Abstract
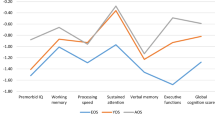
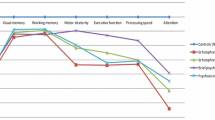
The present study aimed to compare the level and pattern of cognitive deficits in patients with early-onset psychoses with an age, gender and IQ matched control group. In order to ensure a representative sample of patients with psychoses, participants with an IQ of less than 70 were included. Forty-eight patients with an onset of psychoses before the age of 16, and 47 age, gender and IQ matched controls without psychoses were recruited. Psychotic symptomatology was assessed using the Schedules for Clinical Assessment to obtain DSM-IV and ICD-10 diagnoses. Positive and negative symptoms were assessed using the Positive and Negative Symptoms Scale. Levels of cognitive function were measured using a comprehensive neuropsychological battery. A pattern of specific impairments was not found, with few significant differences between the two cohorts. However both cohort groups performed lower than age derived norms. Therefore it appears that there are global cognitive deficits rather than specific deficits in early-onset psychoses when compared to normative data, in-line with conclusions of early-onset schizophrenia research, but patients did not have greater deficit than controls when matched on IQ, gender and age, even after excluding participants with IQ less than 70.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frangou S, Hadjulis M, Vourdas A (2008) The Maudsley early onset schizophrenia study: cognitive function over a 4-year follow-up period. Schizophr Bull 34:52–59
Øie M, Sundet K, Rund BR (2008) Neurocognitive decline in early-onset schizophrenia compared with ADHD and normal controls: evidence from a 13-year follow-up study. Schizophr Bull 36(3):557–565
McClellan J, Prezbindowski A, Breiger D, McCurry C (2004) Neuropsychological functioning in early-onset psychotic disorders. Schizophr Res 68(1):21–26
Watkins JM, Asarnow RF, Tanguay PE (1988) Symptom development in childhood onset schizophrenia. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 29:865–878
Petty LK, Ornitz EM, Michelman JD, Zimmerman EG (1984) Autistic children who become schizophrenic. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:129
Kravariti E, Morris RG, Rabe-Hesketh S, Murray RM, Frangou S (2003) The Maudsley early-onset schizophrenia study: cognitive function in adolescents with recent onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 61(2–3):137–148
Øie M, Sundet K, Rund BR (1999) Contrasts in memory functions between adolescents with schizophrenia or ADHD. Neuropsychologia 37(12):1351–1358
Vance A, Hall N, Bellgrove MA, Casey M, Karsz F, Maruff P (2006) Visuospatial working memory deficits in adolescent onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 87(1–3):223–227
Kumra S, Wiggs E, Bedwell J, Smith AK, Arling E, Albus K, Hamburger SD, McKenna K, Jacobsen LK, Rapoport JL, Asarnow RF (2000) Neuropsychological deficits in pediatric patients with childhood-onset schizophrenia and psychotic disorder not otherwise specified. Schizophr Res 42:135–144
Kravariti E, Morris RG, Rabe-Hesketh S, Murray RM, Frangou S (2003) The Maudsley early-onset schizophrenia study: cognitive function in adolescent-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 65:95–103
Asarnow RF, Asamen J, Granholm E, Sherman T, Watkins JM, Williams ME (1994) Cognitive/neuropsychological studies of children with a schizophrenic disorder. Schizophr Bull 20:647–669
Jaeger J, Czobor P, Berns SM (2003) Basic neuropsychological dimensions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 65:105–116
González-Blanch C, Rodriquez-Sanchez JM, Perez-Iglesias R, Pardo-Garcia G, Martinez-Garcia O, Vazquez-Barquero JL, Crespo-Facorro B (2010) First-episode schizophrenia patients neuropsychologically within the normal limits: evidence of deterioration in speed of processing. Schizophr Res 119(1–3):18–26
Rodriguez-Sanchez JM, Crespo-Facorro B, Gonzalez-Blanch C, Perez-Iglesias R, Vazquez-Barquero JL (2007) Cognitive dysfunction in first-episode psychosis: the processing speed hypothesis. Br J Psychiatry 191(51):s107–s110
MacDonald AW III, Goghari VM, Hicks BM, Flory JD, Carter CS, Manuck SB (2005) A convergent–divergent approach to context processing, general intellectual functioning, and the genetic liability to schizophrenia. Neuropsychology 19(6):814–821
Lussier I, Stip E (2001) Memory and attention deficits in drug naive patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 48(1):45–55
Hoff AL, Harris D, Faustman WO, Beal M, DeVilliers D, Mone RD, Moses JA, Csernansky JG (1996) A neuropsychological study of early-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 20(1–2):21–28
Meehl PE (1970) Nuisance variables and the ex-post facto design. In: Radner M, Winocur S (eds) Minnesota studies in the philosophy of science. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, pp 373–402
Goldstein G, Shemansky WJ (1995) Influences on cognitive heterogeneity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 18(1):59–69
