Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect of adjustment and finishing procedures and thermal aging of monolithic zirconia on the surface roughness, phase transformation, and flexural strength.
Material and methods
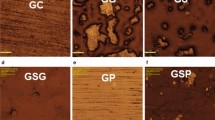
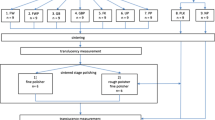
One hundred disk-shaped monolithic zirconia specimens were randomly divided into 5 groups: control, received only glazing; group Gr, was grinded; group GrP, was grinded and polished; group GrG, was grinded and re-glazed; group GrPG, was re-glazed after grinding and polishing. Half of the each group were stored in distilled water for 24 h and the remaining were thermocycled for 5000 cycles. Topographic evaluations were done with profilometer and scanning electron microscope. Phase changes were assessed through X-ray diffractometer. The biaxial flexural strength test was calculated by universal test machine. Statistical analysis was performed by using two-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparison test (p < 0.05).
Results
Group Gr showed statistically higher surface roughness and flexural strength values than the other groups (p < 0.001). However, no significant differences were observed between finishing groups (p >0.05). Phase transformation was occurred in all groups but the differences were not statically significant (p >0.05). Artificial aging had no effect on surface roughness, flexural strength, and phase transformation (p >0.05).
Conclusion
Surface roughness significantly increased after grinding, but finishing procedure approximated it to the control group. Glazing after grinding decreased the flexural strength, but polishing did not. Zirconia polishing system may be an alternative to re-glazing for monolithic zirconia.
Clinical relevance
Polishing is one of the most effective finishing procedures that can improve the physical properties of the material without damaging its mechanical properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pereira GKR, Silvestri T, Camargo R, Rippe MP, Amaral M, Kleverlaan CJ, Valandro LF (2016) Mechanical behaviour of a Y-TZP ceramic for monolithic restorations: effect of grinding and low-temperature aging. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 63:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.02.049
Piconi C, Maccauro G (1999) Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials 20:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00010-6
Zhang Y (2014) Making yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia translucent. Dent Mater 30:1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2014.08.375
Lazar DR, Bottino MC, Ozcan M, Valandro LF, Amaral R, Ussui V, Bressiani AH (2008) Y-TZP ceramic processing from coprecipitated powders: a comparative study with three commercial dental ceramics. Dent Mater 24:1676–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2008.04.002
Caglar I, Ates SM, Yesil DZ (2018) The effect of various polishing systems on surface roughness and phase transformation of monolithic zirconia. J Adv Prosthodont 10:132–137. https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2018.10.2.132
Rosentritt M, Preis V, Behr M, Hahnel S, Handel G, Kolbeck C (2012) Two-body wear of dental porcelain and substructure oxide ceramics. Clin Oral Investig 16:935–943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-011-0589-9
Park C, Vang MS, Park SW, Lim HP (2017) Effect of various polishing systems on the surface roughness and phase transformation of zirconia and the durability of the polishing systems. J Prosthet Dent 117:430–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.10.005
Hmaidouch R, Müller WD, Lauer HC, Weigl P (2014) Surface roughness of zirconia for full-contour crowns after clinically simulated grinding and polishing. Int J Oral Sci 6:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijos.2014.34
Khayat W, Chebib N, Finkelman M, Khayat S, Ali A (2018) Effect of grinding and polishing on roughness and strength of zirconia. J Prosthet Dent 119:626–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2017.04.003
Aravind P, Razak PA, Francis PG, Issac JK, Shanoj RP, Sasikumar TP (2013) Comparative evaluation of the efficiency of four ceramic finishing systems. J Int Oral Health 5:59–64
Fairhurst CW, Lockwood PE, Ringle RD, Thompson WO (1992) The effect of glaze on porcelain strength. Dent Mater 8:203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/0109-5641(92)90084-P
Caglar İ, Yanıkoğlu N (2016) The effect of sandblasting, Er:YAG laser and heat treatment on the mechanical properties of different zirconia cores. Photomed Laser Surg 34:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2015.3980
Mohammadi-Bassir M, Babasafari M, Rezvani MB, Jamshidian M (2017) Effect of coarse grinding, overglazing, and 2 polishing systems on the flexural strength, surface roughness, and phase transformation of yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia. J Prosthet Dent 118:658–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.12.019
