Abstract
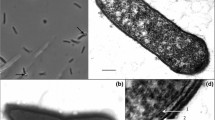
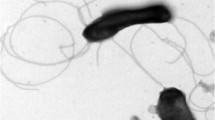
The bacterial strain designated I1-1T was isolated from a hot spring located in the Pingtung area, southern Taiwan. Cells of this organism were Gram reaction negative rods, motile by a single polar flagellum. Optimum conditions for growth were 55°C and pH 7. Strain I1-1T grew well in lower nutrient media such as 5–10% Luria–Bertani broth, and its extracellular products expressed alkaline protease activity. The 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis indicates that strain I1-1T is a member of β-Proteobacteria. On the basis of a phylogenetic analysis of 16S rDNA sequences, DNA–DNA similarity data, whole-cell protein analysis, physiological and biochemical characteristics, as well as fatty acid compositions, the organism belonged to the genus Tepidimonas and represented a novel species within this genus. The predominant cellular fatty acids of strain I1-1T were 16:0 (about 41%), 18:1 ω7c (about 13%), and summed feature 3 [16:1 ω7c or 15:0 iso 2OH or both (about 26%)]. Its DNA base ratio was 68.1 mol%. We propose to classify strain I1-1T (=BCRC 17406T=LMG 22826T) as Tepidimonas taiwanensis sp. nov.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banik RM, Prakash M (2004) Laundry detergent compatibility of the alkaline protease from Bacillus cereus. Microbiol Res 159:135–140
Chang SC, Wang JT, Vandamme P, Hwang JH, Chang PS, Chen WM (2004) Chitinimonas taiwanensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel chitinolytic bacterium isolated from a freshwater pond for shrimp culture. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:43–49
Chen WM, Laevens S, Lee TM, Coenye T, De Vos P, Mergeay M, Vandamme P (2001) Ralstonia taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa species and sputum of a cystic fibrosis patient. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1729–1735
Chung AP, Rainey F, Nobre MF, Burghardt J, da Costa MS (1997) Meiothermus cerbereus sp. nov., a new slightly thermophilic species with high levels of 3-hydroxy fatty acids. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1225–1230
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric DNA–DNA hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Fahy PC, Persley GC (1983) Plant bacterial diseases: a diagnostic guide. Academic Press, New York
Freitas M, Rainey FA, Nobre MF, Silvestre AJ, da Costa MS (2003) Tepidimonas aquatica sp. nov., a new slightly thermophilic beta-proteobacterium isolated from a hot water tank. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:376–381
Gupta R, Beg QK, Khan S, Chauhan B (2002) An overview on fermentation, downstream processing and properties of microbial alkaline proteases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:381–395
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Moreira C, Rainey FA, Nobre MF, da Silva MT, da Costa MS (2000) Tepidimonas ignava gen. nov., sp. nov., a new chemolithoheterotrophic and slightly thermophilic member of the beta-Proteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:735–742
Niehaus F, Bertoldo C, Kahler M, Antranikian G (1999) Extremophiles as a source of novel enzymes for industrial application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:711–729
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pearson K (1926) On the coefficient of racial likeness. Biometrika 18:105–117
Pitcher DG, Saunders NA, Owen RJ (1989) Rapid extraction of bacterial genomic DNA with guanidium thiocyanate. Lett Appl Microbiol 8:151–156
Pot B, Vandamme P, Kersters K (1994) Analysis of electrophoretic whole-organism protein fingerprints. In: Goodfellow M, O’Donnell AG (eds) Chemical methods in prokaryotic systematics. Chichester, Wiley, New York, pp 493–521
Rao MB, Tanksale AM, Ghatge MS, Deshpande VV (1998) Molecular and biotechnological aspects of microbial proteases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:597–635
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids (MIDI technical note 101). Newark, MIDI Microbial ID
Secades P, Guijarro JA (1999) Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease from the fish pathogen Yersinia ruckeri and effect of culture conditions on production. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3969–3975
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
van den Burg B (2003) Extremophiles as a source for novel enzymes. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:213–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Wiegel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TL., Chou, YJ., Chen, WM. et al. Tepidimonas taiwanensis sp. nov., a novel alkaline-protease-producing bacterium isolated from a hot spring. Extremophiles 10, 35–40 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0469-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0469-9