Weickert TW, Goldberg TE, Gold JM, Bieglow LB, Egan MF, Weinberger DR (2000) Cognitive impairments in patients with schizophrenia displaying preserved and compromised intellect. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57(9):907–913
Zabala A, Rapado M, Arango C, Robles O, de la Serna E, Gonzalez C, Rodriquez-Sanchez JM, Andres P, Mayoral M, Bombin I (2010) Neuropsychological functioning in early-onset first-episode psychosis: comparison of diagnostic subgroups. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260(3):225–233
Potter AI, Nestor PG (2010) IQ subtypes in schizophrenia: distinct symptom and neuropsychological profiles. J Nerv Ment Dis 198(8):580–585
Badcock JC, Dragovi M, Waters FAV, Jablensky A (2005) Dimensions of intelligence in schizophrenia: evidence from patients with preserved, deteriorated and compromised intellect. J Psychiatr Res 39(1):11–19
Oie M, Sundet K, Rund BR (2010) Neurocognitive decline in early-onset schizophrenia compared with ADHD and normal controls: evidence from a 13-year follow-up study. Schizophr Bull 36(3):557–565
Arango C, Moreno C, Martinez S, Parellada M, Desco M, Moreno D, Fraguas D, Gogtay N, James A, Rapoport J (2008) Longitudinal brain changes in early-onset psychosis. Schizophrenia Bull 34(2):341–353
Gillberg C, Wahlstrom J, Forsman A, Hellgren L, Gillberg C (1986) Teenage psychoses-epidemiology, classification and reduced optimality in the pre-, peri- and neonatal periods. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 27(1):87–98
Castro-Fornieles J, Parellada M, Gonzalez-Pinto A, Moreno D, Graell M, Baeza I, Otero S, Soutullo CA, Crespo-Facorro B, Ruiz-Sancho A, Desco M, Rojas-Corrales O, Patino A, Carrasco-Marin E, Arango C (2007) The child and adolescent first-episode psychosis study (CAFEPS): design and baseline results. Schizophr Res 91(1–3):226–237
Fraguas D, de Castro MJ, Medina O, Parellada M, Moreno D, Graell M, Merchan-Naranjo J, Arango C (2008) Does diagnostic classification of early-onset psychosis change over follow-up? Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 39(2):137–145
Werry JS, McClellan J, Chard L (1991) Childhood and adolescent schizophrenia, bipolar and schizoaffective disorder: a clinical outcome study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 30(3):457–465
Castle DJ, Wessely S, Van Os J, Murray RM (1998) Psychosis in the inner city: the Camberwell first episode study. Psychology Press Ltd, Hove
Correll CU, Lencz T, Smith CW, Auther AM, Nakayama EY, Hovey L, Olsen R, Shah M, Foley C, Cornblatt BA (2005) Prospective study of adolescents with subsyndromal psychosis: characteristics and outcomes. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 15:418–433
Menzes NM, Milovan E (2000) First-episode psychosis: a comparative review of diagnostic evolution and predictive variables in adolescents versus adults. Can J Psychiatry 45:710–716
Mayoral M, Zabala A, Robles O, Bombin I, Andres P, Parellada M, Moreno D, Graell M, Medina O, Arango C (2008) Neuropsychological functioning in adolescents with first episode psychosis: a two-year follow-up study. Eur Psychiatry 23(5):375–383
Verdoux H, Liraud F, Assens F, Abalan F, van Os J (2002) Social and clinical consequences of cognitive deficits in early psychosis: a two-year follow-up study of first-admitted patients. Schizophr Res 56:149–159
Edwards J, McGorry PD, Waddell FM, Harrigan SM (1999) Enduring negative symptoms in first-episode psychosis: comparison of six methods using follow-up data. Schizophr Res 40:147–158
Singh SP, Cooper JE, Fisher HL, Tarrant J, Lloyd T, Banjo J, Corfe S, Jones P (2005) Measuring onset in first-episode psychosis: the Nottingham onset schedule (NOS). Schizophr Res 41(1):180
Werry JS (1992) Child and adolescent (early-onset) schizophrenia: a review in light of DSM-III-R. J Autism Dev Disord 22(4):601–624
World Health Organisation (1994) Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry. Version 2. Am Psychiatric Pub
American Psychiatric Association (1987) The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
World Health Organisation (1994) The Tenth Revision of the International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) Geneva
McGuffin P, Farmer A, Harvey L (1991) A polydiagnostic application of operational criteria in studies of psychotic illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:764–770
Kay SR, Fisbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative symptom scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1:261–276
Baron-Cohen S, Gillberg C (1992) Can autism be detected at 18 months? The needle, the haystack, and the CHAT. Br J Psychiatry 161:839
Wechsler D (1992) Wechsler intelligence scale for children, 3rd edn. The Psychological Corporation, London
Wechsler D (1992) Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Revised. WAIS-R. The Psychological Corporation, New York
Crawford JR, Allan KM, Jack AM (1992) Short forms of the UK WAIS-R: regression equations and their predictive accuracy in a general population sample. Br J Clin Psychol 31:191–202
Britton PG, Savage RD (1966) A short form of the WAIS for use with the aged. Br J Psychiatry 112:289–299
