Abstract
Objective
This overview analyzed the quality of the systematic reviews (SRs) available on treatments for molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH).
Material and methods
Six electronic databases were searched (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, LILACS, Brazilian Bibliography of Dentistry and Cochrane Library) until March 2022. Two reviewers independently performed the selection, the quality assessment (Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews 2 — AMSTAR-2), and the risk of bias assessment of the SR (Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews — ROBIS).
Results
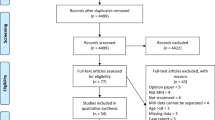
Two hundred nine records were retrieved; after removing duplicates and applying the inclusion/exclusion criteria, 5 SRs remained. Three SRs were rated as showing critically low methodological quality and high risk of bias, and two were rated as moderate methodological quality and low risk of bias. The identified treatments that may be suitable for MIH were classified as (1) non-invasive — casein incorporated into toothpaste and sugar-free chewing gum, toothpaste containing arginine, 0.4% stannous fluoride gel; fluoride varnish; (2) micro-invasive — resin sealants for pits and fissures, microabrasion, dental whitening, resin infiltration; (3) invasive — ART restorations, indirect restorations (metal, composite, or ceramic); and (4) mixed intervention — stainless steel crowns.
Conclusion
Despite the considerable number of published papers included in this set of systematic reviews, the evidence supporting the effectiveness of treatments for treating MIH is limited due to the methodological quality and risk of bias of the systematic reviews, as well as the quality of the primary studies (PROSPERO: CRD42020144831).
Clinical relevance
Different treatments have been purposed for MIH treatment, but there is still not enough scientific evidence of good quality for the establishment of a definitive clinical protocol for the treatment of MIH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lygidakis NA (2010) Treatment modalities in children with teeth affected by molar-incisor enamel hypomineralisation (MIH): a systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 11(2):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03262715
Weerheijm KL (2004) Molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH) clinical presentation aetiology and management. Dent Update 31(1):9–12. https://doi.org/10.12968/denu.2004.31.1.9
Weerheijm KL, Duggal M, Mejàre I, Papagiannoulis L, Koch G, Martens LC (2003) Hallonsten AL (2003) Judgement criteria for molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH) in epidemiologic studies: a summary of the European meeting on MIH held in Athens. Eur J Paediatr Dent 4(3):110–113
Linner T, Khazaei Y, Bücher K, Pfisterer J, Hickel R, Kühnisch J (2021) Hypersensitivity in teeth affected by molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH). Sci Rep 11(1):17922. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95875-x
Raposo F, de Carvalho Rodrigues AC, Lia ÉN, Leal SC (2019) Prevalence of hypersensitivity in teeth affected by molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH). Caries Res 53(4):424–430. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495848
da Costa-Silva CM, Mialhe FL (2012) Considerations for clinical management of molar-incisor hypomineralization: a literature review. Revista Odonto Ciência 27(4):333–338
Lygidakis NA, Garot E, Somani C, Taylor GD, Rouas P, Wong FSL (2021) Best clinical practice guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with molar-incisor-hypomineralisation (MIH): an updated European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry policy document. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-021-00668-5
Humphreys J, Albadri S (2020) Management of molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH): a 1-year retrospective study in a Specialist Secondary Care Centre in the UK. Children (Basel) 7(12) https://doi.org/10.3390/children7120252
Kopperud SE, Pedersen CG, Espelid I (2016) Treatment decisions on molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH) by Norwegian dentists - a questionnaire study. BMC Oral Health 17(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-016-0237-5
Muniz RSC, Carvalho CN, Aranha ACC, Dias F, Ferreira MC (2020) Efficacy of low-level laser therapy associated with fluoride therapy for the desensitisation of molar-incisor hypomineralisation: randomised clinical trial. Int J Paediatr Dent 30(3):323–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.12602
Ozgül BM, Saat S, Sönmez H, Oz FT (2013) Clinical evaluation of desensitizing treatment for incisor teeth affected by molar-incisor hypomineralization. J Clin Pediatr Dent 38(2):101–105
Fragelli CMB, Souza JF, Bussaneli DG, Jeremias F, Santos-Pinto LD, Cordeiro RCL (2017) Survival of sealants in molars affected by molar-incisor hypomineralization: 18-month follow-up. Braz Oral Res 31:e30. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2017.vol31.0030
