Abstract
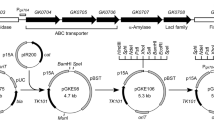
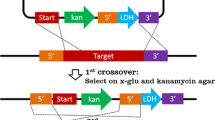
Thermophilic bacteria are of great value for industry and research communities. Unfortunately, the cellular processes and mechanisms of these organisms remain largely understudied. In the present study, we investigate how the inactivation of adenylate kinase (AK) affects the adenine nucleotide homeostasis of a gram-positive moderate thermophile, Geobacillus stearothermophilus strain NUB3621-R. AK plays a major role in the adenine nucleotide homeostasis of living cells and has been shown to be essential for the gram-negative mesophile Escherichia coli. To study the role of AK in the maintenance of adenylate energy charge (EC) and cell viability of G. stearothermophilus, we generated a recombinant strain of this organism in which its endogenous gene coding for the essential protein adenylate kinase (AK) has been replaced with the adk gene from the mesophile Bacillus subtilis. PCR, DNA sequencing and Southern analysis were performed to confirm proper gene replacement and preservation of neighboring genes. The highest growing temperature for recombinant cells was almost 20°C lower than for wild-type cells (56 vs. 75°C). This temperature-sensitive phenotype was secondary to heat inactivation of B. subtilis AK, as evidenced by enzyme activity assays and EC measurements. At higher temperatures (65°C), recombinant cells also had lower EC values (0.09) compared to wild-type cells (0.45), which reflects a disruption of adenine nucleotide homeostasis following AK inactivation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- adk :
-
Adenylate kinase gene
- AK:
-
Adenylate kinase protein
- Ap5A:
-
P1, P5 -Di(adenosine-5′)pentaphosphate
- cat :
-
Chloramphenicol acetyl-transferase gene
- EC:
-
Energy charge
- infA :
-
Initiation factor IF-I gene
- secY:
-
Pre-protein translocase secY subunit gene
- map :
-
Methionine aminopeptidase gene
- RBS:
-
Ribosomal binding site
References
Atkinson DE (1968) The energy charge of the adenylate pool as a regulatory parameter. Interaction with feedback modifiers. Biochemistry 7:4030–4034
Barzu O, Michelson S (1983) Simple and fast purification of Escherichia coli adenylate kinase. FEBS Lett 153:280–284
Blattner FR, Plunkett G III, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, Gregor J, Davis NW, Kirkpatrick HA, Goeden MA, Rose DJ, Mau B, Shao Y (1997) The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453–1474
Breitling R, Schlott B, Behnke D (1994) Modulation of the spc operon affects growth and protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis. J Basic Microbiol 34:145–155
Chang S, Cohen SN (1989) High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet 168:111–115
Chang SY, McGary EC, Chang S (1989) Methionine aminopeptidase gene of Escherichia coli is essential for cell growth. J Bacteriol 171:4071–4072
Chapman AG, Fall L, Atkinson DE (1971) Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli during growth and starvation. J Bacteriol 108:1072–1086
Chen ZF, Wojcik SF, Welker NE (1986) Genetic analysis of Bacillus stearothermophilus by protoplast fusion. J Bacteriol 165:994–1001
Cousin D, Buttin G (1969) Mutants thermosensibles d‘ Escherichia coli K12. III – Une mutation lêtale d’ E. coli affectant l’activité de l’adénylate-kinase. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 117:612–630
Criswell AR, Bae E, Stec B, Konisky J, Phillips GN Jr (2003) Structures of thermophilic and mesophilic adenylate kinases from the genus Methanococcus. J Mol Biol 330:1087–1099
Cummings HS, Hershey JW (1994) Translation initiation factor IF1 is essential for cell viability in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 176:198–205
Ferber DM, Haney PJ, Berk H, Lynn D, Konisky J (1997) The adenylate kinase genes of M. voltae, M. thermolithotrophicus, M. jannaschii, and M. igneus define a new family of adenylate kinases. Gene 185:239–244
Glaser P, Presecan E, Delepierre M, Surewicz WK, Mantsch HH, Barzu O, Gilles AM (1992) Zinc, a novel structural element found in the family of bacterial adenylate kinases. Biochemistry 31:3038–3043
Glembotski CC, Chapman AG, Atkinson DE (1981) Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli CR341T28 and properties of heat-sensitive adenylate kinase. J Bacteriol 145:1374–1385
Haase GH, Brune M, Reinstein J, Pai EF, Pingoud A, Wittinghofer A (1989) Adenylate kinases from thermosensitive Escherichia coli strains. J Mol Biol 207:151–162
Hanahan D, Jessee J, Bloom FR (1991) Plasmid transformation of Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Methods Enzymol 204:63–113
Hansmann S, Martin W (2000) Phylogeny of 33 ribosomal and six other proteins encoded in an ancient gene cluster that is conserved across prokaryotic genomes: influence of excluding poorly alignable sites from analysis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50(Pt 4):1655–1663