Gathercole SE, Willis C, Emslie H (1994) The children’s test of nonword repetition: a test of phonological working memory. Memory 2:103–127
Gathercole SE, Baddeley A (1996) Adult test of nonword repetition. University of Bristol, Bristol
Keefe RS, Roitman SE, Harvey PD, Blum CS, DuPre RL, Prieto DM, Davidson M, Davis KL (1995) A pen-and-paper human analogue of a monkey prefrontal cortex activation task: spatial working memory in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 17(1):25–33
Cohen M (1997) Children’s memory scale. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Gold JM, Carpenter C, Randolph C, Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR (1997) Auditory working memory and Wisconsin card sorting test performance in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54(2):159–165
Reitan RM, Wolfson D (1985) The Halstead–Reitan neuropsychological test battery. Neuropsychology Press, Tucson
Bechtoldt HP, Benton AL, Fogel ML (1962) An application of factor analysis in neuropsychology. Psychol Rec 12:147–156
Warrington EK (1996) The Camden memory tests. Erlbaum, Hove
Happe F (1994) An advanced test of theory of mind: understanding of story characters’ thoughts and feelings by able autistic, mentally handicapped, and normal children and adults. J Autism Dev Disord 24(2):129–154
Robertson IH, Ridgeway V, Nimmo-Smith I (1994) Test of everyday attention for children—TEA-Ch. Thames Valley Test Company
Heinrichs RW, Zakzanis KK (1998) Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology 12(3):426–445
Wechsler D (1987) Manual for the Wechsler memory scale—revised. The Psychological Corporation, New York
Fossati P, Amar G, Raoux N, Ergis AM, Allilaire JF (1999) Executive functioning and verbal memory in young patients with unipolar depression and schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 89(3):171–187
Gold S, Arndt S, Nopoulos P, O’Leary DS, Andreasen NC (1999) Longitudinal study of cognitive function in first-episode and recent onset schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156(9):1342–1348
Wolf R, Vasic N, Hose A, Spitzer M, Walter H (2007) Changes over time in frontotemporal activation during a working memory task in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 91(1–3):141–150
Rund BR, Melle I, Friis S, Johannessen JO, Larsen TK, Midboe LJ, Opjordsmoen S, Simonsen E, Vaglum P, McGlashan T (2007) The course of neurocognitive functioning in first-episode psychosis and its relation to premorbid adjustment, duration of untreated psychosis, and relapse. Schizophr Res 91(1–3):132–140
Gold JM (2004) Cognitive deficits as treatment targets in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 72(1):21–28
Albus M, Hubmann W, Mohr F, Hecht S, Hinterberger-Weber P, Seitz NN, Kuchenhoff H (2006) Neurocognitive functioning in patients with first-episode schizophrenia: results of a prospective 5-year follow-up study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256(7):442–451
Leeson VC, Sharma P, Harrison M, Ron MA, Barnes TRE, Joyce EM (2009) IQ trajectory, cognitive reserve, and clinical outcome following a first episode of psychosis: a 3-year longitudinal study. Schizophr Bull 37(4):768–777
Hoff AL, Svetina C, Shields G, Stewart J, DeLisi LE (2005) Ten year longitudinal study of neuropsychological functioning subsequent to a first episode of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 78(1):27–34
Stirling JD, White C, Lewis S, Hopkins R, Tantam D, Huddy A, Montague L (2003) Neurocognitive function and outcome in first episode schizophrenia: a 10 year follow up of epidemiological cohort. Schizophr Res 65(2–3):75–86
Frangou S, Hadjulis M, Vourdas A (2007) The Maudsley early onset schizophrenia study: cognitive function over a 4-year follow-up period. Schizophr Bull 34(1):52–59
Hill SK, Schuepbach D, Herbener ES, Keshavan MS, Sweeney JA (2004) Pretreatment and longitudinal studies of neuropsychological deficits in antipsychotic-naïve patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 68(1):49–63
Hoff AL, Sakuma M, Wieneke M, Horon R, Kushner M, DeLisi LE (1999) Longitudinal neuropsychological follow-up study of patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156(9):1336–1341
Woodward ND, Purdon SE, Meltzer HY, Zald DH (2005) A meta-analysis of neuropsychological change to clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8(3):457–472
Keefe RS, Silva SG, Perkins DO, Lieberman JA (1999) The effects of atypical antipsychotic drugs on neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia: a review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull 25(2):201–222
Friss S, Sundet K, Rund BR, McGlashan TH (2002) Neurocognitive dimensions characterising patients with first-episode psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 181(43):s85–s90
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walker, DM., Standen, P.J. Level and pattern of neuropsychological functioning in early-onset psychoses. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 20, 551–560 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-011-0219-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-011-0219-8