Preis V, Behr M, Handel G, Schneider-Feyrer S, Hahnel S, Rosentritt M (2012) Wear performance of dental ceramics after grinding and polishing treatments. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 10:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.03.002
Preis V, Behr M, Kolbeck C, Hahnel S, Handel G, Rosentritt M (2011) Wear performance of substructure ceramics and veneering porcelains. Dent Mater 27:796–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2011.04.001
Mitov G, Heintze SD, Walz S, Woll K, Muecklich F, Pospiech P (2012) Wear behavior of dental Y-TZP ceramic against natural enamel after different finishing procedures. Dent Mater 28:909–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2012.04.010
Luthardt RG, Holzhüter M, Sandkuhl O, Herold V, Schnapp JD, Kuhlisch E (2002) Reliability and properties of ground Y-TZP-Zirconia ceramics. J Dent Res 81:487–491. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910208100711
Mohammadi-Bassir M, Rezvani MB, Golzari H, Moravej Salehi E, Fahimi MA, Kharazi Fard MJ (2019) Effect of two polishing systems on surface roughness, topography, and flexural strength of a monolithic lithium disilicate ceramic. J Prosthodont 28:e172–e180. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.12586
Karakoca S, Yilmaz H (2009) Influence of surface treatments on surface roughness, phase transformation, and biaxial flexural strength of Y-TZP ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 91:930–937. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.31477
Kasmac T, Oblak C, Jevnikar P, Funduk N, Marion L (1999) The effect of surface grinding and sandblasting on flexural strength and reliability of Y-TZP zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater 15:426–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0109-5641(99)00070-6
Garvie RC, Nicholson PS (1972) Phase analysis in zirconia systems. J Am Ceram Soc 55:303–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1972.tb11290.x
Wendler M, Belli R, Petschelt A, Mevec D, Harrer W, Lube T, Danzer R, Lohbauer U (2017) Chairside CAD/CAM materials. Part 2: flexural strength testing. Dent Mater 33:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2016.10.008
Huh YH, Park CJ, Cho LR (2016) Evaluation of various polishing systems and the phase transformation of monolithic zirconia. J Prosthet Dent 116:440–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.01.021
Bollen CM, Lambrechts P, Quirynen M (1997) Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: a review of the literature. Dent Mater 13:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0109-5641(97)80038-3
Sabrah AH, Cook NB, Luangruangrong P, Hara AT, Bottino MC (2013) Full-contour Y-TZP ceramic surface roughness effect on synthetic hydroxyapatite wear. Dent Mater 29:666–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2013.03.008
Janyavula S, Lawson N, Cakir D, Beck P, Ramp LC, Burgess JO (2013) The wear of polished and glazed zirconia against enamel. J Prosthet Dent 109:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3913(13)60005-0
Al-Haj Husain N, Camilleri J, Özcan M (2016) Effect of polishing instruments and polishing regimens on surface topography and phase transformation of monolithic zirconia: an evaluation with XPS and XRD analysis. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 64:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.07.025
Lee KR, Choe HC, Heo YR, Lee JJ, Son MK (2016) Effect of different grinding burs on the physical properties of zirconia. J Adv Prosthodont 8:137–143. https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2016.8.2.137
Lee JY, Jang GW, Park II, Heo YR, Son MK (2019) The effects of surface grinding and polishing on the phase transformation and flexural strength of zirconia. J Adv Prosthodont 11:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2019.11.1.1
Kosmac T, Oblak C, Jevnikar P, Fandak N, Marion L (2000) Strength and reliability of surface treated Y-TZP dental ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res 53:304–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4636(2000)53:4%3c304::aid-jbm4%3e3.0.co;2-s
Xu HHK, Jahanmir S, Ives LK (1997) Effect of grinding on strength of tetragonal zirconia and zirconia toughened alumina. Mach Sci Technol 1:49–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/10940349708945637
Guazzato M, Quach L, Albakry M, Swain MV (2005) Influence of surface and heat treatments on the flexural strength of Y-TZP dental ceramic. J Dent 33:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2004.07.001
Funding
This study was supported by the Research Projects Fund of Recep Tayyip Erdogan University (Grant no: TDH-2018–933).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
Isıl Ozturk declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ipek Caglar declares that she has no conflict of interest. Zeynep Yesil Duymus declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, I., Caglar, I. & Duymus, Z.Y. The effect of adjustment and finishing procedure on roughness, strength, and phase transformation of monolithic zirconia. Clin Oral Invest 26, 4761–4768 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04440-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04440-x