Imanaka T, Fujii M, Aramori I, Aiba S (1982) Transformation of Bacillus stearothermophilus with plasmid DNA and characterization of shuttle vector plasmids between Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 149:824–830
Kahru A, Liiders M, Vanatalu K, Vilu R (1982) Adenylate energy charge during batch culture of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris 42. Arch Microbiol 133:142–144
Kahru A, Vilu R (1990) Role of adenine nucleotides in the regulation of bacterial energy metabolism: theoretical problems and experimental pitfalls. Microbios 62:83–92
Kath T, Schmid R, Schafer G (1993) Identification, cloning, and expression of the gene for adenylate kinase from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Arch Biochem Biophys 307:405–410
Konrad M (1993) Molecular analysis of the essential gene for adenylate kinase from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 268:11326–11334
Li X, Lindahl L, Sha Y, Zengel JM (1997) Analysis of the Bacillus subtilis S10 ribosomal protein gene cluster identifies two promoters that may be responsible for transcription of the entire 15-kilobase S10-spc-alpha cluster. J Bacteriol 179:7046–7054
Lin-Chao S, Chen WT, Wong TT (1992) High copy number of the pUC plasmid results from a Rom/Rop-suppressible point mutation in RNA II. Mol Microbiol 6:3385–3393
Munier-Lehmann H, Burlacu-Miron S, Craescu CT, Mantsch HH, Schultz CP (1999) A new subfamily of short bacterial adenylate kinases with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis enzyme as a model: a predictive and experimental study. Proteins 36:238–248
Narumi I Sawakami, K., Nakamoto, S., Nakayama, N., Yanagisawa, T., Takahashi, N., Kihara, H (1992) A newly isolated Bacillus stearothermophilus K1041 and its transformation by electroporation. Biotechnol Tech 6:83–86
Sharp RJ, Riley PW, White D (1992) Heterotrophic thermophilic bacilli. In: Kristjansson JK (ed) Thermophilic bacteria. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 19–50
Shiba K, Ito K, Yura T, Cerretti DP (1984) A defined mutation in the protein export gene within the spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of a new temperature-sensitive secY mutant. EMBO J 3:631–635
Stolworthy TS, Black ME (2001) The mouse guanylate kinase double mutant E72Q/D103N is a functional adenylate kinase. Protein Eng 14:903–909
Studholme DJ, Jackson RA, Leak DJ (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of transformable strains of thermophilic Bacillus species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 172:85–90
Suh JW, Boylan SA, Oh SH, Price CW (1996) Genetic and transcriptional organization of the Bacillus subtilis spc-alpha region. Gene 169:17–23
Swedes JS, Sedo RJ, Atkinson DE (1975) Relation of growth and protein synthesis to the adenylate energy charge in an adenine-requiring mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 250:6930–6938
Vallier H, Welker NE (1990) Genetic map of the Bacillus stearothermophilus NUB36 chromosome. J Bacteriol 172:793–801
Vieille C, Burdette DS, Zeikus JG (1996) Thermozymes. Biotechnol Annu Rev 2:1–83
Vonrhein C, Bonisch H, Schafer G, Schulz GE (1998) The structure of a trimeric archaeal adenylate kinase. J Mol Biol 282:167–179
Wei P, Stewart CR (1993) A cytotoxic early gene of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO1. J Bacteriol 175:7887–7900
Wu LJ, Welker NE (1989) Protoplast transformation of Bacillus stearothermophilus NUB36 by plasmid DNA. J Gen Microbiol 135:1315–1324
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Acknowledgements
This work was in part funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF/MCB - 0212417). R.C. is the recipient of a training fellowship from the W.M. Keck Foundation to the Gulf Coast Consortia through the Keck Center for Computational and Structural Biology. The authors would like to thank the MacKenzie Lab (Rice University, Houston, TX) for equipment, helpful discussions and suggestions. The authors are indebted to Dr. N. Welker (Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA) for help with G. stearothermophilus NUB3621-R transformation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian
The authors would like to dedicate this paper to the memory of Dr. Neil Welker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couñago, R., Shamoo, Y. Gene replacement of adenylate kinase in the gram-positive thermophile Geobacillus stearothermophilus disrupts adenine nucleotide homeostasis and reduces cell viability. Extremophiles 9, 135–144 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0428-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0428-x