Abstract
Objective
This study evaluates the impact of local and systemic administration of penicillin on the antimicrobial properties and growth factors of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) under in vitro conditions.
Materials and methods
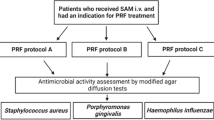
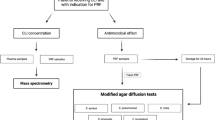
The study involved 12 volunteers. Four tubes of venous blood were collected before systemic antibiotic administration. Two tubes were centrifuged at 2700 RPM for 12 min to obtain PRF, while 0.2 ml of penicillin was locally added into other two tubes. After systemic administration, blood samples were again collected and subjected to centrifugation. The release of growth factors (IGF-1, PDGF, FGF-2, and TGFβ-1) was determined using the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), and an antibiotic sensitivity test was performed for S. aureus and E. coli bacteria.
Results
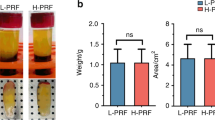
Results showed that local antibiotic addition before PRF centrifugation had a significant antimicrobial effect without affecting growth factor releases. There was no statistically significant difference in antimicrobial properties between PRF prepared with systemic antibiotic administration and PRF prepared without antibiotics.
Materials and methods
The study suggests that incorporating localized antibiotics into PRF results in strong antimicrobial effects without compromise of growth factor release. However, the combination of PRF with systemic antibiotics did not significantly enhance its antimicrobial properties compared to PRF prepared without antibiotics.
Clinical relevance
Local addition of penicillin into PRF provides strong antimicrobial properties which may help reduce dependence on systemic antibiotic regimens, mitigating antibiotic resistance and minimizing associated side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Kumar VR, Gangadharan G (2015) Platelet rich fibrin in dentistry: a review of literature. Int J Med 3:72–76
Saini K, Chopra P, Sheokand V (2020) Journey of platelet concentrates: a review. Biomed Pharmacol J 13:185–191
Agrawal AA (2017) Evolution, current status and advances in application of platelet concentrate in periodontics and implantology. World J Clin Cases 5:159
Varshney S, Dwivedi A, Pandey V (2019) Antimicrobial effects of various platelet rich concentrates-vibes from in-vitro studies-a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 9:299–305
Fabbro MD, Bortolin M, Taschieri S, Ceci C, Weinstein RL (2016) Antimicrobial properties of platelet-rich preparations. A systematic review of the current pre-clinical evidence. Platelets 27:276–285
Miron RJ, Zucchelli G, Pikos MA, Salama M, Lee S, Guillemette V, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Bishara M, Zhang Y, Wang H-L (2017) Use of platelet-rich fibrin in regenerative dentistry: a systematic review. Clin Oral Invest 21:1913–1927
Polak D, Clemer-Shamai N, Shapira L (2019) Incorporating antibiotics into platelet-rich fibrin: a novel antibiotics slow-release biological device. J Clin Periodontol 46:241–247
Yang LC, Hu SW, Yan M, Yang JJ, Tsou SH, Lin YY (2015) Antimicrobial activity of platelet-rich plasma and other plasma preparations against periodontal pathogens. J Periodontol 86:310–318
Kreutzer K, Storck K and Weitz J (2014) Current evidence regarding prophylactic antibiotics in head and neck and maxillofacial surgery. Biomed Res Int 879437:1–7
Yusri S, Elfana A, Elbattawy W, Fawzy El-Sayed KM (2021) Effect of locally delivered adjunctive antibiotics during surgical periodontal therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Invest 25:5127–5138
Figuero E, Serrano J, Arweiler NB, Auschill TM, Gürkan A and Emingil G (2023) Supra and subgingival application of antiseptics or antibiotics during periodontal therapy. Periodontol 2000. 00:1–34
Quirynen M, Siawasch S, Temmerman A, Cortellini S, Dhondt R, Teughels W, Castro A (2023) Do autologous platelet concentrates (APCs) have a role in intra‐oral bone regeneration? A critical review of clinical guidelines on decision‐making process. Periodontol 2000. 00:1–16
Moraschini V, Miron RJ, Mourão CFdAB, Louro RS, Sculean A, da Fonseca LAM, Calasans Maia MD, Shibli JA (2023) Antimicrobial effect of platelet‐rich fibrin: a systematic review of in vitro evidence‐based studies. Periodontol 2000. 00:1–12
