Abstract
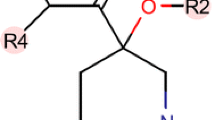
As a tumor suppressor, p53 protein regulates the cell cycle and is involved in preventing tumorgenesis. The protein level of p53 is under the tight control of its negative regulator human double minute 2 (HDM2) via ubiquitination. Therefore, the design of inhibitors of HDM2 has attracted much interest of research on developing novel anticancer drugs. Presently, two classes of molecules, i.e., the 1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-diones (BDPs) and N-Acylpolyamine (NAPA) derivatives were studied by three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) modeling approaches including the comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity index analysis (CoMSIA) as promising p53-HDM2 inhibitors. Based on both the ligand-based and receptor-guided (docking) alignments, two optimal 3D-QSAR models were obtained with good predictive power of q 2 = 0.41, r 2 pred = 0.60 for BDPs, and q 2 = 0.414, r 2 pred = 0.69 for NAPA analogs, respectively. By analysis of the model and its related contour maps, it is revealed that the electrostatic interactions contributed much larger to the compound binding affinity than the steric effects. And the contour maps intuitively suggested where to modify the molecular structures in order to improve the binding affinity. In addition, molecular dynamics simulation (MD) study was also carried out on the dataset with purpose of exploring the detailed binding modes of ligand in the HDM2 binding pocket. Based on the CoMFA contour maps and MD-based docking analyses, some key structural aspects responsible for inhibitory activity of these two classes of compounds were concluded as follows: For BDPs, the R1 and R3 regions should have small electronegativity groups; substituents R2 and R4 should be larger, and R3 substituent mainly involves in H-bonds forming. For NAPA derivatives, bulky and electropositive groups in ring B and ring A, small substituent at region P is favorable for the inhibitory activity. The models and related information, we hope, may provide important insight into the inhibitor-p53-HDM2 interactions and be helpful for facilitating the design of novel potent inhibitors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lane DP (1992) Nature 358:15–16
Gudkov AV, Komarova EA (2007) Hum Mol Genet 16:R67–72
Komarova EA, Gudkov AV (2001) Biochem Pharmacol 62:657–667
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ (2000) Nature 408:307–310
Feki A, Irminger-Finger I (2004) Rev Oncol Hematol 52:103–116
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH (1997) Nature 387:299–303
Kussie PH et al (1996) Science 274:948–953
Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D, Levine AJ (1993) Genes Dev 7:1126–1132
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R (1993) OrenM. EMBO J 12:461–468
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ (1992) Cell 69:1237–1245
Kussie PH, Gorina S, Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Moreau J, Levine AJ et al (1996) Science 274:948–953
Michael D, Oren M (2003) Cancer Biol 13:49–58
Chen F, Wang W, Wafik S (2010) El-Deiry. Biochem Pharmacol 80:724–730
Vassilev LT (2004) Cell Cycle 3:419–421
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z et al. (2004) Science 303:844–848
Brown CJ, Lain S, Verma CS, Fersht AR, Lane DP (2009) Nat Rev Cancer 9:862–873
Ding K, Lu Y, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Qiu S, Ding Y, Gao W, Stuckey J, Krajewski K, Roller PP, Tomita Y, Parrish DA, Deschamps JR, Wang S (2005) J Am Chem Soc 127:10130–10131
Parks DJ, Lafrance LV, Calvo RR, Milkiewicz KL, Gupta V, Lattanze J, Ramachandren K, Carver TE, Petrella EC, Cummings MD, Maguire D, Grasberger BL, Lu T (2005) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:765–770
Lu Y, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Fang X, Gao W, Shangary S, Qiu S, Qin D, Wang S (2006) J Med Chem 49:3759–3762
