Abstract
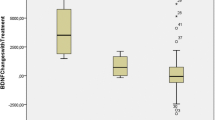
It has been suggested that neurotrophins are involved in the etiopathogenesis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This study aimed to investigate whether there are differences in serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and neurotrophin-3 (NTF3) levels between children with ADHD and healthy controls. A total of 110 treatment-naive children with the combined presentation of ADHD and 44 healthy controls aged 8–18 years were enrolled in this study. The severity of ADHD symptoms was determined by scores on the Conners’ Parent Rating Scale-Revised Short and Conners’ Teacher Rating Scale-Revised Short. The severity of depression and anxiety symptoms of the children were evaluated by the self-report inventories. Serum levels of neurotrophins were measured using commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. The multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) revealed a significant main effect of groups in the levels of serum neurotrophins, an effect that was independent of age, sex, and the severity of the depression and anxiety. The analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) indicated that the mean serum GDNF and NTF3 levels of ADHD patients were significantly higher than that of controls. However, serum BDNF and NGF levels did not show any significant differences between groups. No correlations between the levels of serum neurotrophins and the severity of ADHD were observed. These results suggest that elevated serum GDNF and NTF3 levels may be related to ADHD in children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas R, Sanders S, Doust J, Beller E, Glasziou P (2015) Prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics 135:e994–e1001
Schuch V, Utsumi DA, Costa TV, Kulikowski LD, Muszkat M (2015) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in the light of the epigenetic paradigm. Front Psychiatry 6:126
Lang UE, Jockers-Scherubl MC, Hellweg R (2004) State of the art of the neurotrophin hypothesis in psychiatric disorders: implications and limitations. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 111:387–411
Aloe L, Rocco ML, Bianchi P, Manni L (2012) Nerve growth factor: from the early discoveries to the potential clinical use. J Transl Med 10:239
Meng WD, Sun SJ, Yang J, Chu RX, Tu W, Liu Q (2016) Elevated serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) but not BDNF gene Val66Met polymorphism is associated with autism spectrum disorders. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-9721-9
de Azevedo Cardoso T, Mondin TC, Wiener CD, Marques MB, Fucolo Bde A, Pinheiro RT, de Souza LD, da Silva RA, Jansen K, Oses JP (2014) Neurotrophic factors, clinical features and gender differences in depression. Neurochem Res 39:1571–1578
Domingos da Silveira da Luz AC, Pereira Dias G, do Nascimento Bevilaqua MC, Cocks G, Gardino PF, Thuret S, Nardi AE (2013) Translational findings on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and anxiety: contributions from basic research to clinical practice. Neuropsychobiology 68:129–138
Kotyuk E, Keszler G, Nemeth N, Ronai Z, Sasvari-Szekely M, Szekely A (2013) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) as a novel candidate gene of anxiety. PLoS ONE 8:e80613
Vargas HE, Gama CS, Andreazza AC, Medeiros D, Stertz L, Fries G, Palha J, Cereser KM, Berk M, Kapczinski F, Belmonte-de-Abreu PS (2008) Decreased serum neurotrophin 3 in chronically medicated schizophrenic males. Neurosci Lett 440:197–201
Walz JC, Andreazza AC, Frey BN, Cacilhas AA, Cereser KM, Cunha AB, Weyne F, Stertz L, Santin A, Goncalves CA, Kapczinski F (2007) Serum neurotrophin-3 is increased during manic and depressive episodes in bipolar disorder. Neurosci Lett 415:87–89
Wysokinski A (2016) Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) in depressed patients with schizophrenia. Nord J Psychiatry 70:267–271
Scassellati C, Zanardini R, Tiberti A, Pezzani M, Valenti V, Effedri P, Filippini E, Conte S, Ottolini A, Gennarelli M, Bocchio-Chiavetto L (2014) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 23:173–177
Bergman O, Westberg L, Lichtenstein P, Eriksson E, Larsson H (2011) Study on the possible association of brain-derived neurotrophic factor polymorphism with the developmental course of symptoms of attention deficit and hyperactivity. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 14:1367–1376
Shim SH, Hwangbo Y, Kwon YJ, Jeong HY, Lee BH, Lee HJ, Kim YK (2008) Increased levels of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1824–1828
Lee YH, Song GG (2015) BDNF 196 G/A and COMT Val158Met polymorphisms and susceptibility to ADHD: a meta-analysis. J Atten Disord
Shim SH, Hwangbo Y, Yoon HJ, Kwon YJ, Lee HY, Hwang JA, Kim YK (2015) Increased levels of plasma glial-derived neurotrophic factor in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nord J Psychiatry 69:546–551