Miron RJ, Zhang Y (2018) Autologous liquid platelet rich fibrin: a novel drug delivery system. Acta Biomater 75:35–51
Li F, Jiang P, Pan J, Liu C and Zheng L (2019) Synergistic application of platelet-rich fibrin and 1% alendronate in periodontal bone regeneration: a meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 18(9148183):1–12
Martande SS, Kumari M, Pradeep A, Singh SP, Suke DK, Guruprasad C (2016) Platelet-rich fibrin combined with 1.2% atorvastatin for treatment of intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 87:1039–1046
Pradeep A, Karvekar S, Nagpal K, Patnaik K, Raju A, Singh P (2016) Rosuvastatin 1.2 mg in situ gel combined with 1: 1 mixture of autologous platelet-rich fibrin and porous hydroxyapatite bone graft in surgical treatment of mandibular class II furcation defects: a randomized clinical control trial. J Periodontol 87:5–13
Pradeep A, Nagpal K, Karvekar S, Patnaik K, Naik SB, Guruprasad C (2015) Platelet-rich fibrin with 1% metformin for the treatment of intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 86:729–737
Khorshidi H, Haddadi P, Raoofi S, Badiee P and Dehghani Nazhvani A (2018) Does adding silver nanoparticles to leukocyte-and platelet-rich fibrin improve its properties? Biomed Res Int. 27(8515829):1–5
Siawasch S, Andrade C, Castro A, Teughels W, Temmerman A, Quirynen M (2022) Impact of local and systemic antimicrobials on leukocyte-and platelet rich fibrin: an in vitro study. Sci Rep 12:2710
Bennardo F, Gallelli L, Palleria C, Colosimo M, Fortunato L, De Sarro G, Giudice A (2023) Can platelet-rich fibrin act as a natural carrier for antibiotics delivery? A proof-of-concept study for oral surgical procedures. BMC Oral Health 23:1–10
Wilson W (2008) American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee; American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Circulation 118:887–896
Wang S, Li Y, Li S, Yang J, Tang R, Li X, Li L, Fei J (2021) Platelet-rich plasma loaded with antibiotics as an affiliated treatment for infected bone defect by combining wound healing property and antibacterial activity. Platelets 32:479–491
Peck M, Hiss D, Stephen L, Maboza E (2018) Antibiotic release from leukocyteand platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) an observational study. South Afr Dental J 73:268–270
Miron RJ, Pinto NR, Quirynen M, Ghanaati S (2019) Standardization of relative centrifugal forces in studies related to platelet-rich fibrin. Book title, Wiley Online Library
Miron RJ, Fujioka‐Kobayashi M, Sculean A and Zhang Y (2023) Optimization of platelet‐rich fibrin. Periodontol 2000. 00:1–13
Miron RJ, Kawase T, Dham A, Zhang Y, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Sculean A (2021) A technical note on contamination from PRF tubes containing silica and silicone. BMC Oral Health 21:1–11
Miron RJ, Chai J, Zhang P, Li Y, Wang Y, Mourão CFdAB, Sculean A, Fujioka Kobayashi M, Zhang Y (2020) A novel method for harvesting concentrated platelet-rich fibrin (C-PRF) with a 10-fold increase in platelet and leukocyte yields. Clin Oral Invest 24:2819–2828
Miron RJ, Horrocks NA, Zhang Y, Horrocks G, Pikos MA, Sculean A (2022) Extending the working properties of liquid platelet-rich fibrin using chemically modified PET tubes and the Bio-Cool device. Clin Oral Invest 26:2873–2878
Kram HB, Bansal M, Timberlake O, Shoemaker WC (1991) Antibacterial effects of fibrin glue-antibiotic mixtures. J Surg Res 50:175–178
Funding
This study was supported by the Cukurova University Research Fund, Project number TDH 2021–13751.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.O. and M.C.H. contributed to study conception and design. S.C.K. was responsible for obtaining and preparing the samples for data collection. H.O. performed ELISA analysis. B.A., O.U.T and S.C.I. performed the data analysis and prepared the manuscript. All authors critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The protocol of the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Cukurova University Faculty of Medicine, Adana, Turkey (Approval No: 86/59, Date: 08.03.2019).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ozcan, M., Kabaklı, S.C., Alkaya, B. et al. The impact of local and systemic penicillin on antimicrobial properties and growth factor release in platelet-rich fibrin: In vitro study. Clin Oral Invest 28, 61 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-05428-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-05428-x