR based on the previously published crystal structure of the dopamine D3 receptor (D3DR). A molecular modeling study using homology modeling and docking simulation provided a rational explanation for the behavior of the arylpiperazine ligand. The observed binding modes and receptor–ligand interactions provided us with fresh clues about how to optimize selectivity for D2DR receptors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D2DR:
-
Dopamine receptor type 2
- ecl:
-
Extracellular loop
- etf:
-
Edge-to-face
- D3DR:
-
Dopamine receptor type 3
References
Carlsson J, Coleman RG, Setola V, Irwin JJ, Fan H, Schlessinger A, Sali A, Roth BL, Shoichet BK (2011) Ligand discovery from a dopamine D3 receptor homology model and crystal structure. Nat Chem Biol 7(11):769–778
Filizola M, Devi LA (2012) Structural biology: how opioid drugs bind to receptors. Nature 485(7398):314–317
Chien EY, Liu W, Zhao Q, Katritch V, Han GW, Hanson MA, Shi L, Newman AH, Javitch JA, Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2010) Structure of the human dopamine D3 receptor in complex with a D2/D3 selective antagonist. Science 330:1091–1095
Sukalovic V, Ignjatovic D, Tovilovic G, Andric D, Shakib K, Kostic-Rajacic S, Soskic V (2012) Interactions of N- {[2-(4-phenyl-piperazin-1-yl)-ethyl]-phenyl}-2-aryl-2-yl-acetamides and 1- {[2-(4-phenyl-piperazin-1-yl)-ethyl]-phenyl}-3-aryl-2-yl-ureas with dopamine D2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine 5HT(1A) receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(12):3967–3972
Newman AH, Beuming T, Banala AK, Donthamsetti P, Pongetti K, Labounty A, Levy B, Cao J, Michino M, Luedtke RR, Javitch JA, Shi L (2012) Molecular determinants of selectivity and efficacy at the dopamine D3 receptor. J Med Chem 55(15):6689–6699
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2012) The National Center for Biotechnology Information advances science and health database. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein. Accessed 27 Dec 2012
Van Munster BC, de Rooij SE, Yazdanpanah M, Tienari PJ, Pitkala KH, Osse RJ, Adamis D, Smit O, van der Steen MS, van Houten M, Rahkonen T, Sulkava R, Laurila JV, Strandberg TE, Tulen JH, Zwang L, MacDonald AJ, Treloar A, Sijbrands EJ, Zwinderman AH, Korevaar JC (2010) The association of the dopamine transporter gene and the dopamine receptor 2 gene with delirium, a meta-analysis. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 153B(2):648–655
Accelrys Software Inc. (2009) Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, release 2.5. Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego
Teeter MM, Froimowitz M, Stec B, DuRand CJ (1994) Homology modeling of the dopamine D2 receptor and its testing by docking of agonists and tricyclic antagonists. J Med Chem 37(18):2874–2888
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD—visual molecular dynamics. J Molec Graph 14:33
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Montgomery JA Jr, Vreven T, Kudin KN, Burant JC, Millam JM, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B, Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox JE, Hratchian HP, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Strain MC, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Gonzalez C, Pople JA (2004) Gaussian 03, revision E.01. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford
Vanommeslaeghe K, Hatcher E, Acharya C, Kundu S, Zhong S, Shim J, Darian E, Guvench O, Lopes P, Vorobyov I, MacKerell AD Jr (2010) CHARMM general force field: a force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force field. J Comput Chem 31:671–690
Phillips JC, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J, Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel RD, Kale L, Schulten K (2005) Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem 26:1781–1802
PARADOX cluster at the Scientific Computing Laboratory of the Institute of Physics Belgrade http://www.scl.rs/. Accessed 27 Dec 2012
European Bioinformatics Institute https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembldb/target/results/1/compounds/desc/tab/classification. Accessed 27 Dec 2012
Javitch JA (1998) Mapping the binding-site crevice of the D2 receptor. Adv Pharmacol 42:412–415
Javitch JA, Fu D, Chen J, Karlin A (1995) Mapping the binding-site crevice of the dopamine D2 receptor by the substituted-cysteine accessibility method. Neuron 14(4):825–831