Guney E, Ceylan MF, Kara M, Tekin N, Goker Z, Senses Dinc G, Ozturk O, Eker S, Kizilgun M (2014) Serum nerve growth factor (NGF) levels in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Neurosci Lett 560:107–111
Syed Z, Dudbridge F, Kent L (2007) An investigation of the neurotrophic factor genes GDNF, NGF, and NT3 in susceptibility to ADHD. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144B:375–378
Ribases M, Hervas A, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Bosch R, Bielsa A, Gastaminza X, Fernandez-Anguiano M, Nogueira M, Gomez-Barros N, Valero S, Gratacos M, Estivill X, Casas M, Cormand B, Bayes M (2008) Association study of 10 genes encoding neurotrophic factors and their receptors in adult and child attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 63:935–945
Conner AC, Kissling C, Hodges E, Hunnerkopf R, Clement RM, Dudley E, Freitag CM, Rosler M, Retz W, Thome J (2008) Neurotrophic factor-related gene polymorphisms and adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) score in a high-risk male population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B:1476–1480
Li H, Liu L, Tang Y, Ji N, Yang L, Qian Q, Wang Y (2014) Sex-specific association of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism and plasma BDNF with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a drug-naive Han Chinese sample. Psychiatry Res 217:191–197
Amiri A, Torabi Parizi G, Kousha M, Saadat F, Modabbernia MJ, Najafi K, Atrkar Roushan Z (2013) Changes in plasma Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels induced by methylphenidate in children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 47:20–24
Ramos-Quiroga JA, Corominas-Roso M, Palomar G, Gomez-Barros N, Ribases M, Sanchez-Mora C, Bosch R, Nogueira M, Corrales M, Valero S, Casas M (2014) Changes in the serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder after treatment with atomoxetine. Psychopharmacology 231:1389–1395
Rios M, Fan G, Fekete C, Kelly J, Bates B, Kuehn R, Lechan RM, Jaenisch R (2001) Conditional deletion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the postnatal brain leads to obesity and hyperactivity. Mol Endocrinol 15:1748–1757
Chourbaji S, Hellweg R, Brandis D, Zorner B, Zacher C, Lang UE, Henn FA, Hortnagl H, Gass P (2004) Mice with reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression show decreased choline acetyltransferase activity, but regular brain monoamine levels and unaltered emotional behavior. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 121:28–36
Tzang RF, Hsu CD, Liou YJ, Hong CJ, Tsai SJ (2013) Family-based association of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatr Genet 23(4):177–178
Sánchez-Mora C, Ribasés M, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Casas M, Bosch R, Boreatti-Hümmer A, Heine M, Jacob CP, Lesch KP, Fasmer OB, Knappskog PM, Kooij JJ, Kan C, Buitelaar JK, Mick E, Asherson P, Faraone SV, Franke B, Johansson S, Haavik J, Reif A, Bayés M, Cormand B (2010) Meta-analysis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor p.Val66Met in adult ADHD in four European populations. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 153B(2):512–523
Naumenko VS, Bazovkina DV, Semenova AA, Tsybko AS, Il’chibaeva TV, Kondaurova EM, Popova NK (2013) Effect of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on behavior and key members of the brain serotonin system in mouse strains genetically predisposed to behavioral disorders. J Neurosci Res 91:1628–1638
Gerlai R, McNamara A, Choi-Lundberg DL, Armanini M, Ross J, Powell-Braxton L, Phillips HS (2001) Impaired water maze learning performance without altered dopaminergic function in mice heterozygous for the GDNF mutation. Eur J Neurosci 14:1153–1163
Laurin N, Lee J, Ickowicz A, Pathare T, Malone M, Tannock R, Kennedy JL, Schachar RJ, Barr CL (2008) Association study for genes at chromosome 5p13-q11 in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B:600–605
Sarter M, Gehring WJ, Kozak R (2006) More attention must be paid: the neurobiology of attentional effort. Brain Res Rev 51:145–160
Maness LM, Kastin AJ, Weber JT, Banks WA, Beckman BS, Zadina JE (1994) The neurotrophins and their receptors: structure, function, and neuropathology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 18:143–159
Cho SC, Kim HW, Kim BN, Kim JW, Shin MS, Cho DY, Chung S, Jung SW, Yoo HJ, Chung IW, Chung US, Son JW (2010) Neurotrophin-3 gene, intelligence, and selective attention deficit in a Korean sample with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:1065–1069
Park S, Kim BN, Kim JW, Shin MS, Cho SC, Kim JH, Son JW, Shin YM, Chung US, Han DH (2014) Neurotrophin 3 genotype and emotional adverse effects of osmotic-release oral system methylphenidate (OROS-MPH) in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Psychopharmacol 28:220–226
Pan W, Banks WA, Fasold MB, Bluth J, Kastin AJ (1998) Transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood-brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 37:1553–1561
