Abstract
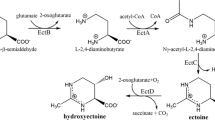
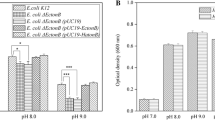
In response to osmotic stress, the halophilic, Gram-positive bacterium Marinococcus halophilus accumulates compatible solutes either by de novo synthesis or by uptake from the medium. To characterize transport systems responsible for the uptake of compatible solutes, a plasmid-encoded gene bank of M. halophilus was transferred into the transport-deficient strain Escherichia coli MKH13, and two genes were cloned by functional complementation required for ectoine and glycine betaine transport. The ectoine transporter is encoded by an open reading frame of 1,578 bp named ectM. The gene ectM encodes a putative hydrophobic, 525-residue protein, which shares significant identity to betaine-carnetine-choline transporters (BCCTs). The transporter responsible for the uptake of glycine betaine in M. halophilus is encoded by an open reading frame of 1,482 bp called betM. The potential, hydrophobic BetM protein consists of 493 amino acid residues and belongs, like EctM, to the BCCT family. The affinity of whole cells of E. coli MKH13 for ectoine (K s=1.6 μM) and betaine (K s=21.8 μM) was determined, suggesting that EctM and BetM exhibit a high affinity for their substrates. An elevation of the salinity in the medium resulted in an increased uptake of ectoine via EctM and glycine betaine via BetM in E. coli MKH13 cells, demonstrating that both systems are osmoregulated.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäfer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Blohn C von, Kempf B, Kappes RM, Bremer E (1997) Osmostress response in Bacillus subtilis: characterization of a proline uptake system (OpuE) regulated by high osmolarity and the alternative transcription factor sigma B. Mol Microbiol 25:175–187
Boscari A, Mandon KM, Dupont L, Poggi M-C, Le Rudulier D (2002) BetS is a major glycine betaine/proline betaine transporter required for early osmotic adjustment in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 184:2654–2663
Bullock WO, Fernandez JM, Short JM (1987) XL1 blue: a high-efficiency plasmid transforming recA Escherichia coli strain with beta-galactosidase selection. Biotechniques 5:376–378
Farrow JA, Ash C, Wallbanks S, Collins MD (1992) Phylogenetic analysis of the genera Planococcus, Marinococcus and Sporosarcina and their relationships to members of the genus Bacillus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 72:167–172
Frings E, Kunte HJ, Galinski EA (1993) Compatible solutes in representatives of the genera Brevibacterium and Corynebacterium: Occurrence of tetrahydropyrimidine and glutamine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 109:25–32
Galinski EA, Herzog RM (1990) The role of trehalose as a substitute for nitrogen-containing compatible solutes (Ectothiorhodospira halochloris). Arch Microbiol 153:607–613
Grammann K, Volke A, Kunte HJ (2002) New type of osmoregulated solute transporter identified in halophilic members of the Bacteria domain: TRAP transporter TeaABC mediates the uptake of ectoine and hydroxyectoine in Halomonas elongata DSM 2581T. J Bacteriol 184:3078–3085
Haardt M, Kempf B, Faatz E, Bremer E (1995) The osmoprotectant proline betaine is a major substrate for the binding-protein-dependent transport system ProU of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet 246:783–786
Hagemann M, Richter S, Mikkat S (1997) The ggtA gene encodes a subunit of the transport system for the osmoprotective compound glucosylglycerol in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 179:714–720
Hirokawa T, Boon-Chieng S, Mitaku S (1998) SOSUI: classification and secondary structure prediction system for membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 414:378–379
Kappes RM, Kempf B, Bremer E (1996) Three transport systems for the osmoprotectant glycine betaine operate in Bacillus subtilis: characterization of OpuD. J Bacteriol 178:5071–5079
Kempf B, Bremer E (1998) Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high-osmolality environments. Arch Microbiol 170:319–330
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Larsen PI, Sydne LK, Landfald B, Strøm AR (1987) Osmoregulation in Escherichia coli by accumulation of organic osmolytes: betaines, glutamic acid, and trehalose. Arch Microbiol 147:1–7
