Abstract
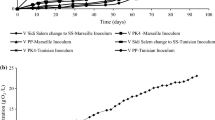
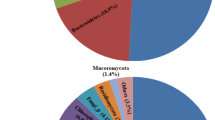
The Tinto River (Huelva, Spain) is a natural acidic rock drainage environment produced by the bio-oxidation of metallic sulfides from the Iberian Pyritic Belt. A geomicrobiological model of the different microbial cycles operating in the sediments was recently developed through molecular biological methods, suggesting the presence of iron reducers, methanogens, nitrate reducers and hydrogen producers. In this study, we used a combination of molecular biological methods and targeted enrichment incubations to validate this model and prove the existence of those potential anaerobic activities in the acidic sediments of Tinto River. Methanogenic, sulfate-reducing, denitrifying and hydrogen-producing enrichments were all positive at pH between 5 and 7. Methanogenic enrichments revealed the presence of methanogenic archaea belonging to the genera Methanosarcina and Methanobrevibacter. Enrichments for sulfate-reducing microorganisms were dominated by Desulfotomaculum spp. Denitrifying enrichments showed a broad diversity of bacteria belonging to the genera Paenibacillus, Bacillus, Sedimentibacter, Lysinibacillus, Delftia, Alcaligenes, Clostridium and Desulfitobacterium. Hydrogen-producing enrichments were dominated by Clostridium spp. These enrichments confirm the presence of anaerobic activities in the acidic sediments of the Tinto River that are normally assumed to take place exclusively at neutral pH.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera A, Manrubia SC, Gomez F, Rodriguez N, Amils R (2006) Eukaryotic community distribution and its relationship to water physicochemical parameters in an extreme acidic environment, Rio Tinto (Southwestern Spain). Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5325–5330
Aguilera A, Souza-Egipsy V, Gomez F, Amils R (2007a) Development and structure of eukaryotic biofilms in an extreme acidic environment, Río Tinto (SW, Spain). Microb Ecol 53:294–305
Aguilera A, Zettler E, Gómez F, Amaral-Zettler L, Rodríguez N, Amils R (2007b) Distribution and seasonal variability in the benthic eukaryotic community of Río Tinto (SW, Spain), an acidic, high metal extreme environment. Syst Appl Microbiol 30:531–546
Amils R, Fernández-Remolar D, Gómez F, González-Toril E, Rodríguez N, Briones C, Prieto-Ballesteros O, Sanz JL, Díaz E, Stevens TO (2008) Subsurface geomicrobiology of the Iberian Pyritic Belt. In: Dion P, Nautiyal CS (eds) Soil biology: microbiology of extreme soils, vol 13. Springer, Berlin, pp 205–223
Asakawa S, Morii H, Akagawa-Matsushita M, Koga Y, Hayano K (1993) Characterization of Methanobrevibacter arboriphilicus SA isolated from a paddy field soil and DNA-DNA hybridization among M. arboriphilicus strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:683–686
Baeseman JL, Smith RL, Silverstein J (2006) Denitrification potential in stream sediments impacted by acid mine drainage: effects of pH, various electron donors, and iron. Microb Ecol 51:232–241
Banda RMH, Dance IG, Bailey TD, Craig DC, Scudder ML (1989) Cadmium polysulfide complexes, [Cd (Sx)(Sy)] 2-: syntheses, crystal and molecular structures, and cadmium-113 NMR studies. Inorg Chem 28:1862–1871
Bijmans MFM, de Vries E, Yang CH, Buisman CJN, Lens PNL, Dopson M (2010) Sulfate reduction at pH 4.0 for treatment of process and wastewaters. Biotechnol Prog 26:1029–1039
Blösl M, Conrad R (1992) Influence of an increased pH on the composition of the nitrate-reducing microbial populations in an anaerobically incubated acidic forest soil. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:624–627
Blothe M, Akob DM, Kostka JE, Goschel K, Drake HL, Kusel K (2008) pH gradient-induced heterogeneity of Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms in coal mining-associated lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1019–1029
Bräuer SL, Yavitt JB, Zinder SH (2004) Methanogenesis in McLean Bog, an acidic peat bog in upstate New York: stimulation by H2/CO2 in the presence of rifampicin, or by low concentrations of acetate. Geomicrobiol J 21:433–443
Burggraf S, Huber H, Stetter K (1997) Reclassification of the crenarchaeal orders and families in accordance with 16S rRNA sequence data. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:657–660
Cadillo-Quiroz H, Yashiro E, Yavitt JB, Zinder SH (2008) Characterization of the archaeal community in a minerotrophic fen and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism-directed isolation of a novel hydrogenotrophic methanogen. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2059–2068
Campbell LL, Postgate JR (1965) Classification of the spore-forming sulfate-reducing bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 29:359–362
Church CD, Wilkin RT, Alpers CN, Rye RO, McCleskey RB (2007) Microbial sulfate reduction and metal attenuation in pH 4 acid mine water. Geochem Trans 8:10
