Abstract
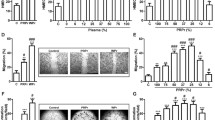
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has been established as an autologous source for therapeutic angiogenesis. The purpose of this study was to evaluate PRP angiogenic effects compared to platelet-poor plasma (PPP) in vitro and in vivo. The effects of PRP on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR2) and CD34 expression were evaluated using real-time PCR, flow cytometry, western blot, immunocytochemistry and pathological study, as were carried out in both human umbilical endothelial cell culture and rat skin. Our findings indicated significant effect of PRP and PPP on VEGFR2 and CD34 expression by human umbilical vein endothelial cells, which was greater in latter. These effects, however, were confirmed by demonstrating an earlier angiogenic effect of PPP in vivo when compared to PRP. The findings of the present study as the first comparative study of PRP versus PPP are novel. Nevertheless, further studies are needed to clarify the underlying mechanism of these findings to improve the therapeutic effects of PRP and PPP.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li X, Hou J, Wu B, Chen T, Luo A (2014) Effects of platelet-rich plasma and cell coculture on angiogenesis in human dental pulp stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells. J Endod 40(11):1810–1814
Kakudo N, Morimoto N, Kushida S, Ogawa T, Kusumoto K (2014) Platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Med Mol Morphol 47(2):83–89
Yamada Y, Ueda M, Hibi H, Baba S (2006) A novel approach to periodontal tissue regeneration with mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma using tissue engineering technology: a clinical case report. Int J Periodontics Restor Dent 26(4):363–369
Cancedda R, Giannoni P, Mastrogiacomo M (2007) A tissue engineering approach to bone repair in large animal models and in clinical practice. Biomaterials 28(29):4240–4250
Mammoto T, Jiang A, Jiang E, Mammoto A (2013) Platelet rich plasma extract promotes angiogenesis through the angiopoietin1-Tie2 pathway. Microvasc Res 89:15–24
Martínez CE, González SA, Palma V, Smith PC (2016) Platelet-poor and platelet-rich plasma stimulate bone lineage differentiation in periodontal ligament stem cells. J Periodontol 87(2):e18–e26
Shahidi M, Esmaeili N, Faranoosh M, Kazemi A, Barati M, Ansarinejad N (2017) Endothelial tip cell formation induced by chronic lymphocytic leukemia plasma (JAK2 positivity amplified this effect). J Hematopathol 10:9–15
Gavard J, Gutkind JS (2006) VEGF controls endothelial-cell permeability by promoting the β-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of VE-cadherin. Nat Cell Biol 8(11):1223–1234
Sasaki H, Zhu L, Fukuda S, Maulik N (1999) Inhibition of NF kappa B activation by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate prevents in vivo hypoxia/reoxygenation-mediated myocardial angiogenesis. Int J Tissue React 22(4):93–100
Bendinelli P, Matteucci E, Dogliotti G, Corsi MM, Banfi G, Maroni P et al (2010) Molecular basis of anti-inflammatory action of platelet-rich plasma on human chondrocytes: mechanisms of NF-κB inhibition via HGF. J Cell Physiol 225(3):757–766
Choi B-H, Zhu S-J, Kim B-Y, Huh J-Y, Lee S-H, Jung J-H (2005) Effect of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) concentration on the viability and proliferation of alveolar bone cells: an in vitro study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34(4):420–424
Weibrich G, Hansen T, Kleis W, Buch R, Hitzler W (2004) Effect of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration. Bone 34(4):665–671
Kaux JF, Drion PV, Colige A, Pascon F, Libertiaux V, Hoffmann A et al (2012) Effects of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the healing of Achilles tendons of rats. Wound Repair Regen 20(5):748–756
Shin HS, Oh HY (2012) The effect of platelet-rich plasma on wounds of OLETF rats using expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 mRNA. Arch Plastic Surg 39(2):106–112
Wiltfang J, Kloss FR, Kessler P, Nkenke E, Schultze-mosgau S, Zimmermann R et al (2004) Effects of platelet-rich plasma on bone healing in combination with autogenous bone and bone substitutes in critical-size defects. Clin Oral Implant Res 15(2):187–193
Thanasas C, Papadimitriou G, Charalambidis C, Paraskevopoulos I, Papanikolaou A (2011) Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous whole blood for the treatment of chronic lateral elbow epicondylitis a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2130–2134
Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Hassanabadi H, Rahimi R, Sedighipour L, Rostami K (2014) Is platelet-rich plasma superior to whole blood in the management of chronic tennis elbow: one year randomized clinical trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil 6(1):12
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Research and Enterprise Committee and the faculty of Allied Medicine, Iran University of Medical Sciences for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interests that could be perceived as influencing the impartiality of the research reported and none of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahidi, M., Vatanmakanian, M., Arami, M.K. et al. A comparative study between platelet-rich plasma and platelet-poor plasma effects on angiogenesis. Med Mol Morphol 51, 21–31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-017-0168-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-017-0168-5