Schrödinger, LLC (2011) Glide, version 5.7. Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Javitch JA, Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H, Chen J (1998) A cluster of aromatic residues in the sixth membrane-spanning segment of the dopamine D2 receptor is accessible in the binding-site crevice. Biochemistry 37(4):998–1006
Accelrys Software Inc. (2009) Discovery Studio Modeling environment, release 2.5: Discovery Studio Visualiser 2.5.1. Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego
Persistence of Vision Raytracer Ltd. (2003–2007) Persistence of Vision Raytracer (POV-Ray). http://www.povray.org/
Shi L, Javitch JA (2004) The second extracellular loop of the dopamine D2 receptor lines the binding-site crevice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(2):440–445
Sukalovic V, Zlatovic M, Andric D, Roglic G, Kostic-Rajaccic S, Soskic V (2004) Modeling of the D2 dopamine receptor arylpiperazine binding site for 1-[2-[5-(1H-benzimidazole-2-thione)]ethyl]-4-arylpiperazines. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 337(9):502–512
Sukalovic V, Zlatovic M, Andric D, Roglic G, Kostic-Rajacic S, Soskic V (2005) Interaction of arylpiperazines with the dopamine receptor D2 binding site. Arzneimittelforschung 55(3):145–152
Gloriam E, Foord M, Blaney E, Garland L (2009) Definition of the G protein-coupled receptor transmembrane bundle binding pocket and calculation of receptor similarities for drug design. J Med Chem 52(14):4429–4442
Bondensgaard K, Ankersen M, Thøgersen H, Hansen B, Wulff B, Bywater R (2004) Recognition of privileged structures by G-protein coupled receptors. J Med Chem 47(4):888–899
Dukic S, Vujovic M, Soskic V, Joksimovic J (1997) Structure–affinity relationship studies on D-2/5-HT1A receptor ligands. 4-(2-Heteroarylethyl)-1-arylpiperazines. Arzneimittelforschung 47(3):239–243
Kostic-Rajacic S, Soskic V, Joksimovic J (1998) Mixed dopaminergic/serotonergic properties of several 2-substituted 4-[2-(5-benzimidazole)ethyl]-1-arylpiperazines. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 331(1):22–26
Newman AH, Grundt P, Cyriac G, Deschamps JR, Taylor M, Kumar R, Ho D, Luedtke RR (2009) N-(4-(4-(2,3-dichloro- or 2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)heterobiarylcarboxamides with functionalized linking chains as high affinity and enantioselective D3 receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 52(8):2559–2570
Schlotter K, Boeckler F, Hubner H, Gmeiner P (2005) Fancy bioisosteres: metallocene-derived G-protein-coupled receptor ligands with subnanomolar binding affinity and novel selectivity profiles. J Med Chem 48(11):3696–3699
Soskic V, Dukic S, Dragovic D, Joksimovic J (1996) Synthesis of N-n-propyl-N-(2-arylethyl)-5-(1H-benzimidazol-2-thione)-ethylamines and related compounds as potential dopaminergic ligands. Arzneimittelforschung 46(8):741–746
Hackling A, Ghosh R, Perachon S, Mann A, Holtje HD, Wermuth CG, Schwartz JC, Sippl W, Sokoloff P, Stark H (2003) N-(omega-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)alkyl)carboxamides as dopamine D2 and D3 receptor ligands. J Med Chem 46(18):3883–3899
Ehrlich K, Gotz A, Bollinger S, Tschammer N, Bettinetti L, Harterich S, Hubner H, Lanig H, Gmeiner P (2009) Dopamine D2, D3, and D4 selective phenylpiperazines as molecular probes to explore the origins of subtype specific receptor binding. J Med Chem 52(15):4923–4935
Grundt P, Carlson EE, Cao J, Bennett CJ, McElveen E, Taylor M, Luedtke RR, Newman AH (2005) Novel heterocyclic trans olefin analogues of N- {4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butyl}arylcarboxamides as selective probes with high affinity for the dopamine D3 receptor. J Med Chem 48(3):839–848
Acknowledgments
This research formed part of project 172032 funded by the Ministry of Education and Science, Republic of Serbia.
PARADOX cluster at the Scientific Computing Laboratory of the Institute of Physics Belgrade, is supported in part by the Serbian Ministry of Education and Science under project no. ON171017, and by the European Commission under FP7 projects HP-SEE, PRACE-1IP, PRACE-2IP, EGI-InSPIRE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukalovic, V., Soskic, V., Sencanski, M. et al. Determination of key receptor–ligand interactions of dopaminergic arylpiperazines and the dopamine D2 receptor homology model. J Mol Model 19, 1751–1762 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1731-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1731-6