Dolfing J, Xu A, Head IM (2010) Anomalous energy yields in thermodynamic calculations: importance of accounting for pH-dependent organic acid speciation. The ISME Journal 4:463–464
Dunfield P, Dumont R, Moore TR (1993) Methane production and consumption in temperate and subarctic peat soils: response to temperature and pH. Soil Biol Biochem 25:321–326
Fernández-Remolar DC, Prieto-Ballesteros O, Rodríguez N, Gómez F, Amils R, Gómez-Elvira J, Stoker CR (2008) Underground habitats in the Río Tinto Basin: a model for subsurface life habitats on Mars. Astrobiology 8:1023–1047
Florencio L, Nozhevnikova A, Van Langerak A, Stams AJM, Field JA, Lettinga G (1993) Acidophilic degradation of methanol by a methanogenic enrichment culture. FEMS Microbiol Lett 109:1–6
García-Moyano A, González-Toril E, Aguilera A, Amils R (2007) Prokaryotic community composition and ecology of floating macroscopic filaments from an extreme acidic environment, Río Tinto (SW, Spain). Syst Appl Microbiol 30:601–614
Ghose TK, Wikén T (1955) Inhibition of bacterial sulphate-reduction in presence of short chain fatty acids. Physiol Plantarum 8:116–135
Gonzalez-Toril E, Llobet-Brossa E, Casamayor EO, Amann R, Amils R (2003) Microbial ecology of an extreme acidic environment, the Tinto River. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4853–4865
Goodwin S, Zeikus JG (1987) Ecophysiological adaptations of anaerobic bacteria to low pH: analysis of anaerobic digestion in acidic bog sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:57–64
Hao C, Zhang H, Haas R, Bai Z, Zhang B (2007) A novel community of acidophiles in an acid mine drainage sediment. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:15–21
Horn MA, Matthies C, Kusel K, Schramm A, Drake HL (2003) Hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis by moderately acid-tolerant methanogens of a methane-emitting acidic peat. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:74–83
Hu B, Chen S (2007) Pretreatment of methanogenic granules for immobilized hydrogen fermentation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:3266–3273
Huang LN, Chen YQ, Zhou H, Luo S, Lan CY, Qu LH (2003) Characterization of methanogenic Archaea in the leachate of a closed municipal solid waste landfill. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 46:171–177
Johnson DB, Hallberg KB (2005) Acid mine drainage remediation options: a review. Sci Total Environ 338:3–14
Klonowska A, Clark M, Thieman S, Giles B, Wall J, Fields M (2008) Hexavalent chromium reduction in Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough causes transitory inhibition of sulfate reduction and cell growth. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:1007–1016
Koschorreck M (2008) Microbial sulphate reduction at a low pH. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:329–342
Koschorreck M, Wendt-Potthoff K, Scharf B, Richnow HH (2008) Methanogenesis in the sediment of the acidic Lake Caviahue in Argentina. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 178:197–204
Lin B, Hyacinthe C, Bonneville S, Braster M, Van Cappellen P, Röling WFM (2007) Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of dissimilatory ferric iron reducers in sediments of the polluted Scheldt estuary, Northwest Europe. Environ Microbiol 9:1956–1968
Lopez-Archilla AI, Marin I, Amils R (2001) Microbial community composition and ecology of an acidic aquatic environment: the Tinto River, Spain. Microb Ecol 41:20–35
López-Archilla AI, González AE, Terrón MC, Amils R (2005) Diversity and ecological relationships of the fungal populations of an acidic river of Southwestern Spain: the Tinto River. Can J Microbiol 50:923–934
Lu S, Gischkat S, Reiche M, Akob DM, Hallberg KB, Kusel K (2010) Ecophysiology of Fe-cycling bacteria in acidic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:8174–8183
Maestrojuán GM, Boone DR (1991) Characterization of Methanosarcina barkeri MST and 227, Methanosarcina mazei S-6T, and Methanosarcina vacuolata Z-761T. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:267–274
Manaia CM, Costa MS (1991) Characterization of halotolerant Thermus isolates from shallow marine hot springs on S. Miguel, Azores. J Gen Microbiol 137:2643–2648
Manish S, Banerjee R (2008) Comparison of biohydrogen production processes. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:279–286
Mateju V, Cizinska S, Krejci J, Janoch T (1992) Biological water denitrification—a review. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:170–183
Muyzer G, Ramsing NB (1995) Molecular methods to study the organization of microbial communities. Water Sci Technol 32:1–9
Muyzer G, Stams AJM (2008) The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:441–454