Klein AB, Williamson R, Santini MA, Clemmensen C, Ettrup A, Rios M, Knudsen GM, Aznar S (2011) Blood BDNF concentrations reflect brain-tissue BDNF levels across species. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 14:347–353
Wechsler D (1974) WISC-R manual for the Wechsler intelligence scale for children—revised. Psychological Corporation, New York
Savasır I, Sahin N (1995) Manual for the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Revised (WISC-R). Turkish Pscyhology Association Publication, Ankara
Gokler B, Unal F, Pehlivanturk B, Cengel Kultur E, Devrim Akdemir D, Taner Y (2004) Reliability and validity of schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school age children present and lifetime version—Turkish version (K-SADS-PL-T). Turkish J Child Adolesc Psychiatry 11:109–116
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Flynn C, Moreci P, Williamson D, Ryan N (1997) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36:980–988
Kaner S, Büyüköztürk Ş, İşeri E (2013) Conners teacher rating scale-revised short: Turkish adaptation study. Educ Sci (in Turk) 38:81–97
Kaner Ş, Büyüköztürk Ş, İşeri E (2013) Conners parent rating scale-revised short: Turkish standardization study. Arch Neuropsychiatr 50:100–109
Conners CK, Sitarenios G, Parker JD, Epstein JN (1998) The revised Conners’ Parent Rating Scale (CPRS-R): factor structure, reliability, and criterion validity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26:257–268
Conners CK, Sitarenios G, Parker JD, Epstein JN (1998) Revision and restandardization of the Conners Teacher Rating Scale (CTRS-R): factor structure, reliability, and criterion validity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26:279–291
Kovacs M (1985) The Children’s Depression, Inventory (CDI). Psychopharmacol Bull 21:995–998
Oy B (1991) Children’s Depression Inventory: a study of reliability and validity. Turk Psychiatry Derg 2:137–140
Birmaher B, Brent DA, Chiappetta L, Bridge J, Monga S, Baugher M (1999) Psychometric properties of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): a replication study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38:1230–1236
Karaceylan F (2005) Reliability and validity of SCARED in Turkish children. Dissertation, Kocaeli University, Kocaeli, Turkey
Tunca Z, Ozerdem A, Ceylan D, Yalçın Y, Can G, Resmi H, Akan P, Ergör G, Aydemir O, Cengisiz C, Kerim D (2014) Alterations in BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor) and GDNF (glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor) serum levels in bipolar disorder: the role of lithium. J Affect Disord 166:193–200
Lee BC, Choi IG, Kim YK, Ham BJ, Yang BH, Roh S, Choi J, Lee JS, Oh DY, Chai YG (2009) Relation between plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in the male patients with alcohol dependence. Alcohol 43:265–269
Niitsu T, Shirayama Y, Matsuzawa D, Shimizu E, Hashimoto K, Iyo M (2014) Association between serum levels of glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor and attention deficits in schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 575:37–41
Wang X, Hou Z, Yuan Y, Hou G, Liu Y, Li H, Zhang Z (2011) Association study between plasma GDNF and cognitive function in late-onset depression. J Affect Disord 132:418–421
Smith MA, Makino S, Altemus M, Michelson D, Hong SK, Kvetnansky R, Post RM (1995) Stress and antidepressants differentially regulate neurotrophin 3 mRNA expression in the locus coeruleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8788–8792
Saruta J, Iida M, Kondo Y, To M, Hayashi T, Hori M, Sato S, Tsukinoki K (2012) Chronic stress induces neurotrophin-3 in rat submandibular gland. Yonsei Med J 53:1085–1092
van der Meer D, Hoekstra PJ, Zwiers M, Mennes M, Schweren LJ, Franke B, Heslenfeld DJ, Oosterlaan J, Faraone SV, Buitelaar JK, Hartman CA (2015) Brain correlates of the interaction between 5-HTTLPR and psychosocial stress mediating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder severity. Am J Psychiatry 172:768–775
Park S, Cho SC, Kim JW, Shin MS, Yoo HJ, Oh SM, Han DH, Cheong JH, Kim BN (2014) Differential perinatal risk factors in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder by subtype. Psychiatry Res 219:609–616
Elfving B, Plougmann PH, Wegener G (2010) Detection of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat blood and brain preparations using ELISA: pitfalls and solutions. J Neurosci Methods 187:73–77
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and their family members who participated in this study. Funding for this study was provided by a grant from the Scientific Research Project Coordination Unit of Necmettin Erbakan University (Project No: 151218004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgiç, A., Toker, A., Işık, Ü. et al. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, glial-derived neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, and neurotrophin-3 levels in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 26, 355–363 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-016-0898-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-016-0898-2