Louis P, Galinski EA (1997) Characterization of genes for the biosynthesis of the compatible solute ectoine from Marinococcus halophilus and osmoregulated expression in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 143:1141–1149
MacMillan SV, Alexander DA, Culham DE, Kunte HJ, Marshall EV, Rochon D, Wood JM (1999) The ion coupling and organic substrate specificities of osmoregulatory transporter ProP in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1420:30–44
Novitsky TJ, Kushner DJ (1976) Planococcus halophilus sp. nov., a faculatively halophilic coccus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 26:53–57
Oren A (1999) Bioenergetic aspects of halophilism. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:334–348
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2444–2448
Peter H, Burkovski A, Krämer R (1996) Isolation, characterization, and expression of the Corynebacterium glutamicum betP gene, encoding the transport system for the compatible solute glycine betaine. J Bacteriol 178:5229–5234
Peter H, Weil B, Burkovski A, Krämer R, Morbach S (1998) Corynebacterium glutamicum is equipped with four secondary carriers for compatible solutes: identification, sequencing, and characterization of the proline/ectoine uptake system, ProP, and the ectoine/proline/glycine betaine carrier, EctP. J Bacteriol 180:6005–6012
Racher KI, Voegele RT, Marshall EV, Culham DE, Wood JM, Jung H, Bacon M, Cairns MT, Ferguson SM, Liang W-J, Henderson PJF, White G, Hallett FR (1999) Purification and reconstituation of an osmosensor: transporter ProP of Escherichia coli senses and responds to osmotic shifts. Biochemistry 39:1676–1684
Rübenhagen R, Rönsch H, Jung H, Krämer R, Morbach S (2000) Osmosensor and osmoregulator properties of the betaine carrier BetP from Corynebacterium glutamicumin proteoliposomes. J Biol Chem 275:735–741
Rübenhagen R, Morbach S, Krämer R (2001) The osmoreactive betaine carrier BetP from Corynebacterium glutamicum is a sensor for cytoplasmic K+. EMBO J 20:5412–5420
Saier MH Jr (1994) Computer-aided analysis of transport protein sequences: gleaning evidence concerning function, structure, biogenesis, and evolution. Microbiol Rev 58:71–93
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Severin J, Wohlfarth A, Galinski E A (1992) The predominant role of the recently discovered tetrahydropyrimidines for the osmoadaptation of halophilic eubacteria. J Gen Microbiol 138:1629–1638
Sleator RD, Gahan CG, Abee T, Hill C (1999) Identification and disruption of BetL, a secondary glycine betaine transport system linked to the salt tolerance of Listeria monocytogenes LO28. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2078–2083
Takami H, Nakasone K, Takaki Y, Maeno G, Sasaki Y, Masui N, Fuji F, Hirama C, Nakamura Y, Ogasawara N, Kuhara S, Horikoshi K (2000) Complete genome sequence of the alkaliphilic bacterium Bacillus halodurans and genomic sequence comparison with Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res 28:4317–4331
Takeshita S, Sato M, Tabo M, Massahashi W, Hashimoto-Gotoh T (1987) High-copy-number and low-copy-number plasmid vectors for lacZ α-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene 61:63–74
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tusnády GE, Simon I (1998) Principles governing amino acid composition of integral membrane proteins: application to topology prediction. J Mol Biol 283:489–506
Tusnády GE, Simon I (2001) The HMMTOP transmembrane topology prediction server. Bioinformatics 17:849–850
Zucker M (2003) Mfold Web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:1–10
Acknowledgments
We thank Erhard Bremer (Philipps University, Marburg) for kindly providing E. coli MKH13. We are grateful to Sharon Taylor for critical reading of the manuscript and to Annette Kraegeloh for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W.D. Grant
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermeulen, V., Kunte, H.J. Marinococcus halophilus DSM 20408T encodes two transporters for compatible solutes belonging to the betaine-carnitine-choline transporter family: identification and characterization of ectoine transporter EctM and glycine betaine transporter BetM. Extremophiles 8, 175–184 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0375-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0375-6