Nagele W, Conrad R (1990) Influence of soil pH on the nitrate-reducing microbial populations and their potential to reduce nitrate to NO and N2O. FEMS Microbiol Lett 74:49–57
Nandi R, Sengupta S (1998) Microbial production of hydrogen: an overview. Crit Rev Microbiol 24:61–84
Rajhi H, Conthe M, Puyol D, Díaz E, Sanz JL (2012) Dark fermentation: Isolation and characterization of hydrogen-producing strains from different sludges. Bioresource Technol (submitted)
Rea S, Bowman JP, Popovski S, Pimm C, Wright ADG (2007) Methanobrevibacter millerae sp. nov. and Methanobrevibacter olleyae sp. nov., methanogens from the ovine and bovine rumen that can utilize formate for growth. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:450–456
Sakai S, Imachi H, Sekiguchi Y, Ohashi A, Harada H, Kamagata Y (2007) Isolation of key methanogens for global methane emission from rice paddy fields: a novel isolate affiliated with the clone cluster rice cluster I. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4326–4331
Sánchez I, Fernández N, Amils R, Sanz JL (2008) Assessment of the addition of “Thiobacillus denitrificans” and “Thiomicrospira denitrificans” to chemolithoautotrophic denitrifying bioreactors. Int Microbiol 11:179–184
Sánchez-Andrea I, Rodriguez N, Amils R, Sanz JL (2011) Microbial diversity in anaerobic sediments at Rio Tinto, a naturally acidic environment with a high heavy metal content. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6085–6093
Sánchez-Andrea I, Knittel K, Amann R, Amils R, Sanz JL (2012a) Quantification of Tinto River sediment microbial communities: the importance of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their role in attenuating acid mine drainage. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(13):4638–4645
Sánchez-Andrea I, Triana D, Sanz JL (2012b) Bioremediation of acid mine drainage coupled with domestic wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol (in press)
Sanz JL, Rodriguez N, Amils R (1997) Effect of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons on the acetoclastic methanogenic activity of granular sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:324–328
Sanz JL, Rodríguez N, Díaz EE, Amils R (2011) Methanogenesis in the sediments of Rio Tinto, an extreme acidic river. Environ Microbiol 13:2336–2341
Show K, Lee D, Chang J (2011) Bioreactor and process design for biohydrogen production. Biores Technol 102:8524–8533
Simek M, Jisova L, Hopkins DW (2002) What is the so-called optimum pH for denitrification in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1227–1234
Stahl DA, Amann R (1991) Development and application of nucleic acid probes. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 205–228
Staley BF, de los Reyes FL III, Barlaz MA (2011) Effect of spatial differences in microbial activity, pH, and substrate levels on methanogenesis initiation in refuse. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2381–2391
Ueno Y, Haruta S, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2001) Microbial community in anaerobic hydrogen-producing microflora enriched from sludge compost. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:555–562
Valls M, Lorenzo V (2002) Exploiting the genetic and biochemical capacities of bacteria for the remediation of heavy metal pollution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:327–338
Verbaendert I, De Vos P, Boon N, Heylen K (2011) Denitrification in Gram-positive bacteria: an underexplored trait. Biochem Soc Trans 39:254–258
Villemur R, Lanthier M, Beaudet R, Lépine F (2006) The Desulfitobacterium genus. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:706–733
Wang X, Hoefel D, Saint CP, Monis PT, Jin B (2007) The isolation and microbial community analysis of hydrogen producing bacteria from activated sludge. J Appl Microbiol 103:1415–1423
Widdel F (1992) The genus Desulfotomaculum. The prokaryotes 2:1792–1799
Williams RT, Crawford RL (1985) Methanogenic bacteria, including an acid-tolerant strain, from peatlands. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:1542–1544
Zettler LAA, Gómez F, Zettler E, Keenan BG, Amils R, Sogin ML (2002) Microbiology: eukaryotic diversity in Spain’s River of Fire. Nature 417:137
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Spanish “Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación” Grant CTM2009-10521 to J.L. Sanz and Grant CGL2009-11059 to R. Amils. Irene Sánchez-Andrea is a pre-doctoral fellow supported by the same Ministerio.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Driessen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Andrea, I., Rojas-Ojeda, P., Amils, R. et al. Screening of anaerobic activities in sediments of an acidic environment: Tinto River. Extremophiles 16, 829–839 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-012-0478-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-012-0478-4