Chen L, Yin H, Farooqi B, Sebti S, Hamilton AD, Chen J (2005) Mol Cancer Ther 4:1019–1025
Lu F, Chi SW, Kim DH, Han KH, Kuntz ID, Guy RK (2006) J Comb Chem 8:315–325
Shangary S, Wang S (2008) Clin Cancer Res 14:5318–5324
Koblish HK, Zhao S, Franks CF, Donatelli RR, LaFrance LV, Leonard KA, Gushue JM, Parks DJ, Calvo RR, Milkiewicz KL, Marugan JJ, Cummings Raboisson P, MD Grasberger BL, Lu T, Molloy CJ, Maroney AC (2006) Mol Cancer Ther 5:160–169
Li Y, Wang YH, Yang L, Zhang SW, Liu CH (2006) J Mol Des 5:1–12
Li Y, Wang YH, Yang L, Zhang SW, Liu CH, Yang SL (2005) J Mol Struct 733:111–118
Wang X, Yang W, Xu X, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang Y (2010) Curr Med Chem 17:2788–2803
Wei SP, Ji ZQ, Zhang HX, Zhang JW, Wang YH, Wu WJ (2010) J Mol Model. doi:10.1007/s00894-010-0765-x
Hardcastle IR, Ahmed SU, Atkins H, Farnie G, Golding BT, Griffin RJ, Guyenne S, Hutton C, Källblad P, Kemp SJ, Kitching MS, Newell DR, Norbedo S, Northen JS, Reid RJ, Saravanan K, Willems HM, Lunec J (2006) J Med Chem 49:6209–6221
Stoll R, Renner C, Hansen S, Palme S, Klein C, Belling A, Zeslawski W, Kamionka M, Rehm T, Mühlhahn P, Schumacher R, Hesse F, Kaluza B, Voelter W, Engh RA, Holak TA (2001) Biochemistry 40:336
Parks DJ, LaFrance LV, Calvo RR, Milkiewicz KL, Gupta V (2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:3310–3314
Leonard K, Marugan JJ, Raboisson P, Calvo R, Gushue JM (2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:3463–3468
Hayashi R, Wang D, Hara T, Iera J, Durell SR, Appella DH (2009) Bioorg Med Chem 17:7884–7893
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Matthew C, Richard DC III, Van Nicole O (1989) J Comput Chem 10:982–1012
Pirhadi S, Ghasemi JB (2010) Europ J Med Chem 1–7
Wold S, Albano C, Dunn WJ, Edlund U, Esbenson K, Geladi P, Hellberg S, Lindburg W, Sjostrom M (1984) Multivariate data analysis in chemistry. In: Kowalski BR (ed) Chemometrics: MaThematics and Statistics in Chemistry, vol 138, NATO ASI Series- Reidel. Dordrecht, Holland, pp 17–96
Kuntz ID, Blaney JM, Oatley SJ, Langridge R, Ferrin TE (1982) J Mol Biol 161:269–288
Jones G, Willett P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R (1997) J Mol Biol 267:727–748
Eldridge MD, Murray CW, Auton TR, Paolini GV, Mee RP (1997) J Comput Aided Mol Des 11:425–445
Muegge I, Martin YC (1999) J Med Chem 42:791–804
van der Spoel D, van Buuren AR, Tieleman DP, Berendsen HJC (1996) J Biomol NMR 8:229–238
Lindahl E, Hess B, van der Spoel D (2001) J Mol Model 7:306–317
van Aalten DMF, Bywater R, Findlay JBC, Hendlich M, Hooft RWW, Vriend G (1996) J Comput Aided Mol Des 10:255–262
Barreca ML, Ortuso F, Iraci N (2007) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:554–560
Liu R, Li X, Li Y, Jin P, Qin W, Qi J (2009) Biosens Bioelectron 25:629–634
Niu C, Xu Y, Xu Y, Luo X (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:23730–23738
Berendsen HJC, Grigerra JR, Straatsma TPJ (1987) Phys Chem 91:6269–6271
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) J Appl Phys 52:7182–7190
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593
Bohm M, Stürzebecher J, Klebe G (1999) J Med Chem 42:458–477
Bringmann G, Rummey CJ (2003) J Chem Inf Comput Sci 43:304–316
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by high-performance computing platform of Northwest A & F University. The research is financially supported by the Fund of Northwest A & F University. The authors are grateful to Prof. L. Yang for access of Sybyl software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Supplementary material is available on the publishers website along with the published article. (PDF 366 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Li, Y., Ma, Z. et al. Structural determinants of benzodiazepinedione/peptide-based p53-HDM2 inhibitors using 3D-QSAR, docking and molecular dynamics. J Mol Model 18, 295–306 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1041-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1041-4