Abstract
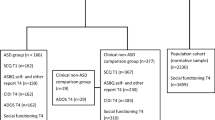
Autism is a categorical developmental disorder characterized by impairment in socialization, communication, and by restricted and circumscribed interests. Several authors have described the presence of subthreshold autistic traits in the general population, pervasive developmental disorders representing the extreme end of their distribution. In this study, we explored the presence of autistic traits in siblings and parents of a proband with autism, and in siblings and parents of a normally developing child, using the previously validated self-report French Autism Quotient, an adaptation of the AQ developed by S. Baron-Cohen. Scores were distributed between two main factors, F1 corresponding to socialization and communication, F2 to imagination and rigidity. Here, we show that both parents and siblings of a child with autism have more symptomatic scores in the domains of communication and socialization. In addition, we show that in these families the parents, but not the siblings, are distributed across different subcategories, according to their scores for the F1 and F2 domains. We hypothesize that these different subgroups may correspond to different underlying genetic mechanisms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I et al (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25:63–78
Abraham BS, Geschwind DH (2008) Advances in autism genetics: on the threshold of a new neurobiology. Nat Rev 9:341–355
Gillis RF, Rouleau GA (2011) The ongoing dissection of the genetic architecture of autistic spectrum disorder. Mol Autism 2(1):12
Plomin R, Haworth CMA, Davis OSP (2009) Common disorders are quantitative traits. Nat Rev Genet 10(12):872–878
Constantino JN, Todd R (2003) Autistic traits in the general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:524–530
Constantino JN, Lajonchere C, Lutz M, Gray T, Abbacchi A, McKenna K, Singh D, Todd RD (2006) Autistic social impairment in the siblings of children with pervasive developmental disorders. Am J Psychiatry 163(2):294–296
Szatmari P, MacLean JE, Jones MB, Bryson SE, Zwaigenbaum L, Bartolucci G, Mahoney WJ, Tuff L (2000) The familial aggregation of the lesser variant in biological and non-biological relatives of PDD probands: a family history study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 41(5):579–586
Schwichtenberg AJ, Young GS, Sigman M, Hutman T, Ozonoff S (2010) Can family affectedness inform infant sibling outcomes of autism spectrum disorders? J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51(9):1021–1030
Virkud YV, Todd RD, Abbacchi AM, Zhang Y, Constantino JN (2009) Familial aggregation of quantitative autistic traits in multiplex versus simplex autism. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 150B(3):328–334
Sebat J, Lakshmi B, Malhotra D, Troge J, Lese-Martin C, Walsh T, Yamrom B, Yoon S, Krasnitz A, Kendall J, Leotta A, Pai D, Zhang R, Lee YH, Hicks J, Spence SJ, Lee AT, Puura K, Lehtimäki T, Ledbetter D, Gregerse PK, Bregman J, Sutcliffe JS, Jobanputr V, Chung W, Warburton D, King MC, Skuse D, Geschwind DH, Gilliam TC, Ye K, Wigler M (2007) Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism. Science 316:445–449
Constantino JN, Davis SA, Todd RD, Schindler MK, Gross MM, Brophy SL, Metzger LM, Shoushtari CS, Spintler R, Reich W (2003) Validation of a brief quantitative measure of autistic traits: comparison of the social responsiveness scale with the autism diagnostic interview-revised. J Autism Dev Disord 33(4):427–433
Constantino JN, Todd RD (2000) Genetic structure of reciprocal social behavior. Am J Psychiatry 157:2043–2045
Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Skinner R et al (1995) The autism spectrum quotient (AQ): evidence from Asperger syndrome/high functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. J Autism Dev Disord 31:5–17
Woodbury-Smith MR, Robinson J, Wheelwright S, Baron-Cohen S (2005) Screening adults for Asperger Syndrome using the AQ: a preliminary study of its diagnostic validity in clinical practice. J Autism Dev Disord 35(3):331–335
Hoekstra RA, Vinkhuyzen AAE, Wheelwright S, Bartels M, Boomsma DI, Baron-Cohen S, Posthuma D, Van der Sluis S (2011) The construction and validation of an abridged version of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ-short). J Autism Dev Disord 41:589–596
Piana H, Fortin C, Noulhiane M, Golse B, Robel L (2007) Investigation of the behavioural phenotype of parents of child with autism through the new FAQ self-report. Encephale 33:285–292
Laroche F, Ramoz N, Leroy S, Fortin C, Rousselot-Pailley B, Philippe A, Colleaux L, Golse B, Mouren-Simeoni M-C, Gorwood P, Galli T, Simonneau M, Krebs M-O, Robel L (2008) Polymorphism of coding trinucleotide repeats of homeogenes in neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Genetics 18(6):295–301
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fourth edition, text revision (DSM IV-TR). American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral disorders (1993) Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines, WHO, Geneva
Lord C, Rutter M, LeCouteur A (1994) Autism diagnostic interview-revised: a revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 24:659–685
Schopler E, Reichler RJ, DeVellis RF, Daly K (1980) Toward objective classification of childhood autism: Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). J Autism Dev Disord 10(1):91–103
Schopler E, Reichler RJ, Bashford A, Lansing MD, Marcus LM (1979) Psychoeducational profile-revised (PEP-R), vol I. University Park Press, Baltimore
Sattler JM, Dumont R (2004) Assessment of children: WISC-IV and WPPSI-III supplement. J.M. Sattler Publisher, San Diego
Rousselot-Pailley B, Fortin C, Golse B, Falissard B, Robel L (2011) The FAQ self-report is a valid instrument to characterize endophenotypes of the autistic spectrum in parents of children with autism. Encephale 37(3):191–198
Fraley C, Raftery AE (2002) Model-based clustering, discriminant analysis, and density estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 97:611–631
Bishop DV, Maybery M, Maley A et al (2004) Using self-report to identify the broad phenotype in parents of children with autistic spectrum disorders: a study using the Autism-Spectrum Quotient. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45(8):1431–1436
Wheelwright S, Auyeung B, Allison C, Baron-Cohen S (2010) Defining the broader, medium and narrow autism phenotype among parents using the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Molecular. Autism 1:10
Constantino JN, Zhang YI, Frazier T, Abbachini AM, Law P (2010) Sibling recurrence and the genetic epidemiology of autism. Am J Psychiatry 167(11):1349–1356
Baron-Cohen S (2006) Two new theories of autism: hypersystemizing and assortative mating. Arch Dis Child 91:2–5
Duvall JA, Ake L, Cantor RM, Todd RD, Constantino JN, Geschwind DH (2007) A quantitative trait locus analysis of social responsiveness in multiplex autism families. Am J Psychiatry 164:656–662
Zietsch BP, Verweij KJ, Heath AC, Martin NG (2011) Variation in human mate choice: simultaneously investigating heritability, parental influence, sexual imprinting, and assortative mating. Am Nat 177(5):605–616
Fowler JH, Settle J, Christakis N (2010) Correlated genotypes in friendship networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(5):1993–1997
Goin-Kochel RP, Abbachi N, Constantino JN, AGRE Consortium (2007) Lack of evidence for increased genetic loading for autism among families of affected females: a replication from family history data in two large samples. Autism 11(3):279–286
Acknowledgments
We thank the Fondation de France for its support, S. Baron-Cohen for his permission to adapt the AQ, Charles Rousselot-Pailley for his valuable help, children and families who agreed to participate in this research.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robel, L., Rousselot-Pailley, B., Fortin, C. et al. Subthreshold traits of the broad autistic spectrum are distributed across different subgroups in parents, but not siblings, of probands with autism. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 23, 225–233 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-013-0451-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-013-0451-5