Olmo-González B, Moreno-López R, Ribera-Uribe M (2020) Dental management strategies for molar incisor hypomineralization. Pediatr Dent J 30(3):139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdj.2020.09.002
Fragelli CMB, Souza JFd, Jeremias F, Cordeiro RdCL, Santos-Pinto L (2015) Molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH): conservative treatment management to restore affected teeth. Braz Oral Res 29:1–7
Harris JD, McCormick FM, Abrams GD, Gupta AK, Ellis TJ, Bach BR Jr, Bush-Joseph CA, Nho SJ (2013) Complications and reoperations during and after hip arthroscopy a systematic review of 92 studies and more than 6,000 patients. Arthroscopy J Arthroscopic & Related Surgery 29(3):589–595
Ismail AI, Bader JD (2004) Evidence-based dentistry in clinical practice. J Am Dent Assoc 135(1):78–83. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.2004.0024
Mulrow CD (1994) Rationale for systematic reviews. BMJ 309(6954):597–599. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.309.6954.597
Ge L, Tian JH, Li YN, Pan JX, Li G, Wei D, Xing X, Pan B, Chen YL, Song FJ et al (2018) Association between prospective registration and overall reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews: a meta-epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol 93:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.10.012
Hopewell S, Boutron I, Altman DG, Ravaud P (2013) Incorporation of assessments of risk of bias of primary studies in systematic reviews of randomised trials: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 3(8):e003342. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003342
Zoltowski APC, Costa AB, Teixeira MAP, Koller SH (2014) Methodological quality of systematic reviews in Brazilian psychology journals quality of systematic reviews in psychology. Psicologia Teoria e Pesquisa 30(1):97–104
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, Moher D, Tugwell P, Welch V, Kristjansson E et al (2017) AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 358:j4008. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j4008
Whiting P, Savović J, Higgins JP, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, Davies P, Kleijnen J, Churchill R (2016) ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol 69:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.06.005
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Pieper D, Tricco AC, Gates M, Gates A, Hartling L (2019) Preferred Reporting Items for Overviews of Reviews (PRIOR): a protocol for development of a reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev 8(1):335. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-1252-9
Schwendicke F, Splieth C, Breschi L, Banerjee A, Fontana M, Paris S, Burrow MF, Crombie F, Page LF, Gatón-Hernández P et al (2019) When to intervene in the caries process? An expert Delphi consensus statement. Clin Oral Investig 23(10):3691–3703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03058-w
da Cunha Coelho ASE, Mata PCM, Lino CA, Macho VMP, Areias C, Norton A, Augusto A (2019) Dental hypomineralization treatment: a systematic review. J Esthet Restor Dent 31(1):26–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/jerd.12420
Elhennawy K, Schwendicke F (2016) Managing molar-incisor hypomineralization: a systematic review. J Dent 55:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2016.09.012
Meier L 2019 Molar- incisor hypomineralization and its treatment peculiarities in children- a systematic review
Somani C, Taylor GD, Garot E, Rouas P, Lygidakis NA, Wong FSL (2021) An update of treatment modalities in children and adolescents with teeth affected by molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH): a systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-021-00635-0
Bandeira Lopes L, Machado V, Botelho J, Haubek D (2021) Molar-incisor hypomineralization: an umbrella review. Acta Odontol Scand 79(5):359–369. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2020.1863461
Bezamat M, Souza JF, Silva FMF, Corrêa EG, Fatturi AL, Brancher JA, Carvalho FM, Cavallari T, Bertolazo L, Machado-Souza C et al (2021) Gene-environment interaction in molar-incisor hypomineralization. PLoS ONE 16(1):e0241898. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241898
Kevrekidou A, Kosma I, Arapostathis K, Kotsanos N (2015) Molar incisor hypomineralization of eight- and 14-year-old children: prevalence, severity, and defect characteristics. Pediatr Dent 37(5):455–461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ACRC and JFS — conceived and designed the analysis. RS, MVG, LMW, and AER — collected the data. RS, MVG, LMW, AER, and LSA — contributed data or analysis tools. ACRC, JFS, RS, MVG, LMW, AER, and LSA — performed the analysis. MVG, RS, and ACRC — wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gevert, M.V., Soares, R., Wambier, L.M. et al. How is the quality of the available evidence on molar-incisor hypomineralization treatment? An overview of systematic reviews. Clin Oral Invest 26, 5989–6002 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04612-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04612-9